Berlin
|
|
- This article is about the city in Germany. For other uses, see Berlin (disambiguation).
| State and Service Flags | |
|---|---|
| Missing image Flag_de-berlin_civil.png State Flag of Berlin Missing image Flag_de-berlin_service.png Service Flag of Berlin State and Service Flags of Berlin | |
| Coat of arms | Map of Germany showing Berlin |
| Missing image Coat_of_arms_Germany_Berlin.png Coat of Arms of Berlin | Missing image Germany_Laender_Berlin.png Map of Berlin in Germany |
| Basic Information | |
| Area: | 891.69 km² |
| Population: | 3,426,000 (January 2005) |
| Population density: | 3797 residents/km² |
| Elevation: | 34 m above sea level |
| Postal codes: | 10001-14199 |
| Area code: | 030 |
| Latitude and Longitude: | Template:Coor dm |
| License plate prefix: | B |
| Organisation: | 12 Bezirke (boroughs), 90 Stadtteile (districts) |
| ISO 3166-2: | DE-BE |
| Website: | www.berlin.de (http://www.berlin.de/english/index.html/) |
| Politics | |
| Mayor: | Klaus Wowereit (SPD) |
| Governing political parties: | SPD and PDS |
| Seat distribution in the State Parliament (141 seats total): | SPD 44 CDU 35 PDS 33 FDP 15 B90/Grüne 14 |
| last election: | 21 October 2001 |
| next election: | 2006 |
| Parliamentary representation | |
| Votes in the Bundesrat: | 4 |
Berlin (pronounced: , German ) is the capital of Germany and its largest city, with 3,426,000 inhabitants (as of January 2005); down from 4.5 million before World War II. It is also the second-largest city in the European Union, according to official city boundary populations, after London. From 1949 to 1990 it was divided into East Berlin and West Berlin.
Berlin is located on the rivers Spree and Havel in the north-east of Germany. It is enclosed by the German state (Bundesland) of Brandenburg, and constitutes a state of its own.
| Contents |
|
2.1 Early settlements |
Political Berlin
The state
Berlin used to be part of Brandenburg province of Prussia but was incorporated into Greater Berlin in 1920. Since German reunification on 3 October 1990 it has been one of the three city states, together with Hamburg and Bremen, that form the present 16 German Bundesländer.
Berlin is governed by the Senate of Berlin, which consists of the Regierender Bürgermeister (governing mayor) and up to eight senators holding ministerial portfolios. The governing mayor is mayor of the city and representative of the Bundesland (state) at the same time. The seat of office for the Berlin Mayor is the Rotes Rathaus. Presently, this office is held by Klaus Wowereit (SPD): for earlier mayors, see the list of Mayors of Berlin.
The city and state parliament is called the Abgeordnetenhaus or House of Representatives. The current Senat consists of a coalition of the social democrat SPD and the socialist PDS.
The boroughs
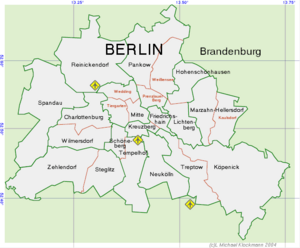
Berlin is subdivided into 12 boroughs, called Bezirke, which have been created from the previously existing 23 boroughs, effective since 1 January 2001.
For a map and a list of the old and new borough names, see Boroughs of Berlin.
Each Borough is governed by a Bezirksamt consisting of five Stadträte (town councillors) and a mayor. The Bezirksamt is elected by the district-parliament, the Bezirksverordnetenversammlung. The Boroughs of Berlin are not independent municipalities, and the political power of the district-parliaments is fairly minimal and dependent on the Senat of Berlin.
The district mayors form the council of mayors, called Rat der Bürgermeister under the leadership of the Regierende Bürgermeister (governing mayor), to advise the Senat.
History
see also: History of Berlin
Early settlements
In about 720 two Slavic tribes settled in the Berlin region. The Heveller settled on the river Havel with their central settlement in Brennabor, which later has become the town of Brandenburg. Close to the river Spree in today's borough of Berlin Köpenick the Sprewanen were found.
The Heveller founded another place on the river Havel in about 750. This seems to be the closest settlement to the area which is today known as Berlin and was called Spandow (today's Spandau). Spandau and Köpenick, which had been protected with barriers around 825, were the major settlements and later towns in the area until the early 11th century.
Berlin and Cölln
Berlin itself is one of Europe's younger cities, with its origin in the 12th century. The city developed out of two settlements, Berlin and Cölln, on both sides of the river Spree, in today's Mitte borough. Cölln is first mentioned in documents on 28 October 1237, Berlin in 1244. Unfortunately, the great town center fire of 1830 damaged most written records of those early days.
The cities formed a trading union in 1307, and participated in the Hanse. Their urban development took place in parallel for 400 years, until Cölln and Berlin were finally unified under the name of Berlin in 1709, including the suburbs Friedrichswerder, Dorotheenstadt, and Friedrichstadt.
Not much is left of these ancient communities, although some remainders can be seen in the Nikolaiviertel near the Rotes Rathaus, and the Klosterkirche, close to today's Alexanderplatz.
Fernsehturm_und_Humboldt_Universitaet.jpg
Urban development between the 15th and 17th centuries
The first City Palace was built on the embankment of the river Spree in 1443 to 1451. At that time Berlin-Cölln numbered about 8,000 inhabitants. In 1576, the bubonic plague killed about 4,000 people in the city.
During the Thirty Years' War (1618-1648), Berlin's population shrank from 10,000 to 6,000.
In 1640 Frederick William took regency in the principality of Brandenburg. During his government Berlin reached 20,000 inhabitants and became significant among the cities in Central Europe for the first time.
A boulevard with six rows of trees was laid down between the Tiergarten park and the Palace in 1647. The boulevard is called Unter den Linden.
Some years later (from 1674 on), the Dorotheenstadt was constructed in a bow of the river Spree, north-west of the Spreeinsel (Spree Island), where the Palace was situated. From 1688 on the Friedrichstadt was built and settled.
Prussia
In 18 January 1701, Frederick III was crowned King Frederick I in Prussia and made Berlin the capital of the new kingdom of Prussia.
In 1709, Berlin-Cölln was joined together with 'Friedrichswerder', 'Dorotheenstadt' and 'Friedrichstadt' under the name Berlin, with 60,000 inhabitants.
Weimar Republic and the Third Reich
The overall impression one gets when visiting Berlin today is one of great discontinuity, visibly reflecting the many ruptures of Germany's difficult history in the 20th century. Although it was the residence of the Prussian kings, Berlin's population did not greatly expand until the 19th century, mainly after becoming the capital of the German Empire in 1871. It remained Germany's capital during the Weimar Republic and under the Nazis' Third Reich. During this period Adolf Hitler had great plans to transform Berlin, because he thought that Berlin was one of the ugliest cities in the world, and he hated it. (Berlin was and is a center of left-wing political activity in Germany, and its residents largely opposed the Nazis' rise to power.) Therefore he and his architect Albert Speer made enormous plans for the new Berlin, the so-called Welthauptstadt Germania.
On the site of today's Parliamentary offices (Paul-Löbe-Haus) adjacent to the Reichstag, Speer planned to construct The Great Hall, 250 m high, seven times higher than St. Peter's Basilica in Rome, and with an enormous dome. It was planned to be large enough to hold 170,000 people, and the sweat and heat produced by those people were predicted to be able to generate clouds and rain inside the dome. From The Great Hall, a southbound avenue was planned, the Avenue of Victory, 23 m wide and 5.6 km long. At the other end there would have been the new railway station, and next to it Tempelhof Airport. Additionally, halfway down the avenue there would have been a huge arch 117 m high, so large that the Arc de Triomphe in Paris would fit inside it. It was projected to be a monument commemorating those fallen during World War I and World War II. The project was to finish in 1950, and Berlin was to be re-named "Germania" on that occasion. But the construction never started, as Hitler decided it would be madness to start such a project during a war. Hitler also thought the Allied airstrikes very practical, mostly because it made demolishing the old Berlin so much cheaper.
Today only a few structures bear witness to the large-scale plans of Germania. Hermann Göring's Reichsluftfahrtministerium (National Ministry of Aviation), Tempelhof International Airport, Olympiastadion, and a series of street lights on the East-West Axis on Kaiserdamm and Straße der 17 Juni are all that remain. Hitler's Reich Chancellery was demolished by Soviet occupation authorities: red marble from the Chancellery was used to renovate the adjacent war-damaged U-Bahnhof Mohrenstraße subway station and the remaining rubble was used in the construction of Soviet War Memorial at Treptower Park in Berlin.
The divided city
By the end of the Second World War, up to 70% of Berlin had been destroyed by concerted Allied air raids and street fighting. The so called "Stunde Null" marked a new beginning for the city. Greater Berlin was divided into four sectors by the Allies under the London Protocol of 1944, one each for
- the United States, consisting of the Boroughs of Neukölln, Kreuzberg, Tempelhof, Schöneberg, Steglitz and Zehlendorf;
- the United Kingdom, consisting of the Boroughs of Tiergarten, Charlottenburg, Wilmersdorf and Spandau;
- France, consisting of the Boroughs of Wedding and Reinickendorf;
- the Soviet Union, consisting of the Boroughs of Mitte, Prenzlauer Berg, Pankow, Weißensee, Friedrichshain, Lichtenberg, Treptow and Köpenick.
The Soviet victors of the Battle of Berlin immediately occupied all of Berlin. They handed the American, British and French sectors (later known as West Berlin) to the American and British Forces in July 1945: the French occupied their sector a little later. The Soviets used the period from May 1945 to July 1945 to dismantle industry, transport and other facilities in West Berlin, including removing railway tracks, as reparations for German war damage in the Soviet Union. This practice also continued in East Berlin and the Soviet occupation zone after 1945.
Berlin's unique situation as a city half-controlled by Western forces in the middle of the Soviet Occupation Zone of Germany made it a natural focal point in the Cold War. Though the city was initially governed by a Four Power Allied Control Council with a leadership that rotated monthly, the Soviets withdrew from the council as East-West relations deteriorated and began governing their sector independently. The council continued to govern West Berlin, with the same rotating leadership policy, though now only involving France, Great Britain, and the United States.
The Berlin Blockade
In response to Allied efforts to fuse the American, French, and British sectors of western Germany into a federal state, American refusal to grant the Soviets war reparations from industrial areas of western Germany, and to a currency reform undertaken by the western powers without Soviet approval, the Soviets blocked ground access to West Berlin on 26 June 1948, in what became known as the "Berlin Blockade". The Western Allies undertook a massive logistical effort to supply the western sectors of the city through the Berlin Airlift, known by the West Berliners as "die Luftbrücke" (the Air Bridge). The blockade lasted almost an entire year, ending when the Soviets once again allowed ground access to West Berlin on 11 May 1949.
East Germany chose Berlin (in practice, East Berlin) as its capital when the country was formed from the Soviet occupation zone in October 1949; however, this was rejected by the western allies, who continued to regard Berlin as an occupied city that was not legally part of any German state. West Germany, formed on 23 May 1949 from the American, British, and French zones, had its seat of government in Bonn, although Berlin was symbolically named as the German capital in the West German Basic Law (Grundgesetz).
The June 17th Uprising
Construction workers building the showpiece Stalin-Allee in East Berlin went on strike on 16 June 1953, to demand a reduction in recent work-quota increases. They called for a general strike the next day, 17 June; the general strike and protest marches turned into rioting and spread throughout East Germany. The uprising had to be suppressed by Soviet troops after the East German police failed to quell the unrest. The continuation of Unter den Linden on the western side of the Brandenburg Gate was renamed Straße des 17. Juni in honor of the uprising, and 17 June was proclaimed a national holiday in West Germany. See Uprising of 1953 in East Germany.
The Wall
Scan0017.jpg
On 13 August 1961 the Berlin Wall was constructed, physically separating West Berlin from East Berlin and the rest of East Germany, as a response to massive numbers of East German citizens fleeing into West Berlin as a way to escape to the west.
Student Movement
In the 1960s, West Berlin became one of the centers of the German student movement. West Berlin was especially popular with young German left-wing radicals, as young men living in West Berlin were exempted from the obligatory military service required in West Germany proper: the Kreuzberg district became especially well-known for its high concentration of young radicals.
The Wall afforded unique opportunities for social gatherings. The physical wall was set some distance behind the actual sector border, up to several meters behind in some places. The West Berlin police were not legally allowed to enter the space between the border and the wall, as it was technically in East Berlin and outside their jurisdiction: many people took the opportunity to throw loud parties in this space, with the West Berlin authorities powerless to intervene.
As many businesses did not want to operate in West Berlin due to its physical and economic isolation from the outside, the West German government subsidized any businesses that did operate in West Berlin.
Reunification
The Berlin Wall was breached on 9 November 1989. By the time of German reunification on 3 October 1990, the Wall had been almost completely demolished, with only small sections remaining. The German Parliament, the Bundestag, voted in June 1991 to move the (West) German capital back from Bonn to Berlin. Berlin once more became the capital of a unified Germany. Ministries and Government Offices moved back from Bonn to Berlin in 1999.
Tourist attractions
Potsdamer_Platz.JPG
Even though Berlin does have a number of impressive buildings from earlier centuries, the city's appearance today is mainly shaped by the key role it played in Germany's history in the 20th century. Each of the national governments which had their seat in Berlin — the 1871 German Empire, the Weimar Republic, Nazi Germany, East Germany, and now the reunified Germany — initiated ambitious construction programs, each with its own distinctive character. Berlin was devastated by bombing raids during World War II, and many of the old buildings that escaped the bombs were eradicated in the 1950s and 1960s in both West and East. Much of this destruction was caused by overambitious architecture programs, especially in order to build new residential or business quarters and main roads. It would not be an exaggeration to say that no other city in the world offers Berlin's unusual mix of architecture, especially 20th-century architecture. The city's tense and unique recent history has left it with a distinctive array of sights.
Not much is left of the actual Berlin Wall. The East Side Gallery in Friedrichshain near the Oberbaumbrücke over the Spree preserves a portion of the Wall. By looking at the architecture it is still possible to tell if one is in the former eastern or western part of the city. In the eastern part, many Plattenbauten can be found, reminders of Eastern Bloc ambitions to create complete residential areas with fixed ratios of shops, kindergartens and schools. Another difference between former east and west is in the design of little red and green men on pedestrian crossing lights (Ampelmännchen in German); the eastern versions received an opt-out during the standardisation of road traffic signs after re-unification, and have survived to become a popular icon in tourist products.
Historical sights in the city centre


- The Brandenburg Gate and Unter den Linden, symbols of Berlin, Prussia, and now Germany. The Brandenburg Gate appears on German Euro coins.
- Reichstag building, the old and new seat of the German parliament, renovated by Sir Norman Foster. Features a glass dome in which you can walk around and watch the parliamentarians from above.
- Gendarmenmarkt, arguably the most beautiful square in Berlin, surrounded by two famous cathedrals and the concert hall.
- Berlin victory column, monument to Prussia's victories.
- The Berliner Dom, an historic cathedral. A large crypt houses the remains of the Prussian royal family.
- Cathedral of St. Hedwig (St.-Hedwigs-Kathedrale)
- Nikolaiviertel with the Nikolaikirche an historical city core, founded in the 13th century.
- Schloss Bellevue, now the residence of the German President
- Schloss Charlottenburg, biggest castle of Berlin
- Memorial to the Murdered Jews of Europe, a Holocaust memorial opened in May 2005.
- The Neptunbrunnen, a famous fountain in Berlin Mitte.
- Tiergarten is Berlin's largest park and a masterpiece of park building. The Tiergarten was largely deforested by 1948 because it served as a source of firewood for the devastated city.
Cold War and sightseeing in the former East Berlin
- The Palast der Republik, the old East German parliament building. It is seen by some as ugly, former East Berliners remember with affection restaurants, shops, clubs, and the concerts that took place there in the 1980s. Although it has some significance as a historical tourist attraction, the German Parliament voted for its demolition, which will commence in 2005. The Palast der Republik is built on the site of the Berlin City Palace, which was demolished in 1950 by the Communists. The Palace Square was renamed Marx-Engels-Platz at the same time.
- The Fernsehturm, the TV tower, the highest building in the city at 368 m (1207 ft), and the second largest structure in Europe (after Moscow's Ostankino Tower). The Fernsehturm is easily visible throughout most of the central districts of Berlin.
- Alexanderplatz, formerly East Berlin's major shopping center, and home to the Centrum-Warenhaus, which was the DDR's department store. It is now a thoroughly Westernized shopping center.
- East Side Gallery a memorial for freedom based on the last parts of the Berlin Wall
- Rotes Rathaus(the Red City Hall), historic town hall famous for its distinctive red-brick architecture
- Rathaus Schöneberg with John-F.-Kennedy-Platz, whence John F. Kennedy made his famous "Ich bin ein Berliner!" speech.
- Checkpoint Charlie, remains and a museum about one of the crossing points (albeit restricted to Allied forces) in the Berlin Wall. The museum, which is a private venture, exhibits interesting material about people who devised ingenious plans to leave the East, but is controversial in the city for its propagandistic Cold War didactics and publicity stunts that many consider tasteless.
Sights of modern Berlin
- Potsdamer Platz, an entire quarter built from scratch after 1995. The historic Potsdamer Platz was not rebuilt as it was divided by the Wall. A must-see for people who like modern city planning.
- Hackescher Markt, Spandauer Vorstadt and Scheunenviertel, the home to fashionable culture, with countless small clothing shops, clubs, bars, and galleries. This includes the New Synagogue area in Oranienburger Straße (originally built in the 1860s in Moorish style with a large golden dome and reconstructed in 1993), and the Hackesche Höfe, a conglomeration of several buildings around several courtyards, nicely reconstructed after 1996. This area was a centre of Jewish culture up until the 1930s.
Panoramic viewing points
Berlin_television_tower.jpg
- Berliner Funkturm— the only observation tower in the world which stands on insulators. Its open-air observation deck is popular for photography.
- Berlin Television Tower [1] (http://www.berlinerfernsehturm.de/) — 368-m high television tower, built in 1969 close to Alexanderplatz. The entire city can be viewed from its 204-m high observation platform.
- Grunewaldturm [2] (http://www.grunewaldturm.de) — this 59-m high historic tower stands on a hill in Grunewald forest close to Wannsee lake.
- Französischer Dom [3] (http://www.franzoesischer-dom-berlin.de) — located on Gendarmenmarkt in the very heart of the city, the platform of the cathedral offers unique views.
- Bierpinsel — literally "Beer Stick". 1970s style tower in the Berlin Borough of Steglitz with a café and bar at the top giving views over south-western Berlin.
- Restaurant of the Forum Hotel Berlin
- Berliner Dom [4] (http://www.berliner-dom.de) — Protestant cathedral situated next to the Lustgarten, with a circular observation platform around the dome.
- Bell tower at the Olympic Stadium [5] (http://www.glockenturm.de) — part of the Reichssportfeld complex, the tower offers a view of the Olympic Stadium and also of the Waldbühne, an open-air stage.
- Siegessäule [6] (http://www.berlin-tourist-information.de/cgi-bin/sehenswertes.pl?id=13353) — the monument at the Großer Stern situated in the middle of the Tiergarten Park where it was relocated in 1938–39 from its previous position in front of the Reichstag.
- Müggelturm — a tower giving panoramic views over the Müggelsee lake.
- Reichstag building— the roof of the parliament building, crowned by a large glass cupola designed by Lord Foster is open to the public giving an impressive view over the city, especially at night.
Further interesting structures (not accessible to public)
- Fernmeldeturm Berlin (Berlin Telephone Tower)
- Richtfunkstelle Berlin-Frohnau
- Transmitter Berlin-Britz
- Radio mast Berlin-Scholzplatz
- Transmitter Berlin-Alley of Stallupone
- Radio mast Berlin-Olympiastadium
- Radar facility Berlin-Teufelsberg
- TV Tower Berlin-Mueggelberge
- Power station Berlin-Wilmersdorf
- Power station Reutter
Famous streets and boulevards
Berlin_Market_Tiergarten_in_Winter.jpg
- Unter den Linden is the street that heads east from the Brandenburg Gate. Many Classical buildings line the street. Part of Humboldt University is located there.
- Friedrichstraße, Berlin's legendary street of the "Golden Twenties" which combines the tradition of the last century with modern architecture of today's Berlin.
- Kurfürstendamm (Ku'damm), with the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Gedächtniskirche (Kaiser Wilhelm Memorial Church), which lies right at the top end of Kurfürstendamm, on Breitscheidplatz (underground station Kurfürstendamm). The church was bombed out in World War II and its ruins have been preserved in their damaged state. Near by is the Ka-De-We Berlin's equivelent to London's Harrods. Also nearby is the Zoologischer Garten, a zoo with a large number of species.
- The Straße des 17. Juni connects the Brandenburg Gate in the East and Ernst-Reuter-Platz in the West, commemorating the uprisings in East Berlin of 17 June 1953. It features the golden Siegessäule (Statue of Victory), which used to stand in front of the Reichstag.
- The Karl-Marx-Allee (formerly Stalinalle), a boulevard lined by monumental landmark buildings designed in the Socialist Classicism of the Stalin era. It is located in Friedrichshain and Mitte.
Education and science
Universities
- Freie Universität Berlin [7] (http://www.fu-berlin.de)
- Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin [8] (http://www.hu-berlin.de)
- Technische Universität Berlin [9] (http://www.tu-berlin.de)
- Charité [10] (http://www.charite.de) (Medical Faculty of Freie and Humboldt-Universität)
- Universität der Künste [11] (http://www.udk-berlin.de)
Universities of applied sciences
- Alice-Salomon-Fachhochschule für Sozialarbeit/-pädagogik [12] (http://www.asfh-berlin.de)
- Evangelische Fachhochschule [13] (http://www.evfh-berlin.de)
- Katholische Fachhochschule [14] (http://www.khsb-berlin.de/)
- Fachhochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft [15] (http://www.fhtw-berlin.de)
- Fachhochschule für Wirtschaft [16] (http://www.fhw-berlin.de)
- Hochschule für Musik Hanns Eisler [17] (http://www.hfm-berlin.de)
- Technische Fachhochschule [18] (http://www.tfh-berlin.de)
Zoos
BerlinZoologischerGartenEntrance.jpg
- Zoologischer Garten Berlin, Berlin's oldest zoo, located in the city center.
- Tierpark Friedrichsfelde, founded by the GDR in a historic castle park in eastern Berlin.
The Arts and Culture
After the fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 many buildings in the former city center of East Berlin (today the district Mitte) were renovated. Many had not been rebuilt since World War II. Illegally occupied by young people, they had become a fertile ground for all sorts of underground and counter-culture gatherings. It was also home to many nightclubs, including Tacheles, Techno clubs Tresor, WMF, Ufo and E-Werk.
The art scene in Berlin is extremely rich and it is home to hundreds of art galleries. The city is host to the Art Forum annual international art fair. Berlin also offers one of the most diverse and vibrant nightlife scenes in Europe. Most Berliners take great pride in their city's reputation as one of the most socially progressive cities on the continent.
Berlin's annual Carnival of Cultures, a multi-ethnic street parade, and Chistopher Street Day celebrations, Central Europe's largest gay-lesbian pride event, are openly supported by the city's government.*[19] (http://www.berlin-tourist-information.de/english/unterwegs/e_uw_berlinprogramm_gay.html)**[20] (http://www.berlin-tourist-information.de/english/zielgruppen/e_zg_gay_bezirke.php).
Another event is the techno-demonstration "Fuckparade" (every year in July or August).
Despite the city's high unemployment levels, a significant number of young Germans and artists continue to settle in the city, and Berlin has established itself as the premiere center of youth and pop culture in Europe.
Signs of this expanding role were the 2003 announcement that the annual Popkomm, Europe's largest music industry convention, would move to Berlin after 15 years in Cologne. Shortly thereafter, German MTV also decided to move its headquarters and main studios from Munich to Berlin. Universal Music opened its European headquarters on the banks of the River Spree in an area known as the mediaspree (http://www.mediaspree.de).
Films
Berlin was the centre of the German Film Industry until 1945. There are many films that were set in or portray the special "Berlin-Atmosphere" from different eras, among them are:-
- Die Symphonie der Großstadt 1927 Documentary Type Film "Day in the life of Berlin"
- Berlin Alexanderplatz 1920s
- The Blue Angel 1930s Depression
- Downfall Final days of the Third Reich 1945
- One, Two, Three Cold War before the Wall 1961
- Cabaret filmed in 1972, set in the early 1930s
- Christiane F. - Wir Kinder vom Bahnhof Zoo 1970s
- Wings of Desire - 1980s divided Berlin
- Run Lola Run, filmed 1998 in post-reunification Berlin
- Good bye, Lenin!, set in East Berlin in 1989
- Der Himmel über Berlin (Wings of Desire) -a cult movie about divided city by Wim Wenders from 1987
Museums
- Archenhold Observatory Archenhold-Sternwarte [21] (http://www.astw.de)
- Museum Island with the Altes Museum, Pergamon Museum and Alte Nationalgalerie
- German Museum of Technology in Kreuzberg, located at the site of an old freight train hub
Berlin_mem.jpg
- Museum for Post and Telecommunication
- Neue Nationalgalerie (New National Gallery), one of the last buildings by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe
- Old National Gallery (Old National Gallery), 19th-century painting and sculpture[22] (http://www.smpk.de/ang/e/s.html)
- Jewish Museum Berlin
- Hamburger Bahnhof (Museum for the Present - Berlin)
- Museum of European Cultures
- Berlin State Gallery [23] (http://www.berlinischegalerie.de/en/71-1-1_0.htm)
- Bauhaus Museum [24] (http://www.bauhaus-archiv.de/english/index.htm)
- Broehan Museum [25] (http://www.broehan-museum.de/home1.htm)
- Deutsche Guggenheim Museum [26] (http://www.deutsche-bank-kunst.com/guggenheim/e/)
- German Film Museum [27] (http://www.berlin-tourist-information.de/english/veranstaltungen/e_ve_filmmuseum.html)
- Kaethe Kollwitz Museum [28] (http://www.dhm.de/museen/kollwitz/english/home.htm)
- Museum of European Cultures [29] (http://www.museen-berlin.de/mek/e/s.html)
- Vitra Design Museum [30] (http://www.design-museum.de/berlin.php)
- The Berggruen Collection (Picasso and his Age) [31] (http://www.smb.spk-berlin.de/shb/e/s.html)
- Berlin Picture Gallery (Gemaeldegalerie) [32] (http://www.museen-berlin.de/gg/e/s.html)
- F.C. Flick Collection [33] (http://www.hamburgerbahnhof.de/FCFC/hbflickausse.html)
- Museum of Natural History [34] (http://www.museum.hu-berlin.de/home.asp?lang=1)
- German Museum of Technology [35] (http://www.dtmb.de/index_en.html)
- Museum of Medical History [36] (http://www.charite.de/kompakt/english/p8.00_frame.html)
- Berlin Wall Documentation Center [37] (http://www.berliner-mauer-dokumentationszentrum.de/index_e.html)
- Prussian Palaces and Gardens in Berlin [38] (http://www.spsg.de/index.php?id=1&sessionLanguage=en)
Theaters
- Schaubühne [39] (http://www.schaubuehne.de)
- Volksbühne [40] (http://www.volksbuehne-berlin.de)
- Deutsches Theater [41] (http://www.deutsches-theater.de)
- Berliner Ensemble [42] (http://www.berliner-ensemble.de)
- Theater des Westens [43] (http://www.theater-des-westens.de)
- Grips-Theater
- Maxim Gorki Theater [44] (http://www.gorki.de)
- Renaissance Theater
Opera houses
Dance clubs
- 2BE Club (Old WMF Location)
- Ausland ausland-berlin.de (http://www.ausland-berlin.de)
- Arena
- Bastard (Prater)
- Big Eden
- Icon
- Kalkscheune kalkscheune.de (http://www.kalkscheune.de/)
- Kato kato-x-berg.de (http://www.kato-x-berg.de/)
- Kinzo
- Knaack Club knaack-berlin.de (http://www.knaack-berlin.de/)
- Magnet magnet-club.de (http://www.magnet-club.de/)
- Maria am Ostbahnhof clubmaria.de (http://www.clubmaria.de/)
- Matrix matrix-berlin.de (http://www.matrix-berlin.de/)
- Polar.tv
- Sage Club sage-club.de (http://www.sage-club.de/)
- Silverwings silverwings.de
- SO36 so-36.de (http://www.so36.de/)
- Soda Club at Kulturbrauerei
- Steinhaus steinhaus-berlin.de (http://www.steinhaus-berlin.de/)
- Sternradio
- Tresor tresorberlin.com (http://www.tresorberlin.com/)
- Watergate water-gate.de (http://www.water-gate.de/)
- WMF (Café Moskau) wmfclub.de (http://www.wmfclub.de/)
- 90°
Transport
Public transport
Template:Commons Template:Commons
- U-Bahn, Metro subway system
- S-Bahn, mostly overground urban railway system
- Straßenbahn, a tram system, mainly in eastern Berlin
- Bus,
- Passenger Ferry
- All means of public transport - U- & S- Bahn, trams, buses and ferries - can be accessed with the same ticket.
- A map of the current public transport network (http://www.bvg.de/images/sunetz_aktuell.pdf) (BVG)
Railway Termini
Berlin was, pre-1945, the hub of the central European railway network. World War Two and the political division of Germany had very negative effects on the railway network in Berlin. Today only two pre-1945 Termini, Berlin-Ostbahnhof and Zoologischer Garten, remain in service. In the early 1950s, in an effort by the East German government to isolate West Berlin, railway services were diverted away from termini in West Berlin . These stations became disused and were demolished during the 1950s and 1960s.
Airports
- Schönefeld International Airport (SXF), to be expanded and renamed Berlin Brandenburg International Airport (BBI) in 2007
- Tegel International Airport (TXL), to close after BBI starts operations (in 2007)
- Tempelhof International Airport (THF), to close 2006
- Berlin Airports Website (http://www.berlin-airport.de)
Ports
- Westhafen (Westport) - largest port in Berlin with an area of 173,000 m²: transshipment of grain, pieced and heavy goods.
- Südhafen (Southport) - an area of about 103,000 m² for transshipment of pieced and heavy goods.
- Osthafen (Eastport) - the area of 57,500 m² is still in use, but partly under urban redevelopment
- Hafen Neukölln (Port Neukölln) - with only 19,000 m² the smallest port; transshipment of building materials.
Power Supply
The power supply of Berlin has some specialities. In World War II it was planned to supply the grid of Berlin over an HV DC-underground cable from Dessau power station . The construction of this facility was begun in 1943, but was abandoned (see Elbe-Project).
During the time of the division, the power grid of former West Berlin was cut off from the power grid of the surrounding countryside. Electricity supply was from thermal power stations in the city (Reuter, Wilmersdorf ,etc.). For buffering the load peaks, accumulators were installed in the 1980s in some of these power stations, which were connected by static invertors to the power grid and were loaded during times of low power consumption and unloaded during times of high consumption. In 1993 the power connections to the surrounding country, which were broken in 1951, were restored again. In the western districts of Berlin nearly all power lines are underground cables - only a 380 kV and a 110 kV-line, which run from Reuter power station to the urban motorway, are overhead lines. In Berlin there is the longest 380 kV three phase cable, the 380kV-crossing Berlin. It may be the most expensive power line in Germany.
Sports
Berlin hosted the 1936 Olympics.
Berlin will participate in hosting the FIFA Football World Cup in Germany in 2006.
Berlin will be hosting the 2009 athletics world championships.
Berlin is home to Hertha BSC Berlin, a high-flying football team in the Bundesliga.
Quotes
(Klaus Wowereit, Governing Mayor, in a television interview, 2004)
" Ich bin ein Berliner."
(John F. Kennedy, President of the USA, 1963 while visiting Berlin)
"Ihr Völker der Welt ... schaut auf diese Stadt!" ("Peoples of the world ... look at this city!")
(Ernst Reuter, Governing Mayor, during the Berlin blockade, 1948)
"Tear down this wall!"
(Ronald Reagan, President of the United States, speech at the Brandenburg Gate, 1987)
(Marlene Dietrich, actress and singer born 1901 in Berlin-Schöneberg)
External links
- Template:Wikitravel
- Official Website (http://www.berlin.de/english/index.html)
- Alt-Berlin (http://www.alt-berlin.info/) Extensive archive of historical maps of Berlin, from 1738 to the present day. (in German and English)
- grosser Tiergarten, Berlin (http://www.web-bb.de/web_berlin/tiergarten01.htm)
- [45] (http://www.berlin-tourist-information.de/english/zielgruppen/e_zg_gay_bezirke.php)Gay Berlin Information
- Berlin statistics (http://www.statistik-berlin.de) (in German)
- City Panoramas (http://www.panorama-cities.net/berlin/berlin.html) - Panoramic Views of Berlin's Highlights
- Berlin Artists (http://dmoz.org/Arts/Music/Bands_and_Artists/B/Berlin/)
- Architecture of Berlin (http://germany.archiseek.com/brandenburg/berlin/index.html)
- Objects of interest and events (http://www.Berlin-Motive.de/index.html)
- Comparison of historic layouts of the city (http://www.stadtentwicklung.berlin.de/planen/stadtmodelle/de/extra_fenster_schwarzplaene.shtml)
- Berlin apartments (http://www.all-berlin-apartments.com)
Template:Germany statesaf:Berlyn ar:برلين be:Бэрлін bg:Берлин bs:Berlin ca:Berlín cs:Berlín cy:Berlin da:Berlin de:Berlin et:Berliin es:Berlín eo:Berlino fr:Berlin gl:Berlín - Berlin gd:Berlin nn:Berlin he:ברלין hu:Berlin id:Berlin io:Berlin it:Berlino ja:ベルリン ku:Berlîn la:Berolinum lv:Berlīne lt:Berlynas nds:Berlin nl:Berlijn no:Berlin pl:Berlin pt:Berlim ro:Berlin ru:Берлин simple:Berlin sk:Berlín sl:Berlin sr:Берлин fi:Berliini sv:Berlin th:เบอร์ลิน uk:Берлін vi:Berlin zh:柏林