Cross-polytope
|
|
In geometry, a cross-polytope, or orthoplex, is a regular, convex polytope that exists in any number of dimensions. The vertices of a cross-polytope consist of all permutations of (±1, 0, 0, …, 0). The cross-polytope is the convex hull of its vertices. (Note: some authors define a convex-polytope only as the boundary of this region).
In 1-dimension the cross-polytope is simply the line segment [−1, +1], in 2-dimensions it is a square (or diamond) with vertices {(±1, 0), (0, ±1)}. In 3-dimensions it is an octahedron—one of the five regular polyhedra known as the Platonic solids. Higher dimensional cross-polytopes are generalizations of these.
| Missing image Square_diamond_(shape).png A 2-dimensional cross-polytope | 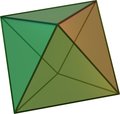
| |
| 2 dimensions | 3 dimensions |
The cross-polytope can also be characterized as the dual polytope of the hypercube.
4 dimensions
The 4-dimensional cross-polytope also goes by the name hexadecachoron or 16-cell. It is one of six regular convex polychora. These polychora where first described by the Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli in the mid-19th century.
The hexadecachoron has 16 cells all of which are regular tetrahedra. It has 32 triangular faces, 24 edges, and 8 vertices. The 24 edges bound 6 squares lying in the 6 coordinate planes. The Schläfli symbol of the hexadecachoron is {3,3,4}. The vertex figures are all regular octahedra. There are 8 tetrahedra, 12 triangles, and 6 edges meeting at every vertex. There are 4 tetrahedra and 4 triangles meeting at every edge. The dual polychoron of the hexadecachoron is the tesseract (the 4-dimensional hypercube).
When interpreted as quaternions the vertices of the hexadecachoron are the eight unit quaternions {±1, ±i, ±j, ±k}. These form a group under quaternionic multiplication called the quaternion group. (Note that the vertices of the 2-dimensional cross-polytope {±1, ±i} form a group under complex multiplication).
Higher dimensions
In n > 4 dimensions there are only three regular polytopes: the simplex, hypercube, and the cross-polytope, of which the last two are dual. The simplex is self-dual.
The n-dimensional cross-polytope has 2n vertices, and 2n facets (n−1 dimensional components) all of which are n−1 simplices. The vertex figures are all n−1 cross-polytopes. The Schläfli symbol of the cross-polytope is {3,3,…,3,4}.
The number of k-dimensional components (vertices, edges, faces, …, facets) in an n-dimensional cross-polytope is given by (see binomial coefficient):
- <math>2^{k+1}{n \choose {k+1}}<math>
For the first few n and k we have:
| n\k | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | ||||
| 2 | 4 | 4 | |||
| 3 | 6 | 12 | 8 | ||
| 4 | 8 | 24 | 32 | 16 | |
| 5 | 10 | 40 | 80 | 80 | 32 |
