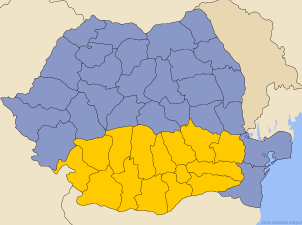
Wallachia
|
|
Wallachia (also spelt Walachia; Romanian: Ţara Rom‚nească - literally "Romanian country"; also Vlahia or Valahia; Turkish: Iflak) formed a Romanian principality in eastern Europe from the late Middle Ages until the mid-19th century.
The capital city changed over time, from Curtea de Argeş to T‚rgovişte and finally Bucharest.
Its name is derived from the Vlachs, another name for Romanians. (see also: Etymology of Vlach)
| Contents |
Geography
Wallachia was situated north of the Danube and south of the Carpathian Mountains. It is divided by the river Olt into two regions: the eastern part is Muntenia and the western part is Oltenia.
Its neighbours were the Ottoman Empire to the south, Transylvania to the north-west and Moldavia to the north-east.
History
Beginning with the tenth century, Byzantine, Slavic and Hungarian sources, and later Western ones mention the existence of small states peopled by Romanians under leaders known as cneji or voievozi - at first in Transylvania, then in the 12th-13th centuries in the territories east and south of the Carpathian Mountains. A specific characteristic of Romanian history from the Middle Ages to modern times is that they lived in three adjacent principalities - Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania, which was an autonomous voivodship of Hungary.
In the 14th century, along with the decline of the neighboring Poles, Hungarians, Tatars, several feudal states formed in the south and the east of the Carpathian Mountains - Wallachia under Basarab I (around 1330) and Moldavia under Bogdan I (around 1359).
In the second half of the 14th century, a new threat appeared - the Ottoman Empire. After having first gained a foothold in Europe in 1354, the Ottoman Turks reached the south bank of the Danube in 1396.
Alone or allied with the neighbouring Christian countries, rather than in alliance with the other two Romanian principalities, Mircea the Elder (1386-1418) and Vlad Tepes (1456-1462) of Wallachia, Stephen the Great (1457-1504) of Moldavia and Janos Hunyadi, prince of Transylvania (heroic figure to both Romanians and Hungarians), fought many defensive battles against the Ottomans, preventing them from expanding into Central Europe.
As the whole Balkan Peninsula became Turkish territory and following the fall of Constantinople to Mehmed II in 1453, the Romanian principalities had to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire for more than three centuries, though there were a few attempts to regain independence: (Michael the Brave in 1600 managed to unite for a short period of time all the three principalities). The tribute paid to the Turks allowed Wallachia (and Moldavia too) to maintain its autonomy.
After 1716, the Ottomans decided to cease choosing the voivode from among the Romanian boyars and instaured the Phanariote regime: the rulers were to be appointed from the influential Greeks of the Phanar neighbourhood of Istanbul.
The Phanariote rule ended only after the uprising of 1821 of Tudor Vladimirescu. In 1831 an act resembling a constitution ("RŤglement Organique") was adopted. In 1859, Wallachia voted to unite with Moldavia to form the state of Romania, under the rule of Alexander John Cuza.
Important rulers
- Litovoi, on the east side of the Olt river, 1247-1277,
- Seneslau, on west side of the Olt river, at Arges, c.a.1247
- Barbat, c.a.1277-c.a.1290
- Tihomir, c.a.1290-c.a.1310
- Basarab I, about 1310 - 1352
- Vladislav I or Vlaicu-Voda, 1364-c.a.1377
- Mircea cel Batrin (Mircea the Elder), 1386-1418
- Vlad Tepes (Vlad the Impaler), 1448, 1456-1462, 1476
- Neagoe Basarab, 1512-1521
- Mihai Viteazul (Michael the Brave), 1593 - 1601
- Constantin Br‚ncoveanu 1688 - 1714
- Alexander John Cuza, 1859 - 1866
See also the complete List of Wallachian rulers.
Coat of Arms of Romania
Wallachia is represented by an eagle in the Coat of Arms of Romania.
External links
- The Romanian Group for an Alternative History Website (http://www.patzinakia.ro/) - provides monument information, original documents, books, studies and other info concerning the Romanian Middle Ages
- orbilat.com: Explaining the etymology of Wallachia (http://www.orbilat.com/General_Survey/Terms--Wallachians_Walloons_Welschen_etc.html)
- Wallachia in pre-history (http://www.ship.edu/~cgboeree/indoeuropean.html)
| Romanian historical regions: |
| Dobrogea : Cadrilater
Moldavia : Bessarabia | Bugeac | Bukovina Transylvania : Banat | Crişana | Maramureş |