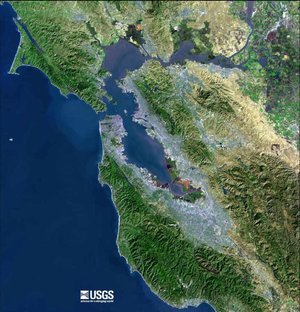
San Francisco Bay Area
|
|
The San Francisco Bay Area, sometimes referred to as The Bay Area or The Bay, is a metropolitan area that lies along the San Francisco Bay. It is a collection of a series of cities, towns, villages, military bases, airports, regional, state, and national parks sprawled over 9 counties and are connected by a massive network of roads, highways, rail, and commuter rail. The city of San Francisco serves as the traditional focal point and the cultural, economic, transportation nerve center of the region. Unlike other major metropolitan areas, the urban areas here are completely independent entities with their own completeley independent governments and public services and city borders instead of one huge city. Because San Francisco was the largest city in the region (until recently surpassed by San Jose) and remains the traditional and cultural center, the region was referred to and is generally confused as the city of San Francisco proper. Realising the independent and relatively 'Balkanized' nature of the region, the region is referred to as the 'Bay Area' instead. San Francisco has only 11% of the Bay Area's population.
| Contents |
The Region
- The region north of the Golden Gate Bridge is known as the North Bay. This area consists of Marin County and extends northward into Napa and Sonoma counties and eastward to Solano County. With some exceptions, this region is extremely affluent, and is generally the least urbanized part of the Bay Area, with many areas of undeveloped park and farm land. It is the only section of the Bay Area that is not served by a commuter rail transit service, though Sonoma-Marin service has entered the planning phase.
- The eastern side of the bay, dominated by the city of Oakland but also including Berkeley, Richmond and several small cities, is known as the East Bay.
The East Bay is split into two regions, the inner East Bay that sits on the bay coastline proper as the outer East Bay is in the inner inland valleys and are landlocked by mountains and valleys.
- The inner East Bay consists of the major cities of Oakland, Berkeley, Richmond, the University of California, Berkeley and smaller suburbs in between the three major cities and south of Oakland such as Emeryville, San Leandro, and Fremont. The inner East Bay is more urban, more densly populated, has a much older building stock (built before World War II), more ethnically diverse, and much poorer and have higher crime rates (especially in Oakland and Richmond). Oakland is the region's chief seaport. The regional basketball, Football and Baseball teams play from Oakland.
- The outer East Bay consists of the major cities of Walnut Creek, Concord, Antioch, to the north (also referred as Central Contra Costa County) and the cities of Dublin, Livermore and San Ramon to the south (sometimes referred to as the Livermore-Amador Valley or the Tri-Valley). They are connected to the inner East Bay by BART and by highways and the Caldecott Tunnel. The outer East Bay is mostly suburban to rural, was mostly built after World War II, and is more affluent.
- The communities along the southern edge of the Bay are known as the South Bay and Silicon Valley, although some Peninsula and East Bay towns are sometimes included in the latter. It includes the cities of San Jose, Fremont, and the high-tech hub of Santa Clara, as well as many smaller communities.
A booming Silicon Valley has shifted the regional population and economic center away from San Francisco and Oakland and towards the South Bay; San Jose is now the largest city in the region. The technology boom has also brought a large amounts of immigrants and driven housing, rents, gasoline prices up to the highest in the nation.
- The area between the South Bay and the City and County of San Francisco is known as the San Francisco Peninsula, locally just as The Peninsula. This area consists of a series of small cities and suburban communities along the Bay such as Palo Alto and Stanford University, San Mateo, Foster City as well as various towns along the Pacific coast such as Pacifica and Half Moon Bay. Because of Stanford University, lack of space, and high cost of living, the Silicon Valley has been slowly creeping up the peninsula.
- The City and County of San Francisco is generally placed in a category by itself geographically, mentally, and culturally. It is separated by water from the north and east, and by county line from its neighbor cities to the South. Locals refer to San Francisco as The City or SF in writing. It is generally not referred to as San Fran or Frisco by locals. By extension, South San Francisco is often referred to as South City even though there are other towns between SSF and SF. San Francisco serves as the cultural and financial center of the region, and once was the population and economic center.
Weather
Because the hills, mountains, and large bodies of water produce such vast geographic diversity within this region, the Bay Area offers a significant variety of microclimates. The areas near the Pacific Ocean are generally characterized by relatively small temperature variations during the year, with cool foggy summers and mild rainy winters. Inland areas, especially those separated from the ocean by hills or mountains, have hotter summers and colder overnight temperatures during the winter. The Bay Area is generally subdivided into several smaller subregions.
Transportation
Airports
The largest and oldest airport in the region and 2nd largest on the west coast. It is the only major international hub airport in California after LAX in Los Angeles.
The second largest airport in the region and a hub for mostly low-cost domestic flights.
The smallest of the major airports. Undergoing a major expansion and renovation to handle major flights.
Public transportation
Numerous and often overlapping bus transit agencies service the area (see Muni, AC Transit, SamTrans, VTA and County Connection). Muni and VTA also operate light rail networks. In addition, the Bay Area is served by a number of mass transit systems:
- Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) - A subway/commuter rail service that serves parts of the Bay Area, including San Francisco, Oakland, Berkeley, Fremont, and Walnut Creek. It has a direct connection to San Francisco's airport while a direct connection to Oakland's airport is in the planning stages.
- Caltrain - A commuter rail service that connects San Jose and cities along the Peninsula with San Francisco, California, and with the BART system by way of the Millbrae Transit Station.
- Amtrak - There are several Amtrak stations throughout the Bay Area. Major stations in Martinez and Emeryville feature Coast Starlight and California Zephyr service. The Starlight also services Oakland and San Jose. The Capitol Corridor connects Bay Area cities to Sacramento, and features a BART transfer station at Richmond.
- ACE - Altamont Commuter Express; a rail service that mainly serves commuters to and from the Central Valley to the Silicon Valley. It travels from Stockton through Pleasanton, Fremont, Santa Clara, and ends at San Jose. It operates only during commute hours on weekdays.
Freeways and highways
I-80_Eastshore_Fwy.jpg
The Bay Area possesses an extensive freeway and highway system.
- Trans-bay crossings
- Interstate 80 - The western terminus of I-80 is located in San Francisco, just west of the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge. The interstate continues to the east, connecting to Oakland and the north coast of the East Bay, and then on to Sacramento and Reno.
- Interstate 580 - This spur route's western terminus is in Marin County. The Interstate crosses the San Pablo Bay over the Richmond-San Rafael Bridge, passes through Oakland, then continues to Livermore, through the Altamont Pass to Tracy, where it intersects with Interstate 5.
- California State Route 92 - CA-92's western terminus is in Half Moon Bay. The two lane highway crosses the Santa Cruz Mountains, connecting to Interstate 280 and U.S. Highway 101, becoming a freeway as it passes through San Mateo before crossing the San Mateo-Hayward Bridge to Hayward.
- California State Route 84 - CA-84 begins at the Pacific Coast near San Gregorio State Beach, and crosses the Santa Cruz Mountains on a scenic route between La Honda and Woodside. It then crosses the Bay over the Dumbarton Bridge from Redwood City to Newark. The route then passes through Fremont, continuing as Niles Canyon Road to Sunol and Livermore.
- The Peninsula to the South Bay
- Interstate 280 and U.S. Highway 101 - 8 lane, and in some parts, 10 lane freeways connecting San Francisco to San Jose, passing through the Peninsula. Highway 101 continues south to Gilroy and Salinas, California, before continuing to Los Angeles. For most of its route I-280 runs along the foothills of the Santa Cruz Mountains, and is very scenic, while 101 is highly urban and is locally known as "the world's longest parking lot."
- California State Routes 1 and 35 - two lane highways also traveling down the Peninsula, CA-1 along the Pacific coast, and CA-35 near the ridge of the Santa Cruz Mountains. CA-1 connects to Half Moon Bay, Santa Cruz and Monterey, before continuing to Los Angeles.
- California State Routes 17 and 9 - highways through the Santa Cruz Mountains, connecting the South Bay to Santa Cruz. Part of CA-17 in San Jose is an 8 lane freeway.
- California Routes 237 and 85 - freeways connecting the west Santa Clara Valley to the east Santa Clara Valley, bypassing Downtown San Jose.
- California State Route 87 - north-south freeway entirely in San Jose, connects Downtown to the Almaden Valley.
- California State Route 152 - two lane highway from Watsonville, crosses the Santa Cruz Mountains to Gilroy, then crosses the Diablo Range through Pacheco Pass to I-5 near Los Banos.
- California State Route 82 - highway running from San Jose to Interstate 280 in San Francisco. It is designated a State Route, although it is much more similar to an inner-city boulevard, and contains either 2, 4, or 6 lanes. Through much of the San Mateo County, it is also known as the El Camino Real. It runs from Daly City in the north through the peninsula and beyond.
- The freeway system in Santa Clara county is augmented by its expressway system.
- North Bay
- US-101 and CA-1 - continue north of San Francisco, crossing the Golden Gate Bridge and connecting San Francisco to Marin and Sonoma counties, and eventually to Oregon.
- California State Route 29 - Four-lane expressway connecting Interstate 80 in Vallejo in Solano County to the towns of American Canyon and Napa. North of Napa, SR-29 is a 2 lane rural highway through the towns of the Napa Valley, California's Wine Country to Clear Lake.
- California State Route 37 - Four and two-lane expressway connecting US-101 in Novato with Interstate 80 in Vallejo, along the northern shore of San Pablo Bay.
- California State Route 12 - A highway connecting Santa Rosa with suburbs to the east and west.
- East Bay
- Interstates 880 and 680 travel up the East Bay from San Jose, 880 close to the bay to Oakland, and 680 inland from San Jose north through Fremont, Pleasanton and Concord; then crosses the Benicia-Martinez bridge and ends at Interstate 80 in Fairfield.
- Interstate 980 is entirely in Downtown Oakland and begins at Interstate 880 and travels north to become California State Route 24 at Interstate 580
- California State Route 13, or the Warren Freeway, is entirely in the Oakland Hills and travels north from Interstate 580 to California State Route 24, where the freeway portion ends. Beyond SR 24, SR 13 is Berkeley's Ashby Avenue.
- California State Route 24 begins at Interstate 580 in Oakland and travels east through the Caldecott Tunnel to Interstate 680 in Walnut Creek.
- California State Route 238/Interstate 238 (Mission Boulevard) is an arterial from Fremont to Hayward, along the base of the hills, then becomes a freeway near Oakland.
- California State Route 4 - western terminus at Interstate 80 in Hercules, travels east through Martinez, Pittsburg, and Antioch, where the freeway portion ends. The highway continues to Brentwood and east to Stockton.
Universities & Colleges
The regions boasts of some of the most prestigious Universities in the world. The Nobel Peace Prize winners combined from these Universities are more than what certain countries have won as a whole.
Public:
- University of California, Berkeley
- University of California, San Francisco
- California State University, East Bay (Formerly Hayward)
- Hastings College of the Law
- San Francisco State University
- San Jose State University
- Sonoma State University
Private:
- California College of the Arts
- Golden Gate University
- Holy Names College
- Mills College
- New College of California
- San Francisco Art Institute
- San Francisco Conservatory of Music
- Santa Clara University
- Stanford University
- University of San Francisco
Sports
Baseball
Basketball
American Football
Hockey
Soccer
College Sports
- Stanford Cardinal
- University of California, Berkeley Golden Bears
- San Jose State Spartans
Regional counties, cities and suburbs
The following lists are based on the ten county definition of the Bay Area. Those places listed in italics would be excluded by the nine county definition which excludes Santa Cruz County.
Counties
- Alameda County
- Contra Costa County
- Marin County
- Napa County
- San Francisco County
- San Mateo County
- Santa Clara County
- Santa Cruz County
- Solano County
- Sonoma County
Cities with more than 100,000 inhabitants
- Antioch
- Berkeley
- Concord
- Daly City
- Fairfield
- Fremont
- Hayward
- Oakland
- Richmond
- San Francisco
- San Jose
- Santa Clara
- Santa Rosa
- Sunnyvale
- Vallejo
Suburbs with 10,000 to 100,000 inhabitants
- Alameda
- Alamo
- Albany
- Ashland
- Bay Point
- Belmont
- Benicia
- Blackhawk-Camino Tassajara
- Brentwood
- Burlingame
- Campbell
- Capitola
- Castro Valley
- Cherryland
- Clayton
- Cupertino
- Danville
- Dixon
- Dublin
- East Palo Alto
- El Cerrito
- El Sobrante
- Foster City
- Gilroy
- Half Moon Bay
- Healdsburg
- Hercules
- Hillsborough
- Lafayette
- Larkspur
- Live Oak
- Livermore
- Los Altos
- Los Gatos
- Martinez
- Menlo Park
- Mill Valley
- Millbrae (Major airport: adjacent to San Francisco International Airport)
- Milpitas
- Moraga
- Morgan Hill
- Mountain View, Contra Costa County
- Mountain View, Santa Clara County
- Napa
- Newark
- Novato
- Oakley
- Orinda
- Pacifica
- Palo Alto
- Petaluma
- Piedmont
- Pinole
- Pittsburg
- Pleasant Hill
- Pleasanton
- Redwood City
- Rohnert Park
- San Anselmo
- San Bruno (Major airport: adjacent to San Francisco International Airport)
- San Carlos
- San Leandro
- San Lorenzo
- San Mateo
- San Pablo
- San Rafael
- San Ramon
- Santa Cruz
- Saratoga
- Scotts Valley
- South San Francisco
- Stanford
- Suisun City
- Tamalpais-Homestead Valley
- Union City
- Vacaville
- Walnut Creek
- Watsonville
- Windsor
Suburbs with fewer than 10,000 inhabitants
- American Canyon
- Amesti
- Angwin
- Aptos
- Aptos Hills-Larkin Valley
- Atherton
- Bayview-Montalvin
- Belvedere
- Ben Lomond
- Bethel Island
- Black Point-Green Point
- Bodega Bay
- Bolinas
- Boulder Creek
- Boyes Hot Springs
- Brisbane
- Broadmoor
- Buena Vista
- Burbank
- Byron
- Calistoga
- Cloverdale
- Clyde
- Colma
- Corralitos
- Corte Madera
- Cotati
- Crockett
- Day Valley
- Deer Park
- Diablo
- Dillon Beach
- Discovery Bay
- East Richmond Heights
- East Foothills
- El Granada
- El Verano
- Eldridge
- Elmira
- Emeryville
- Fairfax
- Fairview
- Felton
- Fetters Hot Springs-Agua Caliente
- Forestville
- Freedom
- Fruitdale
- Glen Ellen
- Graton
- Green Valley
- Guerneville
- Highlands-Baywood Park
- Interlaken
- Inverness
- Kensington
- Kentfield
- Knightsen
- La Honda
- Lagunitas-Forest Knolls
- Larkfield-Wikiup
- Lexington Hills
- Loma Mar
- Los Altos Hills
- Loyola
- Lucas Valley-Marinwood
- Montara
- Monte Rio
- Monte Sereno
- Moss Beach
- Mount Eden
- Muir Beach
- Occidental
- Opal Cliffs
- Pacheco
- Pescadero
- Point Reyes Station
- Port Costa
- Portola Valley
- Rio del Mar
- Rio Vista
- Rodeo
- Rollingwood
- Roseland
- Ross
- Saint Helena
- San Geronimo
- San Gregorio
- San Martin
- Santa Venetia
- Sausalito
- Sebastopol
- Seven Trees
- Sonoma
- Soquel
- Stinson Beach
- Strawberry
- Sunol
- Sunol-Midtown
- Tara Hills
- Temelec
- Tiburon
- Tomales
- Twin Lakes
- Vine Hill
- Waldon
- West Menlo Park
- Woodacre
- Woodside
- Yountville
See also
- United States metropolitan area
- List of San Francisco Bay Area writers
- List of San Francisco Bay Area wildflowers
External links
- Template:Wikitravel
- Bay Area Experiences.com (http://www.bayareaexperiences.com) Community-built site with fun, non-touristy things to do in San Francisco and surrounding areas.de:San Francisco Bay Area
The Bay Area comprises 9 countuies, not 8...San Francsico, Marin, Contra Costa, Alameda, Santa Clara, San Mateo, Sonoma, Solano, and Napa.