Namibia
|
|
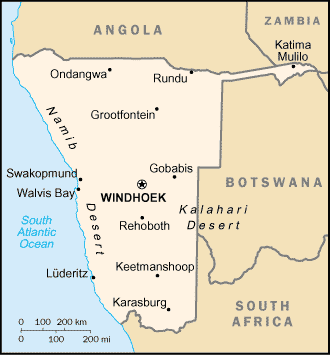
The Republic of Namibia is a country in southwestern Africa, on the Atlantic coast. It is bordered by Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east, and South Africa to the south. It gained independence from South Africa in 1990, and as such it is one of the youngest nations in the world. Its capital is Windhoek.
| |||||
| National motto: Unity, Liberty, Justice | |||||
| |||||
| Official languages | English1 | ||||
| Capital | Windhoek | ||||
| President | Hifikepunye Pohamba | ||||
| Prime minister | Nahas Angula | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 33rd 825,418 km² Negligible | ||||
| Population - Total (2002) - Density | Ranked 143rd 1,820,916 2.2/km² | ||||
| Independence | (from South Africa) March 21, 1990 | ||||
| Currency | Namibian dollar | ||||
| Time zone | UTC +1 | ||||
| National anthem | Namibia, Land of the Brave | ||||
| Internet TLD | .na | ||||
| Calling Code | 264 | ||||
| 1 The majority of the white population speaks either German or Afrikaans. German and Afrikaans were official languages until 1990, when the country gained independence | |||||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Namibia
The dry lands of Namibia, inhabited since the early times by San, Damara, Nama and since about the 14th century A.D. also by immigrating Bantu, who came with the Bantu expansion, were not extensively explored by Europeans until the 19th century, when the land came under German control as South-West Africa, with the exception of Walvis Bay, which was under British control. South Africa occupied the colony during World War I and administered it as a League of Nations mandate territory until after World War II when it unilaterally annexed the territory.
In 1966 the Marxist South-West Africa People's Organisation (SWAPO) guerrilla group launched a war of independence for the area that was soon named Namibia, but it was not until 1988 that South Africa agreed to end its administration in accordance with a United Nations peace plan for the entire region. Independence came in 1990, while Walvis Bay was ceded to Namibia in 1994.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Namibia
The Namibian head of state is the president, who is elected by popular vote every five years. The government is headed by the prime minister, who is appointed by the president, together with his cabinet. SWAPO, the primary force behind independence that has since moved away from its Marxist roots, is currently still the country's largest party.
Namibia's bicameral parliament consists of the National Council, which holds 26 seats occupied by two members chosen from each regional council to serve six-year terms, and the National Assembly of 78 seats, of which 72 members are elected by popular vote and 6 non-voting members are appointed by the president. All serve five-year terms.
The Assembly is the primary legislative body, with the Council playing more of an advisory role. The 1990 constitution is noted for being one of the first to incorporate protection of the environment into its text. The highest judicial body is the Supreme Court, whose judges are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial Service Commission.
Regions
Main article: Regions of Namibia
Namibia is divided into 13 regions: Caprivi, Erongo, Hardap, Karas, Kavango, Khomas, Kunene, Ohangwena,Omaheke, Omusati, Oshana, Oshikoto, and Otjozondjupa.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Namibia
The Namibian landscape consists primarily of central highlands of which the highest point is the Brandberg at 2,606 m. The central plateau runs from north to south, bordered by the Namib Desert and its coastal plains in the west, the Orange River in the south, and the Kalahari Desert in the east. A remarkable strip of land in the northeast known as the Caprivi Strip is the remainder of a narrow corridor for Germany to access the Zambezi River.
The Namibian climate ranges from desert to subtropical and is generally hot and dry; precipitation is sparse and erratic. The cold, north-flowing Benguela current accounts for some of the low precipitation. Besides the capital city Windhoek, in the centre of the country, important towns are the ports of Walvis Bay and Swakopmund, as well as Oshakati, Grootfontein, Tsumeb and Keetmanshoop.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Namibia
The economy is heavily dependent on the extraction and processing of minerals for export. Mining accounts for 20% of GDP. Namibia is the fourth-largest exporter of non-fuel minerals in Africa and the world's fifth-largest producer of uranium. Rich alluvial diamond deposits make Namibia a primary source for gem-quality diamonds. Namibia also produces large quantities of lead, zinc, tin, silver, and tungsten.
About half of the population depends on agriculture (largely subsistence agriculture) for its livelihood. Namibia must import some of its food. Although per capita GDP is five times the per capita GDP of Africa's poorest countries, the majority of Namibia's people live in pronounced poverty because of large-scale unemployment, the great inequality of income distribution, and the large amount of wealth going to foreigners. The Namibian economy has close links to South Africa. Agreement has been reached on the privatisation of several more enterprises in coming years, which should stimulate long-run foreign investment.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Namibia
The majority of the Namibian population is black (87%), mostly of the Ovambo tribe, which forms about half of the population. There are larger groups of Nama and San, who differ significantly in appearance from the country's other black African ethnic groups. There is also a significant group of people with mixed EuroDutch origin e.g. the Baster- 7%. Whites of unmixed ancestry make up about 6% of the population--one of the largest proportions in sub-Saharan Africa. Most whites and coloureds are Afrikaans speakers of South African descent. A much smaller portion is of German and British descent.
While the official language is English, most of the white population speaks either Afrikaans or German, which both were official languages until 1990 when Namibia became independent. The home language of most of the population is Ovambo or one of several other indigenous languages. Christianity is the major religion, with the Lutheran Church being the largest.
See also: Music of Namibia
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Namibia
- Transportation in Namibia
- Military of Namibia
- Constituencies of Namibia
- Regions of Namibia
- Foreign relations of Namibia
- List of Namibians
- List of cities in Namibia
- Frankie Fredericks
- National parks
- Reporters without borders Worldwide Press Freedom Index 2003: Rank 56 out of 166 countries (3-way tie) (31 out of 139 countries - 2002)
External links
Template:Portal Template:Commonscat Template:Wiktionary
Government
- Republic of Namibia (http://www.grnnet.gov.na/intro.htm) - Namibian governmental portal
Overviews
- BBC News - Country Profile: Namibia (http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/country_profiles/1063245.stm)
- CIA World Factbook - Namibia (http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/wa.html)
Directories
- LookSmart - Namibia (http://search.looksmart.com/p/browse/us1/us317836/us317916/us559898/us559899/us10065675/us559939/) directory category
- Open Directory Project - Namibia (http://www.dmoz.org/Regional/Africa/Namibia/) directory category
- Stanford University - Africa South of the Sahara: Namibia (http://www-sul.stanford.edu/depts/ssrg/africa/namibia.html) directory category
- The Index on Africa - Namibia (http://www.afrika.no/index/Countries/Namibia/) directory category
- University of Pennsylvania - African Studies Center: Namibia (http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Country_Specific/Namibia.html) directory category
- Yahoo! - Namibia (http://dir.yahoo.com/Regional/Countries/Namibia/) directory category
Tourism
Other
- Pictures from a trip to Namibia (http://namibia.ianandwendy.com)
| Countries in Africa | ||
|
Algeria | Angola | Benin | Botswana | Burkina Faso | Burundi | Cameroon | Cape Verde | Central African Republic | Chad | Comoros | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Republic of the Congo | Côte d'Ivoire | Djibouti | Egypt | Equatorial Guinea | Eritrea | Ethiopia | Gabon | The Gambia | Ghana | Guinea | Guinea-Bissau | Kenya | Lesotho | Liberia | Libya | Madagascar | Malawi | Mali | Mauritania | Mauritius | Morocco | Mozambique | Namibia | Niger | Nigeria | Rwanda | São Tomé and Príncipe | Senegal | Seychelles | Sierra Leone | Somalia | Somaliland | South Africa | Sudan | Swaziland | Tanzania | Togo | Tunisia | Uganda | Zambia | Zimbabwe | Western Sahara | ||
| Dependencies: Canary Islands | Ceuta and Melilla | Madeira Islands | Mayotte | Réunion | Saint Helena and dependencies | ||
ar:ناميبيا ca:Namíbia cs:Namibie cy:Namibia da:Namibia de:Namibia et:Namiibia es:Namibia eo:Namibio fr:Namibie ko:나미비아 id:Namibia it:Namibia he:נמיביה ks:नमीबिया kw:Namibi la:Namibia lt:Namibija ms:Namibia zh-min-nan:Namibia nl:Namibië nds:Namibia ja:ナミビア nb:Namibia pl:Namibia pt:Namíbia ro:Namibia ru:Намибия sa:नमीबिया sk:Namíbia sl:Namibija fi:Namibia sv:Namibia uk:Намібія zh:纳米比亚