Ilocos Region
|
|
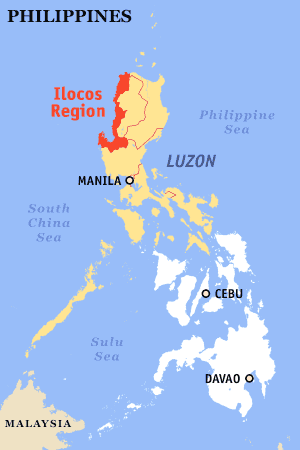
The Ilocos Region of the Philippines, designated as Region I is located in the northwestern part of Luzon. It is bounded by Cordillera Administrative Region and Cagayan Valley to the east, Central Luzon to the south and by the South China Sea to the west.
The region is composed of four provinces, namely: Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, La Union and Pangasinan. Its administrative center is San Fernando City, La Union. The region is occupied mostly by Ilocanos.
REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES
2000 census—4,200,478 (Xth largest).
Provinces—4.
Component Cities—8.
Municipalities—117.
Barangays—3,265.
| Contents |
People and Culture
The Ilocos Region is the historical homeland of the Ilocanos. They constitute a majority in the region: Ilocos Norte (97%), Ilocos Sur (93%), La Union (92%), and Pangasinan (45%). The Pangasinense are concentrated in central Pangasinan province and they number slightly more than the Ilocano population at around 50 percent. Minority groups include the Tingguian and Isneg communities that inhabit the foothills of the Cordillera mountains.
The population is predominantly Roman Catholic with strong adherents of Protestantism such as the Aglipayan denomination further north of the country. There is also an undercurrent of traditional animistic beliefs especially in rural areas. The small mercantile Chinese and Indian communities are primarily Buddhists and Hindus respectively.
See Ilocano and Religion in the Philippines for further discussion of culture, religion, and the Ilocano language.
Economy
The regional economy is anchored in the agricultural sector. Income comes from cultivating rice, tobacco, corn, sugarcane, and fruits; raising livestock such as pigs, chicken, goats, and carabaos (water buffalos); and marine and riverine fishing and shrimping, with aquacultures of fishes like tilapia and milkfish (bangus).
The service and light manufacturing industries are concentrated in the cities. San Fernando City in La Union has an active shipping port and Laoag City in Ilocos Norte has a growing international airport. The government is one of the largest employers along with multinational corporations like Coca-Cola.
The tourism industry focuses on the coastal beaches and on eco-tourism. There are fine sands stretching along Bauang, La Union and the rest of the region. Opportunities to engage in other water sports and activities abound. Eco-tourism takes advantage of the marine and forest resources in the region and displays the natural beauty of the Ilocos.
The region is also rich in crafts, with renowned blanket-weaving and pottery.
Geography
Political
Ilocos Region is composed of 4 provinces and a total of 9 cities.
Provinces
Cities
- Laoag City, Ilocos Norte
- Vigan City, Ilocos Sur
- Candon City, Ilocos Sur
- San Fernando City, La Union
- Alaminos City, Pangasinan
- Urdaneta City, Pangasinan
- Dagupan City , Pangasinan
- San Carlos City, Pangasinan
Physical
Ilocos Region occupies the narrow plain between the Cordillera Central mountain range and the South China Sea. It also occupies the northern portion of the Central Luzon plain, to the northeast of the Zambales Mountains.
Lingayen Gulf is the most notable body of water in the region and it contains a number of islands, including the Hundred Islands National Park. To the north of the region is Luzon Strait.
The Agno river runs through Pangasinan and empties into Lingayen Gulf. The river flow into a broad delta in the vicinity of Lingayen and Dagupan City.
Tourist Attractions
Hundred Islands National Park. Located in the Lingayen Gulf in Pangasinan, the watery park is dotted by 123 small, pristine islands. Three islands have been developed for tourists.
Vigan colonial houses. Vigan City is famous for its cobblestone streets and Spanish-style houses, an architectural remnant of its colonial past. The Mestizo District displays mansions typical of the era. They were owned by prominent Ilocano-Chinese merchant families of that time, hence mestizo or "mixed race."
Ancient churches. The region is dotted by old Catholic churches built by natives for the Spanish. Famous churches can be found in Vigan City, once the seat of the Bishop of Nueva Segovia, and in Manaoag, Pangasinan.
History
The Ilocos Region was first inhabited by the aboriginal Negritos before they were pushed by successive waves of Malay immigrants that penetrated the narrow coast. Tingguians in the interior, Ilocanos in the north, and Pangasinense in the south settled the region.
The Spanish arrived in the 16th century and established Christian missions and governmental institutions to control the native population and convert them to the Roman Catholic church. Present-day Vigan City in Ilocos Sur province became the bishopric seat of Nueva Segovia. Proud Ilocanos in the northern parts were less easily swayed, however, and remained an area filled with deep resentments against Spain. These resentments bubbled to the surface at various points in the region's history as insurrections.
The most notable of the rebellions were that of Diego Silang and his wife Gabriela Silang in 1764, and the Basi Revolt in the 19th century.
In 1901, the region went under American colonial rule, and in 1941, under Japanese occupation.
Several modern presidents of the Republic of the Philippines hailed from the Region: Elpidio Quirino, Ferdinand Marcos, and Fidel Ramos.
Before the Cordillera Administrative Region was formed, Ilocos Region also included the provinces of Abra, Mountain Province, and Benguet.
External links
| Regions and Provinces of Luzon | |
| Ilocos Region: | Ilocos Norte | Ilocos Sur | La Union | Pangasinan |
| Cagayan Valley: | Batanes | Cagayan | Isabela | Nueva Vizcaya | Quirino |
| Central Luzon: | Aurora | Bataan | Bulacan | Nueva Ecija | Pampanga | Tarlac | Zambales |
| CALABARZON: | Batangas | Cavite | Laguna | Quezon | Rizal |
| MIMAROPA: | Marinduque | Occidental Mindoro | Oriental Mindoro | Palawan | Romblon |
| Bicol Region: | Albay | Camarines Norte | Camarines Sur | Catanduanes | Masbate | Sorsogon |
| Cordillera Adm. Region: | Abra | Apayao | Benguet | Ifugao | Kalinga | Mountain Province |
| Metro Manila: | No provinces |
