User:Seav/TestEditLink
|
|
- For other uses see United States (disambiguation)
The United States of America (U.S.A.), also referred to as the United States (U.S.), America, or the States, is a federal republic in North America and the Pacific Ocean. It extends from the Atlantic coast in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west. It shares land borders with Canada in the north and Mexico in the south, shares a marine border with Russia in the west, and has a collection of districts, territories, and possessions around the world including Midway Island and Guam. The country has fifty states, which have a level of local autonomy.
The United States traces its national origin to the declaration by 13 British colonies in 1776 that they were free and independent states. Before the British, and in terms of territory, the Dutch, Spanish and French had a stronger foothold on the New Continent where Native Americans (formerly called Indians) had lived for thousands of years. Since the mid-20th century it has eclipsed most other nations in terms of economic, political, military, and cultural influence.
The country was founded under a tradition of having the rule come from the people under the representative democracy model. The model used by the United States has been adopted by some other countries, such as Mexico.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Main article: History of the United States
Following the European colonization of the Americas, the United States became the world's first modern democracy after its break with Great Britain, with a Declaration of Independence in 1776. The original political structure was a confederation in 1777, ratified in 1781 as the Articles of Confederation. After long debate, this was supplanted by the Constitution of a more centralized federal government in 1789. During the 19th century, many new states were added to the original thirteen as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired a number of overseas possessions. Two major traumatic experiences for the nation were the American Civil War (1861-65) and the Great Depression of the 1930s. Following the end of World War II and then the collapse of the Soviet Union, the U.S. has become the world's most powerful nation-state.
See also: Military history of the United States, Timeline of United States history
Politics
Main article: Politics of the United States
The United States of America consists of 50 states with limited autonomy in which federal law takes precedence over state law. In general, matters that lie entirely within state borders are the exclusive concern of state governments. These include internal communications; regulations relating to property, industry, business, and public utilities; the state criminal code; and working conditions within the state. Many state laws are quite similar from state to state. Finally, there are many areas of overlap between state and federal jurisdictions.
In recent years, the federal government has assumed broader responsibility in such matters as health, education, welfare, transportation, and housing and urban development. The constitutions of the various states differ in some details but generally follow a pattern similar to that of the federal Constitution, including a statement of the rights of the people and a plan for organizing the government. On such matters as the operation of businesses, banks, public utilities, and charitable institutions, state constitutions are often more detailed and explicit than the federal constitution.
The federal government itself consists of three branches: the executive branch, the legislative branch, and the judicial branch. The head of the executive branch is the President of the United States. The legislative branch consists of the United States Congress, while the Supreme Court of the United States is the head of the judicial branch. The President is elected to a four year term by the U.S. Electoral College. The various electors are in turn chosen primarily by the popular votes in the 50 states and the District of Columbia. Members of Congress are elected at varying dates, as are state Governors and state legislatures.
The federal and state government is dominated by two political parties, the Republicans and the Democrats. The dominant political culture in the United States is, as a whole, somewhat to the right of the dominant political culture in European democracies. Given their complex support bases it is difficult to specifically categorize the two major parties' appeal. Within the US political culture, the Republican Party is described as center-right and the Democratic Party is described as center-left. Minor party and independent candidates are very occasionally elected, usually to local or state office, but the United States political system has historically supported "catch all parties" rather than coalition governments. The ideology and policies of the sitting President of the United States commonly play a large role in determining the direction of his political party, as well as the platform of the opposition.
The two parties exist on both the state and federal level, although the parties' organization, platform, and ideologies are not necessarily uniform across all levels of government.
Both major parties draw some support from all the diverse socio-economic classes which compose the mature multi-ethnic capitalist society which makes up the United States. Business interests provide the major funding and support to the Republican Party while labor unions and minority ethnic groups provide major support to the Democrats. Access to funds is vital in the political system due to the financial costs of mounting political campaigns. Thus, through lobbying, corporations, unions, and other organized groups that provide funds and political support to parties and politicians can play a large role in determining the political agendas and government decision-making.
Political divisions
Main article: Political divisions of the United States
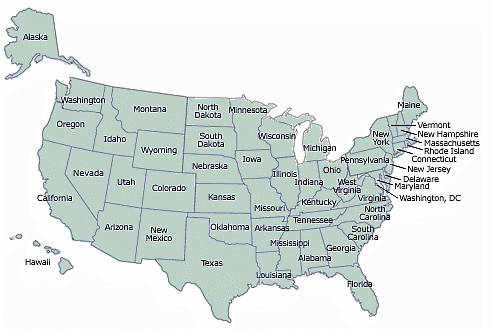
States
Main article: States of the United States
At the time of the Declaration of Independence, the United States consisted of 13 states. In the following years, this number has grown steadily due to expansion to the west, conquest and purchase of lands by the American government, and division of existing states to the current number of 50:
The contiguous part of the United States (i.e. without Hawaii and Alaska or island territories) is called continental United States.
The states are divided into smaller administrative regions, called counties in most states--exceptions being Alaska (boroughs) and Louisiana (parishes). Counties can include a number of cities and towns, or sometimes just a part of one single large city. See County (United States).
Federal district
The District of Columbia is a separate federal district not part of any state and is under the direct authority of Congress. It is there that the nation's capital city—the seat of the federal government—resides.
Dependent areas
Several islands in the Pacific Ocean and Caribbean Sea are dependent territories of the United States:
|
|
|
Puerto Rico and the Northern Marianas are commonwealths of the United States.
The U.S. Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay is leased from Cuba and only mutual agreement or U.S. abandonment of the area can terminate the lease.
The U.S. has made no territorial claim in Antarctica but has reserved the right to do so.
From July 18, 1947 until October 1, 1994, the U.S. administered the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands, but recently entered into a new political relationship with all four political units.
Geography
Main article: Geography of the United States
As the world's third largest nation (total area), the United States landscape varies greatly: temperate forestland on the East coast, mangrove forests in Florida, the Great Plains in the centre of the country, the Mississippi-Missouri river system, the Rocky Mountains west of the plains, deserts and temperate coastal zones west of the Rocky Mountains and temperate rainforests in the Pacific Northwest. The arctic regions of Alaska and the volcanic islands of Hawaii only increase the geographic and climatic diversity.
The climate varies along with the landscape, from sub-tropic in Florida to tundra in Alaska. Large parts of the country have a continental climate, with warm summers and cold winters. Some parts of the United States, particularly parts of California, have a Mediterranean climate.
Economy
Main article: Economy of the United States
The economy of the United States is organized on the capitalist model and is marked by steady growth, low unemployment and inflation, a large trade deficit, and rapid advances in technology. The American economy can be regarded as the most important in the world. Several countries have coupled their currency with the dollar, or even use it as a currency, and the American stock markets are globally seen as an indicator of world economy.
The country has rich mineral resources, with extensive gold, oil, coal and uranium deposits. Agriculture brings the country among the top producers of, among others, corn (maize), wheat, sugar and tobacco. American industry produces cars, airplanes and electronics. The biggest sector is however service industries; about three-quarters of Americans are employed in that sector.
The largest trading partner of the USA is its northern neighbor, Canada. Other major partners are Mexico, the European Union and the industrialized nations in the East Asia, such as Japan and South Korea. Trade with China is also significant.
See also: List of American companies
Culture
Main article: Culture of the United States
American culture has a large influence on the rest of the world, especially the Western world. American music is heard all over the world, and American movies and television shows can be seen almost anywhere. This is in stark contrast to the early days of the American republic, when the country was generally seen as an agricultural backwater with little to offer the culturally advanced world centers of Asia and Europe. Nearing the end of its third century, nearly every major American city offers classical and popular music; historical, scientific and art research centers and museums; dance performances, musicals and plays; outdoor art projects and internationally significant architecture. This development is a result of both contributions by private philanthropists and government funding.
The United States is also a great center of higher education, boasting more than 1,500 universities, colleges, and other institutions of higher learning, the top tier of which may be considered to be among the most prestigious and advanced in the world.
| Date | Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | celebrates beginning of year, marks traditional end of "holiday season" |
| January, third Monday | Martin Luther King, Jr. Day | honors King, Civil Rights leader |
| February, third Monday | Presidents' Day | honors former American Presidents, especially Washington and Lincoln |
| May, last Monday | Memorial Day | honors service men and women who died in service, marks traditional beginning of summer |
| July 4 | Independence Day | celebrates Declaration of Independence, usually called "The Fourth of July" |
| September, first Monday | Labor Day | celebrate achievements of workers, marks traditional end of summer |
| October, second Monday | Columbus Day | honors Christopher Columbus, traditional discoverer of the Americas |
| November 11 | Veteran's Day | traditional observation of a moment of silence at 11 AM remembering those who fought for peace |
| November, fourth Thursday | Thanksgiving | give thanks for autumn harvest, marks traditional beginning of "holiday season" |
| December 25 | Christmas | celebrates the nativity of Jesus Christ, also celebrated as secular winter holiday |
See also: Holidays of the United States
Related Topics
Main article: List of United States-related topics
External links
United States government
- Official website of the United States government (http://www.firstgov.gov) - Gateway to governmental sites
- The White House (http://www.whitehouse.gov) - Official site of the Presidential residence
- Senate.gov (http://www.senate.gov) - Official site of the United States Senate
- House.gov (http://www.house.gov) - Official site of the United States House of Representatives
- SCOTUS (http://www.supremecourtus.gov) - Official site of the Supreme Court of the United States
- Portrait of the USA (http://usinfo.state.gov/usa/infousa/facts/factover/homepage.htm) - Published by the United States Information Agency, September 1997.
- US Census Housing and Economic Statistics (http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/) Updated regularly by US Bureau of the Census.
| Countries in North America |
|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas | Barbados | Belize | Canada | Costa Rica | Cuba | Dominica | Dominican Republic | El Salvador | Grenada | Guatemala | Haiti | Honduras | Jamaica | Mexico | Nicaragua | Panama | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Trinidad and Tobago | United States |
| Dependencies: Anguilla | Aruba | Bermuda | British Virgin Islands | Cayman Islands | Greenland | Guadeloupe | Martinique | Montserrat | Navassa Island | Netherlands Antilles | Puerto Rico | Saint-Pierre and Miquelon | Turks and Caicos Islands | U.S. Virgin Islands |
</div> </div>