Pernambuco
|
|
| Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Capital: | Recife |
| Area: | 98,281 km² |
| Inhabitants: | 7,918,344 |
| Pop. density: | 80.6 inh./km² |
| Timezone: | GMT-3 |
| ISO 3166-2: | BR-PE |
| Governor: | Jarbas Vasconcellos |
| Map | |
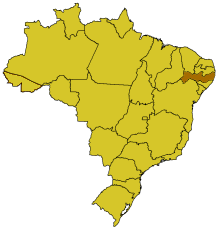 | |
Pernambuco is a state of Brazil, located in the Brazilian Northeast. To the north are the states of Paraíba and Ceará, to the west is Piauí, to the south are Alagoas and Bahia, and to the east is the Atlantic Ocean.
| Contents |
Geography
Pernambuco has a territory covered mostly by the dry thorny scrub vegetation called caatinga. The Rio São Francisco is the main water source for this area. The coastal area is fertile, and was formerly covered by the Mata Atlântica. It is now place to extensive sugar cane plantations.
Fernando de Noronha in the Atlantic Ocean, 535 km Northeast of Recife, also belongs to Pernambuco state.
History
Pernambuco was first colonized by Portuguese settlers.
In 1534, Dom João III, king of Portugal created the Hereditary Captaincies. Pernambuco, one of these captaincies, was granted to Duarte Coelho. The administrator of a captaincy was known as Donatario.
Duarte Coelho had arrived at Pernambuco, then known as Nova Lusitânia (New Lusitania), in 1535 and established his government in the area on which Olinda was to be founded.
After bloodshed battles against the Caetê Indians, which had an alliance with the French, Duarte Coelho founded Olinda at the site of the Marin Indian village. This victory made possible to estabilize the captaincy and to start Portuguese rule.
The village (vilas) of Olinda (first capital) and Igarassu were founded 1537.
Pernambuco was one of the two only prosperous captaincies (the other was São Vincente), mainly due to the plantation of sugar cane and cotton. With the support of Dutch East India Company, The sugar mills (engenho) were constructed and the sugar industry had greatly developed. In 1612, Pernambuco produced 14,000 tons of sugar; by 1640s, more than 24,000 tons of sugar were exported to Amsterdam.
In 1630, Pernambuco, as well as many Portuguese possessions in Brazil, was occupied by the Dutch. Johan Maurits van Nassau-Siegen, count of Nassau, was appointed as ruler of the Nieuw Holland (Dutch colonization enterprise in Brazil).
Nassau's government built Maritania or Mauristaad (Recife) on delta islands, which is somewhat similar to Holland's topography. This moved the political focus from Olinda to Recife. The Nassau's Dutch administration was noted for advancements in urbanism, culture, and science. The Dutch legacy is still recognizable in Pernambuco's people, accent, and architecture.
Portugal reconquered Pernambuco after Second Battle of Guararapes in 1649 and Olinda regained its status of political center. However, Recife remained the commercial /port city.
In 1710 the Mascate War took place in Pernambuco. This conflict set the mascates (traveling salesman) from Recife against the establishment hosted in Olinda and led by the Senhores de Engenho (owners of the sugar mills, literally: sugar mill lords).
Pernambuco was the home to the most important rebellions and insurrections in Brazilian history, especially in the 19th century.
1817 was the year of the Pernambucan Revolution, a republican separatist movement which resulted in the creation of the Republic of Pernambuco. The main cause of the revolution was dissatisfaction with the colonial administration. The republic was declared on March 7, 1817. After military intervention, the secession ended on May 20, 1817. The current flag of Pernambuco is actually the flag of that Republic.
As a reaction to the Emperor Dom Pedro I dissolution of the Constituent Assembly, the Confederation of the Equator was set up on July 2, 1824. The Confederation was another separatism movement which encompassed the provinces of Pernambuco, Paraíba, Rio Grande do Norte, and Ceará. On November 29, 1824, the Confederated forces capitulated to the imperial army.
Pernambuco was the site of the brief liberal republican Praieira revolt in 1848, which was Brazil's response to the European year of failed liberal revolutions. The military officer who put it down was Deodoro da Fonseca, later briefly the first president of the Brazilian republic.
Important Cities
- Cabo de Santo Agostinho
- Recife - State capital.
- Camaragibe
- Nazaré da Mata - Capital of the Maracatu
- Condado - Condado is located at the Zona da Mata region of the state, it's too called by Princesinha da Zona da Mata (The Little Princess of the Woods Zone in portuguese).
- Caruaru - Main city in the country side.
- Garanhuns - Highland city, pleasant climate.
- Goiana
- Jaboatão dos Guararapes
- Olinda - Historical site, first capital.
- Paulista
- Petrolina - Prosperous city in the far west of the state
- Arcoverde
- Pesqueira
- Carpina
- Limoeiro
- Surubim
- Goiana
- Petrolândia
- Floresta
- Triunfo
- Serra Talhada
- Sertânia
- Bom Conselho
- Timbaúba
- Palmares
- Aliança
- Exu
Institutions
- Polytechnic School, Pernambuco University [1] (http://www.upe.poli.br)
- Federal University of Pernambuco
- Federal Rural University of Pernambuco www.ufrpe.br
- Pernambucan Football Federation
External links
- The Dutch in Brazil (http://www.geocities.com/Athens/Styx/6497/brazil.html)
- Brazilian Embassy in London (http://www.brazil.org.uk/page.php?cid=279)
- Recife Guide: information about Recife and Olinda, with photos (http://www.recifeguide.com/)
- Cabo de Santo Agostinho city (http://www.cabo.pe.gov.br/)
| States of Brazil | 
|
|---|---|
| Acre | Alagoas | Amapá | Amazonas | Bahia | Ceará | Espírito Santo | Goiás | Maranhão | Mato Grosso | Mato Grosso do Sul | Minas Gerais | Pará | Paraíba | Paraná | Pernambuco | Piauí | Rio de Janeiro | Rio Grande do Norte | Rio Grande do Sul | Rondônia | Roraima | Santa Catarina | São Paulo | Sergipe | Tocantins | |
| Federal District: Brazilian Federal District | |
Pernambuco is also the name of a tropical tree used for lumber and red dye. Species Caesalpinia echinata. It was also called brazilwood, and gave its name to the country, rather than the other way around.de:Pernambuco es:Pernambuco (estado) eo:Pernambuko fr:Pernambouc (État) gl:Estado de Pernambuco ka:პერნამბუკუ nl:Pernambuco no:Pernambuco pl:Pernambuco pt:Pernambuco