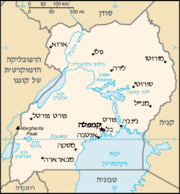
Uganda
|
|
The Republic of Uganda, a country in east-central Africa, bordered in the east by Kenya, in the north by Sudan, by the Democratic Republic of Congo in the west, Rwanda in the southwest and Tanzania in the south. The southern part of the country includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, within which it shares borders with Kenya and Tanzania.
Uganda takes its name from the historical Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a portion of the south of the country, including the capital Kampala.
| |||||
| Motto: For God and My Country | |||||
| Anthem: Oh Uganda, Land of Beauty | |||||
| |||||
| Capital | Kampala Template:Coor dm | ||||
| Largest city | Kampala | ||||
| Official languages | English | ||||
| Government | Non-party republic Yoweri Museveni | ||||
| Independence | October 9, 1962 | ||||
| Area • Total • Water (%) | 236,040 km² (81st) 15.39 | ||||
| Population • 2000 est. • ? census • Density | 24,699,073 (42nd) ? 105/km² (?) | ||||
| GDP (PPP) • Total • Per capita | 2003 estimate $6.198 billion (108th) $245 (170th) | ||||
| Currency | Shilling (UGX)
| ||||
| Time zone • Summer (DST) | Local time (UTC+3) not observed (UTC+3) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .ug | ||||
| Calling code | +256 (+006 from Kenya and Tanzania)
| ||||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Uganda
Little is known about the history of the region now covered by Uganda until the arrival of the Arabs and Europeans in the mid 1800s. Humans are known to have lived in the area since at least the first millennium BC.
When Arabs and Europeans arrived in the 19th century, they encountered a number of kingdoms in the area. They included Ankole, Buganda, Bunyoro, Busoga, and Toro. The largest and most important of these kingdoms was Buganda, which exists as part of Uganda today. Islam and Christianity were introduced to these kingdoms.
The area was placed under the charter of the British East Africa Company in 1888, and was ruled as a protectorate by the United Kingdom from 1894. As several other territories and chiefdoms were integrated, the final protectorate called Uganda took shape in 1914.
By 1966, the first Prime Minister, Milton Obote, had overthrown the constitution and declared himself president, ushering in an era of coups and counter-coups which would last until the mid-1980s. 1971 saw Idi Amin take power, ruling the country with the military for the coming decade.
His rule cost an estimated 300,000 Ugandans' lives, and he forcibly removed the entrepreneurial East Indian minority from Uganda, decimating the economy. His reign was ended by a Tanzanian invasion in November 1978 to April 1979. The situation improved little with the return of Milton Obote, who was deposed once more in 1985.
The current president, Yoweri Museveni, has been in power since 1986 and in generally viewed as being part of a new generation of African leaders. There is controversy, however, about the proposed change to the constitution that would allow him to run for a third term. Relative stability has been brought to the country with the exception of the North, which continues to struggle with a rebel insurgency. Uganda has demonstrated the most effective national response to HIV/AIDS of any African country.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Uganda
The President of Uganda, currently Yoweri Museveni, is both head of state and head of government. The president appoints a prime minister who aids him in his tasks. The current prime minister is Apolo Nsibambi. The parliament is formed by the National Assembly, which has 303 members. 86 of these members are nominated by interest groups, including women and the Ugandan army. The remaining members are elected for five-year terms during general elections.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Uganda
Although landlocked, Uganda has access to several large water bodies, including Lake Victoria, Lake Albert, Lake Kyoga and Lake Edward. The country is located on a plateau, averaging about 900 m above sea level. Although generally tropical in nature, the climate differs between parts of the country. Most important cities are located in the south, near Lake Victoria, including the capital Kampala and the nearby city of Entebbe.
Uganda is divided into 56 districts, spread across four administrative divisions: North, East, South and West. The districts are all named after their 'chief town'. The city of Kampala, for example, is in the district of Kampala.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Uganda
Uganda has substantial natural resources, including fertile soils, regular rainfall, and sizable mineral deposits of copper and cobalt. Agriculture is the most important sector of the economy, employing over 80% of the work force, with coffee accounting for the bulk of export revenues. Since 1986, the government - with the support of foreign countries and international agencies - has acted to rehabilitate an economy decimated during the regime of Idi Amin and subsequent civil war. Stabilising measures have included currency reform, raising producer prices on export crops, increasing prices of petroleum products, and improving civil service wages. The policy changes are especially aimed at dampening inflation, boosting production and improving the balance of payments.
UgandaCoffee.jpg
During 1990-2001, the economy turned in a solid performance based on continued investment in the rehabilitation of infrastructure, improved incentives for production and exports, reduced inflation, gradually improved domestic security, and the return of exiled Indian-Ugandan entrepreneurs. Ongoing Ugandan involvement in the war in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, corruption within the government, and slippage in the government's determination to press reforms raise doubts about the continuation of strong growth. In 2000, Uganda qualified for the enhanced Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) debt relief initiative worth $1.3 billion and Paris Club debt relief worth $145 million. These amounts combined with the original HIPC debt relief added up to about $2 billion. Growth for 2001-02 was solid despite continued decline in the price of coffee, Uganda's principal export. Prospects for 2003 are mixed, with probable strengthening of coffee prices yet with halting growth in the economies of major export customers.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Uganda
Uganda is home to many different ethnic groups, none of whom form a majority of the population. Around forty different languages are currently in use in the country; English was appointed as the country's official language by the Museveni government. The language with the largest number of native speakers is Luganda, spoken in the Buganda region which encompasses Kampala. Kiswahili is widely used as a basic trade language.
Christian and Muslim missionaries first arrived in the 1860s, attempting to convert the Bugandan king. At present, about two-thirds of the population has adopted Christianity. The remaining one-third is split about evenly between Muslims and members of traditional faiths.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Uganda
Due to the large number of tribes, many still living within their own kingdoms, culture within Uganda is diverse. A lot of the Asians (mostly from India) who were expelled during the regime of Amin are returning to Uganda.
Human rights
Main article: Human rights in Uganda
Respect for human rights in Uganda has been advanced significantly since the mid-1980s. There are, however, numerous areas which have continue to attract concern.
The conflict in the north continues to generate reports of abuses by both the rebel Lord's Resistance Army and the Uganda People's Defence Force. Torture continues to be a widespread practice amongst security organisations. Attacks on political freedom in the country, including the arrest and beating of opposition Members of Parliament, has led to international criticism, culminating in May 2005 in a decision by the British government to withhold part of its aid to the country.
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Uganda
- Education in Uganda
- Transportation in Uganda
- Military of Uganda
- Foreign relations of Uganda
- List of national parks of Uganda
- List of cities in Uganda
- Islam in Uganda
See also
External links
Government
- Government of Uganda (http://www.government.go.ug/) official site
- Parliament of the Republic of Uganda (http://www.parliament.go.ug/) official site
- Uganda Tourist Board (http://www.visituganda.com/) official site
News
- allAfrica.com - Uganda (http://allafrica.com/uganda/) news headline links
- East African Procurement News (http://www.procnews.com/) business weekly
- Monitor (http://www.monitor.co.ug/) independent national newspaper
- My Uganda (http://www.myuganda.co.ug/) news and community
- New Vision (http://www.newvision.co.ug/) government-owned national newspaper
Overviews
- BBC News Country Profile - Uganda (http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/country_profiles/1069166.stm)
- CIA World Factbook - Uganda (http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ug.html)
- Library of Congress Country Study - Uganda (http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/ugtoc.html) data as of December 1990
Directories
- LookSmart - Uganda (http://search.looksmart.com/p/browse/us1/us317836/us317916/us559898/us559899/us10065672/us559962/) directory category
- Open Directory Project - Uganda (http://dmoz.org/Regional/Africa/Uganda/) directory category
- Stanford University - Africa South of the Sahara: Uganda (http://www-sul.stanford.edu/depts/ssrg/africa/uganda.html) directory category
- UgandaOnline (http://www.ugandaonline.net/) directory
- University of Pennsylvania - African Studies Center: Uganda (http://www.sas.upenn.edu/African_Studies/Country_Specific/Uganda.html) directory category
- Yahoo! - Uganda (http://dir.yahoo.com/Regional/Countries/Uganda/) directory category
Tourism
Other
- MarketUganda.com (http://www.marketuganda.com/) Uganda businesses
- Ugandan Manufacturers Association (http://www.uma.co.ug/)
| Countries in Africa | ||
|
Algeria | Angola | Benin | Botswana | Burkina Faso | Burundi | Cameroon | Cape Verde | Central African Republic | Chad | Comoros | Democratic Republic of the Congo | Republic of the Congo | Côte d'Ivoire | Djibouti | Egypt | Equatorial Guinea | Eritrea | Ethiopia | Gabon | The Gambia | Ghana | Guinea | Guinea-Bissau | Kenya | Lesotho | Liberia | Libya | Madagascar | Malawi | Mali | Mauritania | Mauritius | Morocco | Mozambique | Namibia | Niger | Nigeria | Rwanda | São Tomé and Príncipe | Senegal | Seychelles | Sierra Leone | Somalia | Somaliland | South Africa | Sudan | Swaziland | Tanzania | Togo | Tunisia | Uganda | Zambia | Zimbabwe | Western Sahara | ||
| Dependencies: Canary Islands | Ceuta and Melilla | Madeira Islands | Mayotte | Réunion | Saint Helena and dependencies | ||