Dominican Republic
|
|
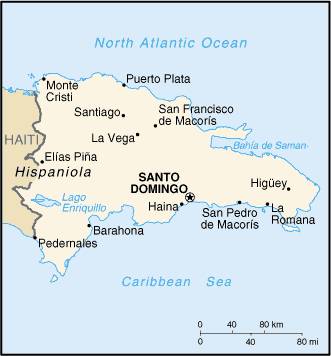
The Dominican Republic is a Spanish-speaking representative democracy located on the eastern portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, bordering Haiti. A legacy of unsettled, mostly non-representative, rule for much of the 20th century — most notably the thirty-two year reign of the military leader Rafael Leónidas Trujillo — lasted until 1961.
The Dominican Republic ("do-MIN-i-kun")also called Quisqueya by its inhabitants, should not be confused with Dominica ("do-min-EE-ka"), another Caribbean country.
| ||||
| National motto: Dios, patria, libertad (Spanish: God, Country, Liberty) | ||||
| ||||
| Official language | Spanish | |||
| Capital | Santo Domingo | |||
| President | Leonel Fernández | |||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 138th 48,730 km² 1,6% | |||
| Population - Total (July 2004 est) - Density | Ranked 86th 8,833,634 181/km² | |||
| Independence since | from Haiti 27 February 1844/Spain | |||
| Currency | Peso | |||
| Time zone | UTC -4 | |||
| National anthem | Quisqueyanos valientes | |||
| Internet TLD | .do | |||
| Calling Code | +1 809 and +1 829 | |||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of the Dominican Republic
The country has had a history of changing ownership, with Spain, France, Haiti, Spain again, and the United States (twice) taking their turns at ruling Dominican territory amid attempts at independence and self-rule. In the beginning the island was primarily inhabited by the Taino nation. A branch of the Arawaks. Taino means "The good" in that native language. A system of cacicazgos (chiefdoms) Marien, Maguana, Higuey, Magua and Xaragua were there names. These chiefdoms were then subdivided into subchiefdoms. The cacicagzos were based on a system of tribute, consisting of the food grown by the taino.
The arrival of the Guamikena (the covered ones)
In October of 1492, the europeans arrived and the taino believing that these beings from over the horizon were in someway supernatural feted them with all the honors available to them. This was a totally different society from the one the Europeans came from. One of the things that piqued the curiosity was the amount of clothing worn by the Europeans. Therefore they came to call them guamikena. Guacanagarix the chief who hosted Columbus and his men treated them kindly and provided him with everything they desired.
The twentieth century was marked by repeated U.S. intervention in local affairs. Apart from tentative U.S. support for the Trujillo dictatorship (1930-1961) (though this faded during his final years,) the most infamous example of this is the 1965 invasion by American troops in the midst of a Dominican civil war, an uprising that was sparked by an attempt to restore the republic's first democratically-elected president of the 20th century, Juan Bosch, who had been overthrown by a right-wing coup in 1963. This invasion had the effect of establishing the rule of Joaquín Balaguer (1966-1978), and ensuring that Juan Bosch's constitutional government never returned to power. The Johnson administration justified the 1965 intervention by stating that it suspected many of Bosch's supporters were pro-Cuban Communists.
Politics
Main article: Politics of the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a representative democracy whose national powers are divided among independent executive, legislative, and judicial branches. The president appoints the cabinet, executes laws passed by the legislative branch, and is commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The president and vice president run for office on the same ticket and are elected by direct vote for four-year terms.
Legislative power is exercised by a bicameral National Congress — the Senate (32 members), and the Chamber of Deputies (150 members). Presidential elections are held in years evenly divisible by four. Congressional and municipal elections are held in even-numbered years not divisible by four.
Provinces
Main article: Provinces of the Dominican Republic
Geography
Isla_Saona.jpg
Main article: Geography of the Dominican Republic
The capital is Santo Domingo. The second largest city is Santiago de los Caballeros, more commonly referred to as simply Santiago.
The country has three major mountain ranges: The Central Mountains, which originate in Haiti and span the central part of the island, ending up in the south. This mountain range boasts the highest peak in the Antilles, Pico Duarte (3 175 m above sea level). The Septentrional Mountains, running parallel to the Central Mountains, separate the Cibao Valley and the Atlantic coastal plains. The highest point here is Pico Diego de Ocampo. The lowest and shortest of the three ranges is the Eastern Mountains, in the eastern part of the country. There are also the Sierra Bahoruco and the Sierra Neyba in the southwest. This is a country of many rivers, including the navigable Soco, Higuamo, Romana, Yaque del Norte, Yaque del Sur, Yuna, Yuma, and Bajabonico.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of the Dominican Republic
The majority of Dominicans are of mixed European and African descent. About 11% of Dominicans are primarily of African descent, including many Haitian migrants and their descendants. About 16% of Dominicans are of Spanish or other European origin. Some are Asian, mostly of Chinese descent, and Middle Easterners, mostly Arab. Dominican culture is essentially Hispanic, and also has many African, Antilliean, and United States influences.
Since the early 1960s, economic problems have led to a vast migration of Dominicans to the US, mainly to large east coast cities. New York City's Washington Heights is so densely populated by Dominicans, it is sometimes referred to as Quisqueya Heights. Quisqueya is believed to be the name given to the eastern side of Hispaniola by its original inhabitants, the Arawak Indians, although this version is disputed by some historians. Dominicans are now one of the largest Latino groups in the US.
In recent years, illegal immigration from Haiti has worsened as Haiti's population explodes and the Dominican economy improves.
Economy
Main article: Economy of the Dominican Republic
Culture
Main article: Culture of the Dominican Republic
89% of Dominicans are baptised in the Roman Catholic Church
The Dominican Republic is known for a form of music called merengue, which has been popular since the mid- to late-1800s.
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in the Dominican Republic
- Transportation in the Dominican Republic
- Military of the Dominican Republic
- Foreign relations of the Dominican Republic
- Charytin
- List of Dominicans
External links
- DRINDEX: Information, Flights, Real-estate & More on the Dominican Republic (http://www.dominicanrepublicindex.com)
- DR1: a portal in English for the Dominican Republic (http://www.dr1.com)
- Dominican impressions: The Enchantment of the Dominican Republic. Photo galleries for locals and vacationers alike, featuring aerial views of the north coast of the Dominican Republic. (http://www.dominicanimpressions.com)
Online Dominican Newspapers (in Spanish)
- [1] (http://www.listin.com.do)
- [2] (http://www.diariolibre.com)
- [3] (http://www.elcaribecdn.com)
- [4] (http://www.hoy.com.do)
- [5] (http://www.diarioadiario.com.do)
| Countries in West Indies |
|---|
|
Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas | Barbados | Cuba | Dominica | Dominican Republic | Grenada | Haiti | Jamaica | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Trinidad and Tobago |
|
Dependencies: Anguilla | Aruba | British Virgin Islands | Cayman Islands | Guadeloupe | Martinique | Montserrat | Navassa Island | Netherlands Antilles | Puerto Rico | Turks and Caicos Islands | U.S. Virgin Islands |
| | Missing image Caricom-Flag.png Flag of the Caribbean Community |
|---|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas¹ | Barbados | Belize | Dominica | Grenada | Guyana | Haiti | Jamaica | Montserrat | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Suriname | Trinidad and Tobago | |
| Associate members: Anguilla | Bermuda | Cayman Islands | British Virgin Islands | Turks and Caicos Islands | |
| Observer status: Aruba | Colombia | Dominican Republic | Mexico | Netherlands Antilles | Puerto Rico | Venezuela | |
| ¹ member of the community but not the Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy. | edit (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Template:Caricom&action=edit)
|
ca:República Dominicana cs:Dominikánská republika da:Dominikanske Republik de:Dominikanische Republik et:Dominikaani Vabariik el:Δομινικανή Δημοκρατία es:República Dominicana eo:Domingo fr:République dominicaine gl:República Dominicana ko:도미니카 공화국 ht:Repiblik Dominikan hr:Dominikanska Republika id:Republik Dominika it:Repubblica Dominicana he:הרפובליקה הדומיניקנית lv:Dominikana lt:Dominikos Respublika hu:Dominikai Köztársaság ms:Republik Dominican zh-min-nan:Dominic Kiōng-hô-kok nl:Dominicaanse Republiek nds:Dominikaansche Republiek ja:ドミニカ共和国 nb:Den dominikanske republikk pl:Dominikana pt:República Dominicana ru:Доминиканская Республика sk:Dominikánska republika sl:Dominikanska republika fi:Dominikaaninen tasavalta sv:Dominikanska republiken tr:Dominik Cumhuriyeti uk:Домініканська Республіка zh:多明尼加