CAST-128
|
|
- The following article is about the block cipher. For the axion observatory in Switzerland, see CAST (axion observatory).
In cryptography, CAST-128 (alternatively CAST5) is a block cipher used in a number of products, notably as the default cipher in some versions of GPG and PGP. It has also been approved for Canadian government use by the Communications Security Establishment. The algorithm was created in 1996 by Carlisle Adams and Stafford Tavares using the CAST design procedure; another member of the CAST family of ciphers, CAST-256 (a former AES candidate) was derived from CAST-128. According to some sources, the "CAST" name is based on the initials of its inventors, though Bruce Schneier reports the authors' claim that "the name should conjure up images of randomness" (Schneier, 1996).
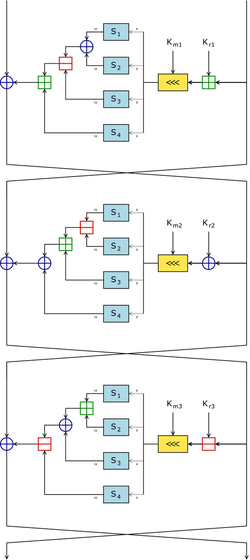
CAST-128 is a 12- or 16-round Feistel network with a 64-bit block size and a key size of between 40 to 128 bits (but only in 8-bit increments). The full 16 rounds are used when the key size is longer than 80 bits. Components include large 8×32-bit S-boxes based on bent functions, key-dependent rotations, modular addition and subtraction, and XOR operations. There are three alternating types of round function, but they are similar in structure and differ only in the choice of the exact operation (addition, subtraction or XOR) at various points.
Although Entrust holds a patent on the CAST design procedure, CAST-128 is available worldwide on a royalty-free basis for commercial and non-commercial uses.
See also
References
- C.M. Adams. (1997). "Constructing Symmetric Ciphers Using the CAST Design Procedure", Designs, Codes, and Cryptography, 12(3), pp. 283–316.
- C.M. Adams, "CAST Design Procedure Addendum".
- Bruce Schneier, 1996, Applied Cryptography, 2nd edition. John Wiley & Sons. pp334–335. ISBN 0-471-11709-9
External links
- RFC 2144 — The CAST-128 Encryption Algorithm (http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc2144.html)
- CAST related publications (http://adonis.ee.queensu.ca:8000/cast/)
- SCAN's entry for CAST-128 (http://www.users.zetnet.co.uk/hopwood/crypto/scan/cs.html#CAST-128)
- List of algorithms approved for Canadian government use (http://www.cse-cst.gc.ca/en/services/crypto_services/crypto_algorithms.html)
| Block ciphers edit (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Template:Block_ciphers&action=edit) |
| Algorithms: 3-Way | AES | Akelarre | Blowfish | Camellia | CAST-128 | CAST-256 | CMEA | DEAL | DES | DES-X | FEAL | FOX | FROG | G-DES | GOST | ICE | IDEA | Iraqi | KASUMI | KHAZAD | Khufu and Khafre | LOKI89/91 | LOKI97 | Lucifer | MacGuffin | Madryga | MAGENTA | MARS | MISTY1 | MMB | NewDES | RC2 | RC5 | RC6 | REDOC | Red Pike | S-1 | SAFER | SEED | Serpent | SHACAL | SHARK | Skipjack | Square | TEA | Triple DES | Twofish | XTEA |
| Design: Feistel network | Key schedule | Product cipher | S-box | SPN Attacks: Brute force | Linear / Differential cryptanalysis | Mod n | XSL Standardisation: AES process | CRYPTREC | NESSIE Misc: Avalanche effect | Block size | IV | Key size | Modes of operation | Piling-up lemma | Weak key |