Luzon
|
|
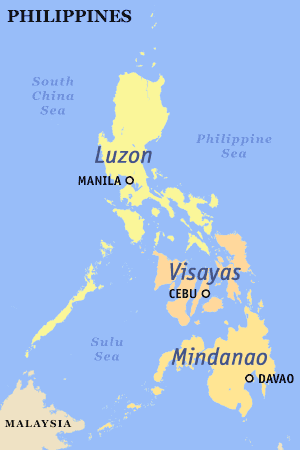
Luzon refers to the largest and most important island in the Philippines and to one of the three island groups in the country, with Visayas and Mindanao being the other two.
As an island, Luzon is the Philippine's largest at 104,688 square kilometers, and is also the world's 17th largest island. Located on it is the country's capital, Manila, and the most populous city, Quezon City. The island is very mountainous, and is home to Mt. Pulag, the second highest mountain in the country and Mayon, the most famous volcano. To the west of Luzon island is the South China Sea (or Luzon Sea in Philippine territorial waters), to the east is the Philippine Sea, and to the north are Luzon Strait, Babuyan Channel, and Balintang Channel.
The island group of Luzon encompasses Luzon island itself, plus the Batanes and Babuyan groups of islands to the north, and the islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque, Masbate, Romblon, Mindoro, and Palawan in the south. The island group is divided into eight regions, which are further subdivided into 38 provinces.
Luzon Island
The island of Luzon is 104,688 square kilometers in land area, making it the largest among the country's islands. The main part of the island is roughly rectangular in shape and has the long Bicol Peninsula protruding to the southeast.
The northern part of the island contains the largest mountain range in the country, the Cordillera Central. Mount Pulag, the second highest mountain in the country, is located there and rises 2,922 meters high. To the east of the Cordillera Central is the large Cagayan Valley, which serves as the basin for the Cagayan River, the longest river in the Philippines. To the east of the valley rises the Sierra Madre mountain range, easily the longest range in the country.
The Sierra Madre snakes southwards into the central and southern part of the island. Between it and the Zambales Mountains to the west is the largest plain, the Central Luzon plain. This plain, approximately 11,000 km² in size, is the country's largest producer of rice. Among the rivers irrigating this plain, the longest are Agno to the north, and Pampanga to the south. In the middle of the plain rises the solitary Mount Arayat. To the west, in the Zambales Mountains, rises Mount Pinatubo, made famous because of its enormous 1991 eruption.
The Zambales mountains extends to the sea in the north, forming Lingayen Gulf, home to the Hundred Islands National Park. To the south, the mountains also extend into the sea, forming the Bataan Peninsula, which encloses the Manila Bay. This natural harbor is considered to be one of the best natural ports in East Asia, due to its size and strategic geographical location.
To the southeast of Manila Bay is the largest lake in the country, and also the largest inland lake in Southeast Asia, the Laguna de Bay (Old Spanish, Lake of Ba-y town). This 949-square-kilometer lake is drained by the Pasig River into Manila Bay. Pasig River is one of the most important rivers in the country due to its historical significance and because it runs through the center of Metro Manila.
Located just 20 kilometers southwest of Laguna de Bay is Taal Lake, within the southwestern portion of the island. This caldera of a lake contains the smallest volcano of the country, Taal Volcano, which rises on the island in the center of the lake. The volcano in turn,has a lake in its crater. All the surrounding areas of Taal Lake were once part of a massive prehistoric volcano that covered the southern portion of the province of Cavite, Tagaytay City, and the whole of Batangas province.
Off the southwestern portion of Luzon is the island of Mindoro, separated by the Verde Island Passages. The passages connect the South China Sea to the east with the Tayabas Bay. To the south of the bay is the island of Marinduque.
The southeastern portion of Luzon is dominated by the Bicol Peninsula. This is a mountainous and narrow region that extends approximately 150 km southeast. Along it are numerous gulfs and bays. In the north is Lamon Bay, which contains Alabat Island and is south of the Polillo Islands of Quezon province. Other bays and gulfs include San Miguel Bay, Lagonoy Gulf, Ragay Gulf, and Sorsogon Bay.
To the east of the peninsula lies the island of Catanduanes. Leading to it is the Caramoan Peninsula. Off the southeast tip of Bicol is Samar island, separated by San Bernardino Strait. Bicol Peninsula is connected to the main part of Luzon through the Tayabas Isthmus. Extending south from the isthmus is the Bondoc Peninsula.
The Bicol Peninsula is also home to numerous volcanoes. The most famous is Mayon Volcano in Albay. This 2,460-meter high volcano is symmetrically shaped, rivaling that of Mount Fuji in Japan and is considered a symbol of the Bicol Region. Other notable mountains are Mount Isarog and Mount Iriga in Camarines Sur, and Mount Bulusan in Sorsogon.
Located off the southwestern coast of the Bicol Peninsula are the islands of Ticao, Burias, and Masbate.
See also Geography of the Philippines.
Island Group of Luzon
The island group of Luzon is an arbitrary grouping of islands which encompasses eight administrative regions. These regions are further subdivided into 38 provinces, of which only eight are not on Luzon island itself. The island group includes the Batanes and Babuyan islands to the north, and the islands of Catanduanes, Masbate, Marinduque, Romblon, Mindoro, and Palawan in the south.
Regions of Luzon
The eight regions are listed below and each is individually discussed in the succeeding paragraphs. Its administrative centers are for formality's sake only, meaning, there is no 'valid' regional administrative center (except in the case of Administrative regions), the power being vested by the provincial governments. The regional centers are only the head tourist offices for the region.
- Ilocos Region (Region I)
- Cagayan Valley (Region II)
- Central Luzon (Region III)
- CALABARZON (Region IV-A)
- MIMAROPA (Region IV-B)
- Bicol Region (Region V)
- Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR)
- National Capital Region (NCR)
Ilocos Region (Region I) is located in the northwest portion of the main island. Its provinces are: Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, La Union, and Pangasinan. Its inhabitants are mostly of Ilocano descent and the main languages are Ilokano and Pangasinan. The region's administrative center is San Fernando City, La Union.
Cagayan Valley (Region II) is located in the northeast portion of the main island and also covers the Batanes and Babuyan islands to the north. The valley is surrounded by the Cordillera Central and Sierra Madre mountain ranges. Running through its center is the country's longest river, Cagayan River. Its provinces are Batanes, Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino. The region's administrative center is Tuguegarao City in Cagayan province.
Central Luzon (Region III) contains the largest plain of the country and produces most of the country's rice supply. Its provinces are Aurora, Bataan, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Pampanga, Tarlac, and Zambales. The region's administrative center is San Fernando City, Pampanga. The former United States Navy base of Subic Bay, now a free port, is located in Zambales province.
CALABARZON (Region IV-A), one of the newest regions of the country, was previously a part of Southern Tagalog (Region IV). It is one of the most populated areas of the country. The name of the region is actually an acronym that stands for its provinces, which are Batangas, Cavite, Laguna, Quezon, and Rizal. The Tagalogs are the dominant ethnic group in this region, with Tagalog as the main language. Its' recognized administrative center is Manila, which is in Metro Manila, however, some government officials still consider {{Quezon City]], which is also in Metro Manila as the administrative center, and also, Lucena City, in Quezon province.
MIMAROPA (Region IV-B), along with CALABARZON is the newest region of the country, and was previously a part of Southern Tagalog (Region IV). It contains most of the islands in the Luzon group. The name of the region is actually an acronym that stands for its provinces, which are Marinduque, Occidental Mindoro, Oriental Mindoro, Palawan, and Romblon.
Bicol Region (Region V) occupies the Bicol Peninsula at the southeastern end of Luzon island, plus the outlying islands which include the island provinces of Catanduanes and Masbate. The remaining mainland provinces are Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, and Sorsogon. The region's administrative center is Legazpi City in Albay. The inhabitants are of Bicolano descent with Bikol as the main language.
Cordillera Administrative Region (CAR) almost completely covers the Cordillera Central mountain range of Northern Luzon. CAR, created in 1989 is a special administrative region for the indigenous tribes of these mountains. Its provinces are Abra, Apayao, Benguet, Ifugao, Kalinga, and Mountain Province. The regional center is Baguio City.
National Capital Region (NCR) is a special administrative region that contains the capital of the country, Manila; the country's most populous city, Quezon City; and an additional 15 more cities and municipalities. The region is more popularly known as Metro Manila. It is the only region in the country that has no provinces, and is the most densely populated with over 10 million people living in an area 636 square kilometers large.
See also Regions of the Philippines, Provinces of the Philippines, Visayas, and Mindanao.
| Regions and Provinces of Luzon | |
| Ilocos Region: | Ilocos Norte | Ilocos Sur | La Union | Pangasinan |
| Cagayan Valley: | Batanes | Cagayan | Isabela | Nueva Vizcaya | Quirino |
| Central Luzon: | Aurora | Bataan | Bulacan | Nueva Ecija | Pampanga | Tarlac | Zambales |
| CALABARZON: | Batangas | Cavite | Laguna | Quezon | Rizal |
| MIMAROPA: | Marinduque | Occidental Mindoro | Oriental Mindoro | Palawan | Romblon |
| Bicol Region: | Albay | Camarines Norte | Camarines Sur | Catanduanes | Masbate | Sorsogon |
| Cordillera Adm. Region: | Abra | Apayao | Benguet | Ifugao | Kalinga | Mountain Province |
| Metro Manila: | No provinces |
de:Luzon es:Luzon et:Luzon fr:Luçon (Philippines) ja:ルソン島 nl:Luzon no:Luzon pl:Luzon fi:Luzon tl:Luzon