Geography of Senegal
|
|
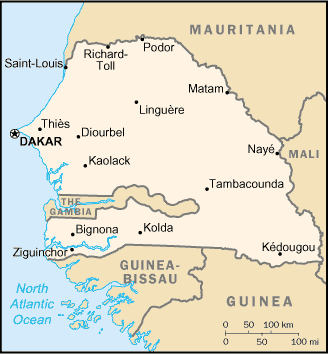
Senegal is a coastal West African nation located 14 degrees north of the Equator and 14 degrees west of the Prime Meridian. The country's total area is 196,190 km,² of which 192,000 km² is land and 4,190 km² is water, making the nation slightly smaller than Britain or the U.S. state of South Dakota.
Senegal is bordered to the west by the North Atlantic Ocean. On land, the nation's largest border is Mauritania to the north, an 813 km border along the Senegal River. To the west is the 419 km border with Mali. In the southwest is Guinea (330 km border) and to the south-southwest is Guinea-Bissau (338 km), both borders running along the Casamance River. Senegal is one of only a handful of countries to have an exclave within its borders—the small nation of The Gambia in the interior, which has a 740 km border with Senegal. The Gambia penetrates more than 320 km into Senegal, from the Atlantic coast to the center of Senegal along the Gambia River, which bisects Senegal's territory. In total, Senegal has 2,640 km of land borders, and 531km of coastline and shoreline. Senegal makes maritime claims of a 44 km (24 nautical mile) contiguous zone, a 22 km (12 nautical mile) territorial sea, and a 370 km (200 nautical mile) exclusive economic zone. It also claims a 370 km (200 nautical mile) continental shelf, or to the edge of the continental margin.
Well-defined dry and humid seasons result from northeast winter winds and southwest summer winds. Dakar's annual rainfall of about 610 mm (24 in) occurs between June and October when maximum temperatures average 27 °C (82 °F); December to February minimum temperatures are about 17 °C (63 °F). Interior temperatures are higher than along the coast, and rainfall increases substantially farther south, exceeding 1.5 m (60 in) annually in some areas.
The lowest point in Senegal is the Atlantic Ocean, at sea level. The higest point is an unnamed feature near Nepen Diakha in the Fouta Djallon foothills at 581 m (1900 ft).
Climate: tropical; hot, humid; rainy season (May to November) has strong southeast winds; dry season (December to April) dominated by hot, dry, harmattan wind
Terrain: generally low, rolling, plains rising to foothills in southeast
Natural resources: fish, phosphates, iron ore
Land use:
arable land:
12%
permanent crops:
0%
permanent pastures:
16%
forests and woodland:
54%
other:
18% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 710 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: lowlands seasonally flooded; periodic droughts
Environment - current issues: wildlife populations threatened by poaching; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; overfishing
Senegal is a party to several environmental treaties:
- Comprehensive Test Ban Treaty
- Convention on Biological Diversity
- Convention on Fishing and Conservation of Living Resources of the High Seas
- Convention on the International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Flora and Fauna
- International Convention for the Regulation of Whaling
- Montreal Protocol
- United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
- United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
- Ramsar Convention
- 1978 Convention on Ship Pollution
Senegal has signed, but not ratified the Convention on Marine Dumping.