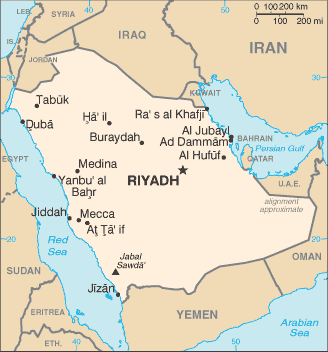
Geography of Saudi Arabia
|
|
Location: Southwest Asia, largest country of Arabia, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen. Considered to be one of the fifteen states that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity."
Geographic coordinates: Template:Coor dm
Map references: Middle East
Area:
total:
2,217,949 km²
land:
2,217,949 km²
water:
0 km²
Land boundaries:
total:
4,415 km
border countries:
Iraq 814 km, Jordan 728 km, Kuwait 222 km, Oman 676 km, Qatar 60 km, UAE 457 km, Yemen 1,458 km
Coastline: 2,640 km
Maritime claims:
contiguous zone:
18 nautical miles (33 km)
continental shelf:
not specified
territorial sea:
12 nautical miles (22 km)
Climate: harsh, dry desert with great extremes of temperature
Terrain: mostly uninhabited, sandy desert
Elevation extremes:
lowest point:
Persian Gulf 0 m
highest point:
Jabal Sawda' 3,133 m
Natural resources: petroleum, natural gas, iron ore, gold, copper
Land use:
arable land:
2%
permanent crops:
0%
permanent pastures:
56%
forests and woodland:
1%
other:
41% (1993 est.)
Irrigated land: 4,350 km² (1993 est.)
Natural hazards: frequent sand and dust storms
Environment - current issues: desertification; depletion of underground water resources; the lack of perennial rivers or permanent water bodies has prompted the development of extensive seawater desalination facilities; coastal pollution from oil spills
Environment - international agreements:
party to:
Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified:
none of the selected agreements
Geography - note: extensive coastlines on Persian Gulf and Red Sea provide great leverage on shipping (especially crude oil) through Persian Gulf and Suez Canal