Bahrain
|
|
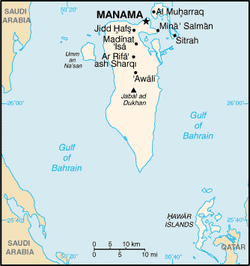
The Kingdom of Bahrain, or Bahrain (formally spelled Bahrein), is a borderless island nation in the Persian Gulf (Southwest Asia/Middle East, Asia). Saudi Arabia is to the west and is connected to Bahrain by the King Fahd Causeway, and Qatar is to the south across the Persian Gulf. The Qatar-Bahrain Friendship Bridge, currently in planning, will link Bahrain to Qatar as the longest fixed link in the world.
| |||||
| National motto: Bahrainona بحريننا | |||||

| |||||
| Official languages | Arabic and English | ||||
| Capital | Manama | ||||
| King | Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa | ||||
| Prime Minister | Khalifa bin Salman Ali Khalifa | ||||
| Crown Prince | Salman bin Hamad bin Isa Al-Khalifa | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 175th 665 km² 0% | ||||
| Population | Ranked 157th
| ||||
| Independence - From Persia - From the United Kingdom | |||||
| Currency | Bahraini Dinar (BHD) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC+3 | ||||
| National anthem | Bahrainona (Our Bahrain) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .bh | ||||
| Calling Code | 973 | ||||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Bahrain
Bahrain has been populated by humans since prehistoric times. Its strategic location in the Persian Gulf has brought rule and influence from the Assyrians, Babylonians, Greeks, Persians, and finally the Arabs, under whom the island became Muslim. Bahrain was in the ancient times known as Dilmun, Tylos (its Greek Given name), Awal, as well as Persian name Mishmahig when it was a part of the Persian Empire.
The islands of Bahrain, positioned in the middle south of the Persian Gulf, have attracted the attention of many invaders in history. Bahrain, meaning "Two Seas" refers to the fact that the islands contain the two sources of water, sweet water springs and salty water in the surrounding seas.
A strategic position between East and West, fertile lands, fresh water, and pearl diving made Bahrain a centre of urban settlement throughout history. Some 2300 years BC, Bahrain became a centre of one of the ancient empires trading Mesopotamia (now Iraq) and the Indus Valley (now the region near India). This was the civilization of Delmon that was linked to the Sumerian Civilization in the third millennium BC. Bahrain also became part of the Babylon empire about 600 BC. Historical records referred to Bahrain the "Life of Eternity", "Paradise", etc. Bahrain was also called the "Pearl of the Persian Gulf".
Bahrain up until 1521 comprised the bigger region of Ahsa, Qatif (both are now the eastern province of Saudi Arabia) as well as Awal (now Bahrain Islands). The region stretched from what is now Kuwait to Oman. This was Iqlim Al-Bahrain (Province of Bahrain). In 1521, the Portuguese separated Awal (now Bahrain) from the rest and since then the name of Bahrain specifically referred to today's Bahrain.
The modern history of Bahrain begins with increasing British involvement in the region, aimed at isolating Iran. The British provided support to the Al-Khalifa family, who established a power base in the island and built alliances with the British in order to separate the island from Iran. The British gained free access to the Persian Gulf through this agreement. In November of 1957, the Iranian parliament unilaterally decreed Bahrain as the Fourteenth Province of Iran. Later the British would directly become involved in the politics of Bahrain by handpicking an Emir of the island. Eventually Iran and Britain agreed that the matter of Dominion of Bahrain would be put to international judgment and requested the United Nations General Secretary to take on this responsibility. In a Plebiscite to decide the country's future, the majority of the population of Bahrain chose to reject Iran's claims, and to define themselves, as well as their culture to be Arabic, and not Persian.
Oil was discovered in the early 20th century and brought rapid modernization and improvements to Bahrain. It also made relations with Britain tighter, and this was evidenced by the British moving more bases to the island nation. British influence would continue to grow, culminating with the appointment of Charles Belgrave as an advisor; Belgrave established modern education systems in Bahrain.
After World War II, increasing anti-British feeling spread throughout the Arab world and led to some riots in Bahrain. The British withdrew from Bahrain in 1971, making it an independent emirate. The oil boom of the 1980s greatly benefitted Bahrain, but its downturn was not as badly felt, as the economy of Bahrain began to diversify.
In 1994, a wave of rioting by disaffected Shia Islamists was touched off after women athletes participated in a marathon race. The Kingdom was badly affected by sporadic violence during the mid-1990s in which over forty people were killed.
In 1999, Sheikh Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa succeeded his father as head of state and instituted elections for parliament, gave women the vote and released all political prisoners.
Politics
Template:Politics of Bahrain Main article: Politics of Bahrain
Bahrain is a hereditary kingdom under the rule of the Al-Khalifa family. The King is the chief executive and head of state. The prime minister is head of government. Both these posts are filled by members of the Al-Khalifa family, the king being Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa, the Prime Minister, his uncle Khalifa bin Salman Ali Khalifa. Both rule through consultation with ministers. The judiciary system is relatively independent of the government and is based on diverse legal sources, including Shi'a and Sunni Islamic law. The new king has worked to improve civil rights and increase democratic reforms. Municipal elections were held in 2002, and legislative elections will be held in 2004. King Hamad has also stated his intention to have a house of the legislative portion of the government that is composed of delegates elected by both males and females.
Governorates
Bahrain_governorates_numbered.png
Map of Bahrain showing governorates
Main article: Governorates of Bahrain
Bahrain is split into five governorates. Until July 3 2003, it was divided into twelve municipalities; see Municipalities of Bahrain.
For further information, see: Decree-Law establishing governorates (http://www.capital.gov.bh/pages/pdf/govlawe.pdf) from the Bahrain official website
Economy
Main article: Economy of Bahrain
In Bahrain, petroleum production and processing account for about 60% of export receipts, 60% of government revenues, and 30% of GDP. Economic conditions have fluctuated with the changing fortunes of oil since 1985, for example, during and following the Persian Gulf crisis of 1990-91. With its highly developed communication and transport facilities, Bahrain is home to numerous multinational firms with business in the Persian Gulf. A large share of exports consists of petroleum products made from imported crude. Construction proceeds on several major industrial projects. Unemployment, especially among the young, and the depletion of both oil and underground water resources are major long-term economic problems.
Geography
Bahrain is a generally flat and arid archipelago, comprising of a low desert plain rising gently to a low central escarpment, in the Persian Gulf, east of Saudi Arabia. The highest point is the 122m Jabal ad Dukhan.
Considered to be one of the fifteen states that comprise the so-called "Cradle of Humanity" in the Middle East, Bahrain has a total area of 620 km², which is slightly larger than the Isle of Man. As an archipelago of 33 islands, Bahrain does not share a land boundary with another country but does have a 161 km coastline and claims a further 12 nm of territorial sea and a 24 nm contiguous zone. Bahrain enjoys mild winters and endures very hot, humid summers.
Bahrain's natural resources include large quantities of oil and associated and nonassociated natural gas as well as fish stocks, which is perhaps fortunate as arable land constitutes only 1% of the country. Desert constitutes 92% of Bahrain and periodic droughts and dust storms are the main natural hazards for Bahrainis.
Environmental issues facing Bahrain include desertification resulting from the degradation of limited arable land and coastal degradation (damage to coastlines, coral reefs, and sea vegetation) resulting from oil spills and other discharges from large tankers, oil refineries, and distribution stations.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Bahrain
The official religion of Bahrain is Islam, with the population overwhelmingly comprised of Shi'a and Sunni Muslims, but there are also small indigenous Jewish and Christian minorities. Most Bahrainis are of Arab origin, although some tribes trace their roots back to Persia.
Nowadays Bahrain is a cosmopolitan society with mixed communities: two thirds of Bahrain's population consists of Arabs while the rest are immigrants and guest workers that are largely from Iran, South Asia and Southeast Asia. A Financial Times published on 31 May 1983 found that "Bahrain is a polyglot state, both religiously and racially. Leaving aside the temporary immigrants of the past 10 years, there are at least eight or nine communities on the island".
The present communities may be classified as Al-Khalifa, Arab tribes allied to Al-Khalifa, the Baharnah (Shia Arabs), the Howilla (Sunni Arabs from Persia), Sunni Arabs (from the mainland), Ajam (Persian Shia), Indians who traded with Bahrain and settled before the age of oil (used to be called Banyan), a tiny Jewish community, and a miscellaneous grouping.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Bahrain
As flashy and modern as central Manama may be, the basic rhythms of life in the island's many villages (and in parts of Manama itself) remain remarkably traditional. By the same token, where there's tradition in the Persian Gulf there's Islamic conservatism: women cover themselves from head to foot and women travellers are expected to wear long skirts and one-piece bathing suits. Bahrain's population is 85% Muslim and Islam is the state religion. Arabic is the official language but English is widely spoken.
Traditional craftwork continues in several places around Bahrain: dhows (fishing boats) are built on the outskirts of Manama and Muharraq, cloth woven at Bani Jamrah and pottery thrown at A'ali. A few goldsmiths still operate in the Manama souk, though a lot of the work is now done abroad. One of the mainstays of Bahraini culture is the drinking of traditional Arabian coffee. You can't go far without finding a coffee pot in a shop or a souk. Traditional Arabian street food like shawarma (lamb or chicken carved from a huge rotating spit and served in pita bread) and desserts such as baklava are also ubiquitous.
Holidays
Bahrain holds the Bahrain Grand Prix. In 2004, it was held on April 4.
| Date | English Name | Local Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 1 | New Year's Day | - | - |
| December 16 | National Day | - | - |
| December 17 | Accesion Day | - | - |
| date varies | Feast of the Sacrifice or the Big Feast | Eid ul-Adha | Commemorates Abraham's willingness to sacrifice his son, occurs at the end of the month of hajj |
| date varies | the Little Feast | Eid ul-Fitr | Commemorates end of Ramadan |
| date varies | Hijri New Year | Muharram | Islamic New Year |
| date varies | Al-Isra' ul-Miraj | - | Commemorates Muhammad's trip to heaven |
| date varies | Prophet Muhammads birthday | Mawlid al-Nabi | - |
| date varies | Ashoura | death of imam Husain Al Shaheed (AS) | - |
Education
Main article: Education in Bahrain
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Bahrain
- Islam in Bahrain
- Transportation in Bahrain
- Military of Bahrain
- Foreign relations of Bahrain
- Bahrain International Airport
- List of cities in Bahrain
- List of rulers of Bahrain
External links
- Government web site (http://www.bahrain.gov.bh/english/index.asp)
- Wikisource:Category:Bahrain
- Voice of Bahrain (http://vob.org/) run by the Bahrain Freedom Movement
- BahrainWiki (http://wiki.bahraini.tv/)
- Bahrain News Agency (http://www.bna.bh/) in English (http://english.bna.bh/)
- BBC News Country Profile - Bahrain (http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/world/middle_east/country_profiles/790690.stm)
- CIA World Factbook - Bahrain (http://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/ba.html)
- Library of Congress Country Study - Bahrain (http://lcweb2.loc.gov/frd/cs/bhtoc.html) data as of January 1993
- LookSmart - Bahrain (http://search.looksmart.com/p/browse/us1/us317916/us559898/us560105/us560109/) directory category
- Open Directory Project - Bahrain (http://dmoz.org/Regional/Middle_East/Bahrain/) directory category
- Yahoo! - Bahrain (http://dir.yahoo.com/Regional/Countries/Bahrain/) directory category
- Business news for Bahrain and the region (http://www.ameinfo.com/)
- Kyle's pictures from Bahrain (http://photos.kyleh.net)
- Mishmahig Islands (Bahrain), How it was separated from Iran? (http://www.iranchamber.com/geography/articles/mishmahig_islands_bahrain.php)
- Personal photos from Bahrain (http://www.kevin-mccoy.com/gallery/spbahrain)
- Financial institutions in Bahrain (http://based.in/?Bahrain)
- Manama, Bahrain (http://www.thepersiangulf.org/cities/manama.html)
| Countries and Territories in Southwest Asia |
|
Afghanistan | Armenia | Azerbaijan | Bahrain | Cyprus | Gaza Strip | Georgia | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Oman | Qatar | Russia | Saudi Arabia | Syria | Turkey | United Arab Emirates | West Bank | Yemen |
| Countries and territories in the Middle East |
|---|
| Bahrain | Cyprus | Egypt | Gaza Strip | Iran | Iraq | Israel | Jordan | Kuwait | Lebanon | Oman | Qatar | Saudi Arabia | Syria | Turkey | United Arab Emirates | West Bank | Yemen |
]]