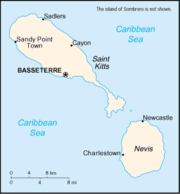
Saint Kitts and Nevis
|
|
The Federation of Saint Kitts and Nevis is an island nation in the Caribbean.
| ||||
| National motto: Country Above Self | ||||
| ||||
| Official language | English | |||
| Capital | Basseterre | |||
| Queen | Elizabeth II | |||
| Governor General | Sir Cuthbert Sebastian | |||
| Prime Minister | Dr. Denzil Douglas | |||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 186th 261 km² Negligible | |||
| Population - Total - Density | Ranked 186th 38,819 (July 2000) 149/km² | |||
| Independence - Date | From the United Kingdom September 19, 1983 | |||
| Currency | East Caribbean dollar (EC$) | |||
| Time zone | UTC -4 | |||
| National anthem | O Land of Beauty! | |||
| Internet TLD | .kn | |||
| Calling Code | 1-869 | |||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Originally colonies of the United Kingdom, Saint Kitts and Nevis along with Anguilla, became an associated state with full internal autonomy in 1967. Anguilla rebelled and was allowed to secede in 1971. St. Kitts and Nevis achieved independence in 1983. In August 1998, a vote in Nevis on a referendum to separate from St. Kitts fell short of the two-thirds majority needed. In late September 1998, Hurricane Georges caused approximately $445 million in damages and limited GDP growth for the year.
Alexander Hamilton, the first United States Secretary of the Treasury, was born on Nevis and spent his childhood there and on the island of St. Croix.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Saint Kitts and Nevis
The country is an independent Commonwealth Realm with Queen Elizabeth II as its head of state, represented in St. Kitts and Nevis by a governor general, who acts on the advice of the Prime Minister and the cabinet. The prime minister is the leader of the majority party of the house, and the cabinet conducts affairs of state.
St. Kitts and Nevis has a unicameral legislature, known as the National Assembly. It is comprised of fourteen members - eleven elected representatives - three of whom are from the island of Nevis - and three members who are appointed by the Governor-General. The three appointed members are known as Senators, with two being appointed on the advice of the Prime Minister, and one on the advice of the leader of the opposition. Though they are referred to as Senators, they do not form a separate house of parliament, as in some other countries. Both representatives and senators serve five-year terms. The prime minister and the cabinet are responsible to the Parliament.
Saint Kitts and Nevis are a full & participating member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS).
Parishes
There are fourteen parishes:
- Christ Church Nichola Town
- Saint Anne Sandy Point
- Saint George Basseterre
- Saint George Gingerland
- Saint James Windward
- Saint John Capisterre
- Saint John Figtree
- Saint Mary Cayon
- Saint Paul Capisterre
- Saint Paul Charlestown
- Saint Peter Basseterre
- Saint Thomas Lowland
- Saint Thomas Middle Island
- Trinity Palmetto Point
Geography
Main article: Geography of Saint Kitts and Nevis
The country has two main islands, Saint Kitts and Nevis. The highest peak is Mount Liamuiga, which tops at 1 156 m.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis was the last sugar monoculture in the Eastern Caribbean. Faced with a sugar industry that was finding it increasingly difficult to earn a profit, the Government of St. Kitts and Nevis embarked on a program to diversify the agricultural sector and stimulate the development of other sectors of the economy.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Saint Kitts and Nevis
As of July 2000, there were 38 819 inhabitants; their average life expectancy was 70.73 years. Emigration has historically been very high, and the population is about 25% lower than at its peak of about 51,100 in 1960.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Saint Kitts and Nevis
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Transportation in Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Military of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Foreign relations of Saint Kitts and Nevis
| Countries in West Indies |
|---|
|
Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas | Barbados | Cuba | Dominica | Dominican Republic | Grenada | Haiti | Jamaica | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Trinidad and Tobago |
|
Dependencies: Anguilla | Aruba | British Virgin Islands | Cayman Islands | Guadeloupe | Martinique | Montserrat | Navassa Island | Netherlands Antilles | Puerto Rico | Turks and Caicos Islands | U.S. Virgin Islands |
| | Missing image Caricom-Flag.png Flag of the Caribbean Community |
|---|---|
| Antigua and Barbuda | Bahamas¹ | Barbados | Belize | Dominica | Grenada | Guyana | Haiti | Jamaica | Montserrat | Saint Kitts and Nevis | Saint Lucia | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Suriname | Trinidad and Tobago | |
| Associate members: Anguilla | Bermuda | Cayman Islands | British Virgin Islands | Turks and Caicos Islands | |
| Observer status: Aruba | Colombia | Dominican Republic | Mexico | Netherlands Antilles | Puerto Rico | Venezuela | |
| ¹ member of the community but not the Caribbean (CARICOM) Single Market and Economy. | edit (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Template:Caricom&action=edit)
|