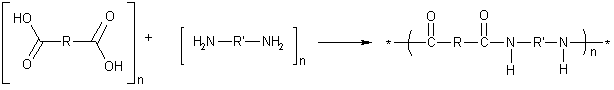Condensation polymer
|
|
| This article is in need of attention. |
| Please improve (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php?title=Condensation_polymer&action=edit) this article. |
Condensation polymers are any class of polymers formed through a condensation reaction, as opposed to addition polymers which involve the reaction of unsaturated monomers. Types of condensation polymers include polyamides and polyesters.
Condensation polymerisation is a process by which two molecules join together, with the loss of a small molecule which is often water.
This often involves linking monomers with an -OH (hydroxyl) group and a freely ionized -H on either end (such as a hydrogen from the -NH2 in nylon or proteins). Normally, two or more different monomers are used in the reaction. The bonds between the hydroxyl group, the hydrogen atom and their respective atoms break forming water from the hydroxyl and hydrogen, and the polymer.
Polyester is created through ester linkages between monomers, which involve the functional groups carboxy and hydroxy (an organic acid and an alcohol monomer).
Nylon is a common condensation polymer. It is manufactured by reacting di-amines with carboxyl derivatives. In this example the derivative is a di-carboxylic acid, but di-acyl chlorides are also used:
The carboxylic acids and amines link to form peptide bonds, also known as amide groups. Proteins are condensation polymers made from amino acid monomers. Carbohydrates are also condensation polymers made from sugar monomers such as glucose and galactose.
Condensation polymerization is occasionally used to form simple hydrocarbons. This method, however, is expensive and ineffective, so the addition polymer of ethene (polyethylene) is generally used.
Condensation Polymers, unlike Addition polymers are bio-degradable. The peptide or ester bonds between monomers can be hydrolysed by acid catalysts or bacterial enzymes breaking the polymer chain into smaller pieces.
The most commonly known condensation polymers are proteins, fabrics such as nylon, silk, or polyester.
- See also: Biopolymer, Polyester, Polyamide