Senegal
|
|
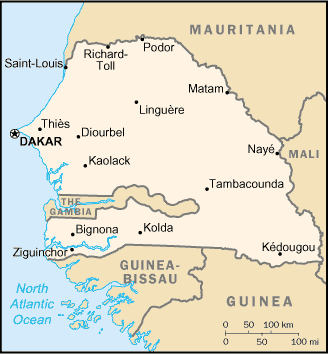
The Republic of Senegal is a country south of the Senegal River in West Africa. Senegal is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Mauritania to the north, Mali to the east, and Guinea and Guinea-Bissau to the south. The Gambia forms a virtual enclave within Senegal, following the Gambia River more than 300 km inland. The Cape Verde islands lie some 560 km off the Senegalese coast.
| ||||
| National motto: Un Peuple, Un But, Une Foi (French: One People, One Goal, One Belief) | ||||
| Missing image LocationSenegal.png image:LocationSenegal.png | ||||
| Official languages | French | |||
| Capital | Dakar | |||
| President | Abdoulaye Wade | |||
| Prime Minister | Macky Sall | |||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 85th 196,190 km² 2.1% | |||
| Population - Total (2002) - Density | Ranked 75th 10,284,929 52/km² | |||
| Independence - Date | From France 1959 | |||
| Currency | CFA Franc | |||
| Time zone | UTC 0 | |||
| National anthem | Pincez Tous vos Koras, Frappez les Balafons | |||
| Internet TLD | .sn | |||
| Calling Code | 221 | |||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Senegal
Islam, the dominant religion in Senegal, first came to the region in the 11th century. Of the native kingdoms, the Jolof Empire of the 14th century was the most powerful. Various European powers came to the area from the 15th century onward, until France ended up in possession of what had become an important slave trade departure point.
Dakar became the capital of the French colony of French West Africa in 1902. In January 1959, Senegal and the French Sudan merged to form the Mali Federation, which became fully independent on June 20, 1960, as a result of the independence and the transfer of power agreement signed with France on April 4, 1960. Due to internal political difficulties, the Federation broke up on August 20, 1960. Both Senegal and French Sudan (renamed the Republic of Mali) proclaimed independence individually.
Senegal joined with The Gambia to form the nominal confederation of Senegambia in 1982. However, the envisaged integration of the two countries was never carried out, and the union was dissolved in 1989. Despite peace talks, a separatist group in the southern Casamance region has sporadically clashed with government forces since 1982. Senegal has a long history of participating in international peacekeeping.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Senegal
The Senegalese republic's head of state is the president, elected by universal adult suffrage to a five-year term, who appoints the prime minister who in turn appoints the cabinet in consultation with the president. The unicameral Senegalese parliament is the National Assembly or Assemblée Nationale with 120 members, who are elected by direct, popular vote to serve five-year terms, separately from the president.
The Court of Final Appeals or Cour de Cassation and the Constitutional Council, the justices of which are named by the president, are the nation's highest tribunals. The law on decentralisation, which came into effect in January 1997, distributed significant central government authority to regional assemblies. Senegal is characterised by a democratic multiparty political culture and has enjoyed relatively stable governments since independence.
Regions
Main article: Regions of Senegal
Senegal is subdivided into 11 regions (régions, singular - région):
Geography
Main article: Geography of Senegal
The Senegalese landscape consists mainly of the rolling sandy plains of the western Sahel which rise to foothills in the southeast. Here is also found Senegal's highest point, an otherwise unnamed feature near Nepen Diakha at 581 m. The northern border is formed by the Senegal River, other rivers include the Gambia and Casamance Rivers. The capital Dakar lies on the Cap-Vert peninsula, the westernmost point of continental Africa.
Senegal2.jpg
The local climate is tropical with well-defined dry and humid seasons that result from northeast winter winds and southwest summer winds. Dakar's annual rainfall of about 24 in (600 mm) occurs between June and October when maximum temperatures average 27 °C; December to February minimum temperatures are about 17 °C. Interior temperatures are higher than along the coast, and rainfall increases substantially farther south, exceeding 1500 mm annually in some areas.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Senegal
In January 1994, Senegal undertook a bold and ambitious economic reform programme with the support of the international donor community. This reform began with a 50 percent devaluation of Senegal's currency, the CFA franc, which was linked at a fixed rate to the former French franc and now to the euro. Government price controls and subsidies have been steadily dismantled. After seeing its economy contract by 2.1 percent in 1993, Senegal made an important turnaround, thanks to the reform programme, with real growth in GDP averaging 5 percent annually during 1995-2001. Annual inflation had been pushed down to less than 1 percent, but rose to an estimated 3.3 percent in 2001. Investment rose steadily from 13.8 percent of GDP in 1993 to 16.5 percent in 1997.
SenegalStreet.jpg
As a member of the West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU), Senegal is working toward greater regional integration with a unified external tariff. Senegal also realised full Internet connectivity in 1996, creating a miniboom in information technology-based services. Private activity now accounts for 82% of GDP. On the negative side, Senegal faces deep-seated urban problems of chronic unemployment, trade union militancy, juvenile delinquency, and drug addiction.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Senegal
Ethnicity
Senegal has a wide variety of ethnic groups and, accordingly, multiple languages are spoken. French is the official language but is used regularly only by the literate minority. The Wolof are the largest single group in Senegal at 43%, other ethnic groups include the Fula (24%), the Serer (15%), the Jola (4%), Mandinka (3%), beside numerous smaller communities. About 50,000 Europeans (mostly French) and Lebanese reside in Senegal, mainly in the cities. Among those cities as well, there are also some Chinese and Vietnamese minorities.
Religion
Most Senegalese (90%) are Muslim, with a minority of some 9% adhering to Christian faiths (mostly Roman Catholic), as well as a small (1%) group that follows indigenous beliefs. Senegal has one Roman Catholic archdiocese, the Archdiocese of Dakar.
Habitation patterns
About 70% of Senegal's population lives in rural areas. Density in these areas varies from about 77 km² in the west-central region to 2 km²in the arid eastern section.
Culture
SenegalMbour.jpg
Main article: Culture of Senegal
- List of Senegalese
- Cinema of Senegal
- Music of Senegal
- List of writers from Senegal
- The Senegalese writer and film director Ousmane Sembène is considered to be the 'father' of African Cinema.
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Senegal
- Transportation in Senegal
- Military of Senegal
- Foreign relations of Senegal
- Indigenous cultures, kingdoms and ethnic groups of Senegal
Miscellaneous topics
External links
Template:Portal Template:Commonscat Template:Wiktionary
Government
- Template:Fr icon Gouvernement du Sénégal (http://www.gouv.sn) - Official governmental website (in French)
- Embassy of the Republic of Senegal in London (http://www.senegalembassy.co.uk/) government information and links
News
- allAfrica.com - Senegal (http://allafrica.com/senegal/) news headline links
Overviews
- BBC News Country Profile - Senegal (http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/country_profiles/1064496.stm)
- CIA World Factbook - Senegal (http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/sg.html)
Directories
- LookSmart - Senegal (http://search.looksmart.com/p/browse/us1/us317836/us317916/us559898/us559899/us10065674/us559945/) directory category
- Open Directory Project - Senegal (http://dmoz.org/Regional/Africa/Senegal/) directory category
- Stanford University - Africa South of the Sahara: Senegal (http://www-sul.stanford.edu/depts/ssrg/africa/sene.html) directory category
- The Index on Africa - Senegal (http://www.afrika.no/index/Countries/Senegal/index.html) directory category
- University of Pennsylvania - African Studies Center: Senegal (http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Country_Specific/Senegal.html) directory category
- Yahoo! - Senegal (http://dir.yahoo.com/Regional/Countries/Senegal/) directory category
Tourism
Other
- Template:Fr icon Teranga Senegal (http://www.teranga-senegal.com) - French Portal - Travel guide (in French)
| Countries in Africa | ||
|
Algeria | Angola | Benin | Botswana | Burkina Faso | Burundi | Cameroon | Cape Verde | Central African Republic | Chad | Comoros | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Republic of the Congo | Côte d'Ivoire | Djibouti | Egypt | Equatorial Guinea | Eritrea | Ethiopia | Gabon | The Gambia | Ghana | Guinea | Guinea-Bissau | Kenya | Lesotho | Liberia | Libya | Madagascar | Malawi | Mali | Mauritania | Mauritius | Morocco | Mozambique | Namibia | Niger | Nigeria | Rwanda | São Tomé and Príncipe | Senegal | Seychelles | Sierra Leone | Somalia | Somaliland | South Africa | Sudan | Swaziland | Tanzania | Togo | Tunisia | Uganda | Zambia | Zimbabwe | Western Sahara | ||
| Dependencies: Canary Islands | Ceuta and Melilla | Madeira Islands | Mayotte | Réunion | Saint Helena and dependencies | ||
da:Senegal de:Senegal et:Senegal es:Senegal eo:Senegalo fr:Sénégal gd:Senegal ko:세네갈 io:Senegal id:Senegal is:Senegal it:Senegal lt:Senegalas ms:Senegal nl:Senegal (land) nds:Senegal ja:セネガル nb:Senegal pl:Senegal pt:Senegal ro:Senegal ru:Сенегал simple:Senegal sk:Senegal sl:Senegal fi:Senegal sv:Senegal tr:Senegal uk:Сенегал zh:塞内加尔