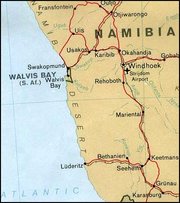
Walvis Bay
|
|
Walvis Bay, Namibia
| Area | 1,124 km² (696.9 mi²) | |
|---|---|---|
| Established | 1840 | |
| Population | 45,400 | |
| Population Density | 30.4/km² (65.2/mi²) | |
| Administrative Division | Erongo | |
| Mayor | Augustinus Katiti | |
| Time Zone | South African Standard Time: UTC+1 | |
| Latitude and Longitude | Latitude: 22.95°S | Longitude: 14.50°E |
Walvis Bay, (Afrikaans: Walvisbaai meaning "Whale Bay"), is an area in Namibia with a chequered history. The bay has been a haven for sea vessels because of its natural deep-water harbour. Being rich in plankton and marine life, these waters drew large numbers of whales. This attracted whalers and fishing vessels. A succession of colonists exploited the location and resources of this strategic harbour settlement. The harbour’s value in relation to the sea route around the Cape of Good Hope had caught the attention of world powers since it was discovered. This explains the complicated political status of Walvis Bay down the years. Walvis Bay is 30 km (18,6 mi) from Swakopmund.
History
In 1487, the renowned Portuguese navigator Bartholomew Dias anchored his flagship São Cristavao in Walvis Bay on 8 December 1487, on his expedition to discover a sea route to the East via the Cape of Good Hope. He named the bay "O Golfo de Santa Maria da Conceição." However, the Portuguese did not formally stake claim to Walvis Bay.
Nothing much was done with Walvis Bay until 1840, when in the scramble for Africa, Britain, a premier seafaring nation at the time, annexed Walvis Bay and a small area surrounding the territory to forestall German ambitions in the region and to ensure safe passage of British ships around the Cape. In 1910, Walvis Bay, as well as the Cape Colony, became part of the newly formed Union of South Africa. However, a dispute arose with Germany over the enclave’s boundaries. This was eventually settled in 1911 and Walvis Bay was allocated an area of 1,124 km² (697,5 mi²).
South African Forces ousted the Germans in 1915 and Walvis Bay was quickly integrated into the new martial law regime established in South-West Africa. South Africa was later rewarded control over South West Africa by the League of Nations. Civilian rule was restored in South-West Africa in 1921 and Walvis Bay became an integral part of South West Africa. In 1971, with independence for South-West Africa imminent, South Africa transferred power over Walvis Bay back to its Cape Province.
In its attempt to avoid losing control of Walvis Bay in 1977 to a possibly hostile SWAPO led government, the then South African Government reimposed direct rule and reasserted its claim of sovereignty based on the original annexation. In 1978, the United Nations Security Council provided for bilateral negotiations between South Africa and a future Namibia to resolve the political status of Walvis Bay.
In 1990, South-West Africa gained independence. A new nation, Namibia, was born but Walvis Bay remained under South African control. It took until 1994 for Walvis Bay to be formally returned to Namibia after the local business community and investors in Walvis Bay applied pressure on the South African authorities to resolve the political status of Walvis Bay. It was formally transferred to Namibian sovereignty at midnight on 28 February 1994.
External links
- Walvisbay Port Information (http://www.ports.co.za/walvis-bay.php)
- Walvis Bay City Council (http://www.walvisbaycc.org.na/)