Metro Manila
|
|
Manila_Skyline.jpg
Metro Manila (Kalakhang Maynila in Filipino), also simply called Manila outside the metropolis, is the metropolitan area that contains the City of Manila, the capital of the Philippines. The metropolis is officially called the National Capital Region (NCR, Pambansang Kabiserang Rehiyon in Filipino) and is composed of Manila plus 16 neighboring cities and municipalities, including Quezon City, the capital from 1948-1976. Metro Manila is the political, economic, social, and cultural center of the country, and it is one of the largest metropolitan areas in the world. Metro Manila is often simply referred to as Manila, especially by non-residents, and is abbreviated as M.M. or "M.L.A." The region is also sometimes called the Greater Manila Area, but this term usually also includes adjacent towns not strictly a part of Metro Manila.
Metro Manila is the smallest of the country's regions, but the most populous and the most densely populated, having a population of around 10 million (2000 census) in an area only 636 square kilometers large. It is also the only region without any provinces. The region is bordered by the provinces of Bulacan to the north, Rizal to the east, and Cavite and Laguna to the south. Metro Manila is also sandwiched by the Manila Bay to the west and the Laguna de Bay to the southeast with the Pasig River running between them, bisecting the region.
The term Metro Manila should not be confused with the metro rail system of the region, and the word metro itself always describes the metropolitan area (as in the metro). The railways are called by their abbreviations, such as the LRT and the MRT.
| Contents |
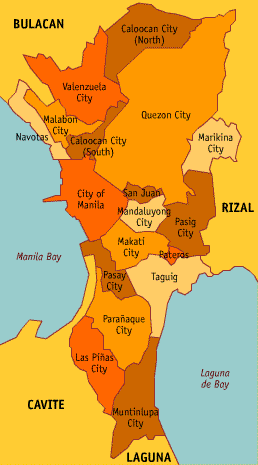
Cities and Municipalities
Metro Manila is composed of fourteen cities and three municipalities. Each is governed by a Mayor who all belong to the Metro Manila Mayor's League.
| City | Population¹ | Area (km²) | Pop. Density (per km²) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quezon City | 2,173,831 | 161.12 | 13,492 |
| Manila | 1,581,082 | 38.55 | 41,014 |
| Caloocan City | 1,177,604 | 53.33 | 22,081 |
| Pasig City | 505,058 | 31.00 | 16,292 |
| Valenzuela City | 485,433 | 44.58 | 10,889 |
| Taguig City | 467,375 | 47.88 | 9,761 |
| Las Piñas City | 472,780 | 41.54 | 11,381 |
| Parañaque City | 449,811 | 47.69 | 9,432 |
| Makati City | 444,867 | 27.36 | 16,260 |
| Marikina City | 391,170 | 33.97 | 11,515 |
| Muntinlupa City | 379,310 | 46.70 | 8,122 |
| Pasay City | 354,908 | 19.00 | 18,679 |
| Malabon City | 338,855 | 15.76 | 21,501 |
| Mandaluyong City | 278,474 | 11.26 | 24,731 |
| Municipality | Population¹ | Area (km²) | Pop. Density (per km²) |
| Navotas | 230,403 | 10.77 | 21,393 |
| San Juan | 117,680 | 5.94 | 19,811 |
| Pateros | 57,407 | 2.10 | 27,337 |
¹ 2000 Census
Interesting Spots
Being the political, economic, and cultural center of the Philippines, Metro Manila is the location of many interesting places and areas. In the city of Manila, one can visit the Malacañang Palace, the official residence of the Philippine President, and Intramuros, which was the seat of the Spanish colonial government in the country.
Makati City is acknowledged as the financial capital of the country where one can find the Makati Central Business District. Ortigas Center, located at the boundary where Mandaluyong City, Pasig City, and Quezon City meet is another fast-developing commercial and business center.
The night life in Metro Manila is very vibrant and bohemian. The districts of Malate and Ermita in Manila are popular tourist spots, while some prefer to go to Timog Avenue and Libis in Quezon City, or the Ayala Center and Rockwell Center in Makati City.
In Pasay City, one can go and taste Philippine cultural arts at the Cultural Center of the Philippines (CCP) Complex. The complex houses the massive main building of CCP, Philippine International Convention Center (PICC), Tanghalang Fracncisco Balagtas (Folk Arts Theater), the Manila Film Center, and the Coconut Palace. Manila also hosts the National Museum of the Filipino People, National Library of the Philippines, and Rizal Park (also called Luneta).
For other places, go to the articles of the individual cities and municipalities of Metro Manila.
Transportation
See also: Transportation in the Philippines
Roadways
For a very comprehensive information on the roadways of the metropolis, see also: Major Roads in Metro Manila
The metropolis has an extensive system of highways connecting the various cities and municipalities. The major roads include ten radial roads, which branch out from central Manila and five circumferential roads which form concentric arcs around downtown Manila. Most of these roads are very important transportation arteries. One is the C-4 (Circumferential Road 4), also called Epifanio de los Santos Avenue or more popularly as EDSA. It is the major thoroughfare in Metro Manila as it connects five cities in Metro Manila, namely Pasay, Makati, Mandaluyong, Quezon City, and Caloocan. Some other important roads are R-1 (Radial Road 1) or the Manila-Cavite Expressway (Coastal Road); R-3 or the South Luzon Expressway (SLEX); R-7, which consists of España Boulevard, Quezon Avenue, and Commonwealth Avenue; and R-8 or the ultra-modern North Luzon Expressway (NLEX). One of its newest roads, the Diosdado Macapagal Boulevard, parallel to the President Manuel Roxas Boulevard, is one of the destinations of Manila's elite.
Metro Manila is notorious for its traffic jams. A trip that should take 20 minutes will last an hour or more especially during rush hours. Consequently, the Metro Manila Development Authority (see also section below) has constructed many projects to decongest traffic.
Such projects of the MMDA for motorists are the construction of flyovers (elevated roads), interchanges, loading bays for Public Utility Vehicles (PUVs), emergency bays, and U-Turn slots over various intersections and thoroughfares, and the completion of the comprehensive railway system (see below). It has also been engaged in road widening with the support of the Department of Public Works and Highways. MMDA has also utilized projects for the pedestrians such as the installation of footbridges, waiting sheds, and men's urinals to various roads in the metropolis. The agency has also implemented various schemes for motorists such as the Uniform Vehicular Volume Reduction Scheme (UVRRS), more popularly known as "color coding", where vehicles whose plate numbers end in different digits are banned from traveling on different days, the Yellow Lane scheme, where yellow-plated PUBs (Public Utility Buses) will only use the two outermost lanes in EDSA, and the Organized Bus Route (OBR) for Metro Manila.
Railways
Manila_MRT.jpg
As of 2005 there are 3 commuter train systems in Metro Manila. For information on the Manila LRT and MRT systems, see the Manila Light Rail Transit System and Manila Metro Rail Transit System articles.
There is also a motor railway currently used by indigent Metro Manila residents. This railway is part of the Luzon railway system. Its main terminal is located in Tondo, Manila. See Philippine National Railways.
Ninoy Aquino International Airport
The country's main airport is the Ninoy Aquino International Airport (NAIA) which straddles the boundary between Parañaque City and Pasay City. It presently consists of two terminals, while a third one will open in June 2005. There is also a separate domestic terminal. There are two main runways and the hangar of Philippine Airlines is located near the Villamor Air Base.
Terminals
The first terminal, NAIA-1, is the original terminal and was constructed in 1981. The 67,000 square meter terminal was designed by Filipino architect Leandro V. Locsin and has a design capacity of 4.5 million passengers per year. It currently serves all non-Philippine Airlines international flights. The terminal has reached capacity in 1991 and has been over capacity ever since.
The second terminal, NAIA-2, was finished in 1998 and is named the Centennial Terminal since 1998 was the centennial year of the declaration of Philippine independence. The 75,000 square meter terminal was originally designed by Aéroports de Paris to be a domestic terminal, but the design was later modified to accommodate international flights. It has a capacity of 2.5 million passengers per year in its international wing and 5 million in its domestic wing, which later will expand to nine million passengers yearly. Terminal 2 is the home of Philippine Airlines and is used for both its domestic and international flights since it has the most number of flights out of the NAIA terminals.
The third, much larger terminal, NAIA-3, was approved for construction in 1997 and is nearly complete. The modern US$500 million, 189,000 square meter facility was designed by Skidmore, Owings and Merrill (SOM) to have a capacity of 13 million passengers per year. However, a legal dispute between the government of the Philippines and the project's main contractor, PIATCO, over alleged anomalies in the Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) contract, is holding completion and opening of the terminal. On December 2004, the Philippine Government took over the management of the facility through an order of the Pasay City Regional Trial Court (RTC). NAIA-3 is set to open its gates to the world on June 22, 2005.
The Domestic Terminal on the old Airport Road was built in 1948 and handles all domestic air traffic, excluding Philippine Airlines. Currently, the terminal is composed of two single-story buildings and serves the domestic flights of other local carriers, which are Cebu Pacific, Air Philippines, Asian Spirit, Southeast Asian Airlines (Seair), and Laoag International Airlines.
The Metropolitan Manila Development Authority
The Metropolitan Manila Development Authority (MMDA) is the administrative body in charge of the metropolis' development, and solving perennial problems such as traffic management, flood control, garbage disposal and sewage maintenace. It closely coordinates with various other organizations such as the Pasig River Rehabilitation Commission (PRRC) and the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH), as well as the local government units of the component cities and municipalities. Its agency's head is appointed by the president, which is now presided by Chairman Bayani Fernando.
History
For full details of Metro Manila's early history, see Manila: History.
(what R.A. founded Metro Manila, and the Metro Manila Commission?)
External Links
- ClickTheCity.com (http://www.clickthecity.com): Metro Manila's Entertainment Guide and Directory.
- MMDA.gov.ph (http://www.mmda.gov.ph): Metropolitan Manila Development Authority
| Regions and Provinces of Luzon | |
| Ilocos Region: | Ilocos Norte | Ilocos Sur | La Union | Pangasinan |
| Cagayan Valley: | Batanes | Cagayan | Isabela | Nueva Vizcaya | Quirino |
| Central Luzon: | Aurora | Bataan | Bulacan | Nueva Ecija | Pampanga | Tarlac | Zambales |
| CALABARZON: | Batangas | Cavite | Laguna | Quezon | Rizal |
| MIMAROPA: | Marinduque | Occidental Mindoro | Oriental Mindoro | Palawan | Romblon |
| Bicol Region: | Albay | Camarines Norte | Camarines Sur | Catanduanes | Masbate | Sorsogon |
| Cordillera Adm. Region: | Abra | Apayao | Benguet | Ifugao | Kalinga | Mountain Province |
| Metro Manila: | No provinces |