Alexander the Great
|
|
Alexander III (late July, 356 BC–June 10, 323 BC), commonly known in the West as Alexander the Great or Alexander of Macedon, in Greek Template:Polytonic ("Megas Alexandros"), King of Macedon (336 BC-323 BC), was one of the most successful military commanders of the ancient world. He is known in some eastern traditions such as the Middle-Persian literature as Alexander the Cursed due to his burning of the Persian capital and national library.
Following the unification of the multiple city states of Ancient Greece under the rule of his father, Philip II of Macedon, Alexander conquered the Persian Empire, including Anatolia, Syria, Egypt, Bactria and Mesopotamia, and extended the boundaries of his own empire as far as India. Alexander integrated non-Greeks into his army and administration, leading some scholars to credit him with a “policy of fusion.” After twelve years of constant military campaigning, Alexander died, probably of malaria or typhoid. His conquests ushered in centuries of Greco-Macedonian settlement and rule over non-Greek areas, a period known as the Hellenistic Age. Alexander himself lived on in the history and myth of both Greek and non-Greek peoples. Already during his lifetime, and especially after his death, his exploits inspired a literary tradition in which he appears as a towering legendary hero in the tradition of Achilles.
| Contents |
Early life
Alexander was the son of King Philip II of Macedon and of Epirote princess Olympias. According to Plutarch (Alexander 3.1,3), Olympias was impregnated not by Philip, who was afraid of her and her affinity for sleeping in the company of snakes, but by Zeus. Plutarch (Alexander 2.2-3) relates that both Philip and Olympias dreamt of their son's future birth. Olympias dreamed of a loud burst of thunder and of lightning striking her womb. In Philip's dream, he sealed her womb with the seal of the lion. Alarmed by this, he consulted the seer Aristander of Telmessus, who determined that his wife was pregnant and that the child would have the character of a lion. Aristotle was Alexander's tutor; he gave Alexander a thorough training in rhetoric and literature and stimulated his interest in science, medicine, and philosophy.
After his visit to the Oracle of Ammon at Siwah, according to all five of the extant historians (Arrian, Curtius, Diodorus, Justin, and Plutarch), rumors spread that the Oracle had revealed Alexander's father was Zeus, rather than Philip. According to Plutarch (Alexander 2.1), his father descended from Heracles through Caranus and his mother descended from Aeacus through Neoptolemus and Achilles.
The ascendance of Macedon
When Philip led an attack on Byzantium in 340 BC, Alexander, aged 16, was left in command of Macedonia. In 339 BC Philip divorced Alexander's mother, leading to a quarrel between Alexander and his father which threw into question Alexander's succession to the Macedonian throne. In 338 BC, Philip created The League of Corinth. Alexander also assisted his father at the decisive battle of Chaeronea in this year. In 336 BC, Philip was assassinated at the wedding of his daughter Cleopatra to King Alexander of Epirus. The assassin was supposedly a former lover of the king, the disgruntled young nobleman (Pausanias), who held a grudge against Philip because the king had ignored a complaint he had expressed. His murder was once thought to have been planned with the knowledge and possible involvement of Alexander or Olympias, but in recent years Alexander's involvement has been questioned, and there is some reason to believe that it may have been instigated by Darius III Codomannus, the recently crowned King of Persia. Plutarch mentions an irate letter from Alexander to Darius III, where Alexander blames Darius and Bagoas for his father's murder, stating that it was Darius who had been bragging to the rest of the Greek city states how he managed to have Philip assassinated.
After the death of Philip, Alexander, then aged 20, was acclaimed by the army as the new king of Macedon. Greek cities like Athens and Thebes, which had pledged allegiance to Philip were not quick to pledge it to a 20-year-old boy. He immediately ordered the execution of all of his potential rivals and marched south with his armies in a campaign to solidify control of Greece and confront the Persian Empire.
Period of conquests
The defeat of the Persian empire
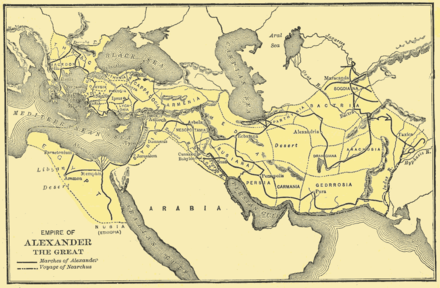
Alexander's army crossed the Hellespont with about 40,000 Greek and Macedonian soldiers. After an initial victory against Persian forces at the Battle of Granicus, Alexander accepted the surrender of the Persian provincial capital and treasury of Sardis and proceeded down the Ionian coast. At Halicarnassus, Alexander successfully waged the first of many sieges, eventually forcing his opponents, the mercenary captain Memnon of Rhodes and the Persian satrap of Caria Orontobates to withdraw by sea. Alexander left Caria in the hands of Ada, the sister of Mausolus, whom Orontobates had deposed. From Halicarnassus, Alexander proceeded into mountainous Lycia and the Pamphylia plain, asserting control over all coastal cities and denying them to his enemy. From Pamphylia onward the coast held no major ports, so Alexander moved inland. At Pisidian Termessus Alexander humbled but did not storm the city. At the ancient Phrygian capital of Gordium, Alexander "undid" the tangled Gordian knot, a feat said to await the future "king of Asia." According to the most vivid story, Alexander proclaimed that it did not matter how the knot was undone, and hacked it apart with his sword.
Alexander's army crossed the Cilician Gates and met and defeated the main Persian army under the command of Darius III Codomannus at the Battle of Issus in 333 BC. Proceeding down the Mediterranean coast, he took Tyre and Gaza after famous sieges (see Siege of Tyre). Alexander passed near but probably did not visit Jerusalem.
In 332-331 BC Alexander was welcomed as a liberator in Egypt and was pronounced the son of Zeus by Egyptian priests of the god Ammon at the Oracle of the god at the Siwah oasis in the Libyan Desert. He founded Alexandria in Egypt, which would become the prosperous capital of the Ptolemaic dynasty after his death. Leaving Egypt, Alexander marched eastward into Assyria (now Iraq) and defeated Darius and a third Persian army at the Battle of Gaugamela. Darius was forced to flee the field after his charioteer was killed, and Alexander chased him as far as Arbela. While Darius fled over the mountains to Ecbatana (modern Hamadan), Alexander marched to Babylon.
From Babylon, Alexander went to Susa, one of the Achaemenid capitals, and captured its treasury. Sending the bulk of his army to Persepolis, the Persian capital, by the Royal Road, Alexander stormed and captured the Persian Gates (in the modern Zagros Mountains), then sprinted for Persepolis before its treasury could be looted. Alexander allowed the League forces to loot Persepolis, and he set fire to the royal palace of Xerxes, allegedly in revenge for the burning of the Athenian Acropolis during the Second Persian War. He then set off in pursuit of Darius, who was kidnapped, and then murdered by followers of Bessus, his Bactrian satrap and kinsman. Bessus then declared himself Darius' successor as Artaxerxes V and retreated into Central Asia to launch a guerrilla campaign against Alexander. With the death of Darius, Alexander declared the war of vengeance at an end, and released his Greek and other allies from service in the League campaign (although he allowed those that wished to re-enlist as mercenaries in his imperial army). His three-year campaign against Bessus and his successor Spitamenes took him through Media, Parthia, Aria, Drangiana, Arachosia, Bactria and Scythia. In the process he captured and refounded Herat and Samarkand, and he founded a series of new cities, all called Alexandria, including one near modern Kandahar in Afghanistan, and Alexandria Eschate ("The Furthest") bordering today's Chinese Turkestan.
Hostility toward Alexander
During this time, Alexander adopted some elements of Persian dress and customs at his court, notably the custom of proskynesis, a symbolic kissing of the hand that Persians paid to their social superiors, but a practice of which the Greeks disapproved; the Greeks regarded the gesture as the preserve of deities, and believed that Alexander meant to deify himself by requiring it. This cost him much in the sympathies of many of his Greek countrymen. Here, too, a plot against his life was revealed, and his Companion and friend Philotas was executed for treason for failing to bring the plot to his attention. Although Philotas was convicted by the assembled Macedonian army, most historians consider this one of the king's greatest crimes, along with his order to assassinate his senior general Parmenion, Philotas' father. In a drunken quarrel at Macaranda Samarkand, he also murdered the man who had saved his life at the Granicus, Clitus the Black. Later in the Central Asian campaign, a second plot against his life, this one by his own Pages, was revealed, and his official historian, Callisthenes of Olynthus (who had fallen out of favor with the king by leading the opposition to his attempt to introduce proskynesis), was implicated on what most historians regard as trumped-up charges.
The invasion of India
Le_Brun,_Alexander_and_Porus.jpg
With the death of Spitamenes and his marriage to Roxana (Roshanak in Bactrian) to cement his relations with his new Central Asian satrapies, in 326 BC Alexander was finally free to turn his attention to India. King Omphis, ruler of Taxila, surrendered the city to Alexander. Many people had fled to a high fortress/rock called Aornos. Alexander took Aornos by storm (see siege of Aornos). Alexander fought an epic battle against the Indian monarch Porus in the Battle of Hydaspes (326). After victory, Alexander made an alliance with Porus and appointed him as satrap of his own kingdom. Alexander continued on to conquer all the headwaters of the Indus River.
East of Porus' kingdom, near the Ganges River, was the powerful kingdom of Magadha. Exhausted and frightened by the prospect of facing another giant Indian army at the Ganges River, his army mutinied at the Hyphasis (modern Beas), refusing to march further East. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer, Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return. Alexander was forced to turn south, conquering his way down the Indus to the Ocean. He sent much of his army to Carmania (modern southern Iran) with his general Craterus, and commissioned a fleet to explore the Persian Gulf shore under his admiral Nearchus, while he led the rest of his forces back to Persia by the southern route through the Gedrosia (modern Makran in southern Pakistan).
After India
Discovering that many of his satraps and military governors had misbehaved in his absence, Alexander executed a number of them as examples on his way to Susa. As a gesture of thanks, he paid off the debts of his soldiers, and announced that he would send those who were over-aged and the disabled veterans back to Macedonia under Craterus, but his troops misunderstood his intention and mutinied at the town of Opis, refusing to be sent away and bitterly criticizing his adoption of Persian customs and dress and the introduction of Persian officers and soldiers into Macedonian units. Alexander executed the ringleaders of the mutiny, but forgave the rank and file. In an attempt to craft a lasting harmony between his Macedonian and Persian subjects, he held a mass marriage of his senior officers to Persian and other noblewomen at Opis, but few of those marriages seem to have lasted much beyond a year.
His attempts to merge Persian culture with his Greek soldiers also included training a regiment of Persian boys in the ways of Macedonians. It is not certain that Alexander adopted the Persian royal title of shahanshah ("great king" or "king of kings"), but most historians think that he did.
After traveling to Ecbatana to retrieve the bulk of the Persian treasure, his closest friend and probable lover Hephaestion died of an illness. Alexander was distraught. He conducted a campaign of extermination against the Cossaens to assuage his grief. On his return to Babylon, he fell ill and died.
While invading the ancient city of Mali along shore of India he recieved a wound from an arrow in his chest causing him near death. Many historians argue if this was the cause of his death.
Alexander's marriages and sexuality
Alexander's greatest emotional attachment is generally considered to have been to his companion, cavalry commander (chiliarchos) and most probably lover, Hephaestion. They had most likely been best friends since childhood, for Hephaestion too received his education at the court of Alexander's father. Hephaestion makes his appearance in the histories at the point when Alexander reaches Troy. There the two friends made sacrifices at the shrines of the two heroes Achilles and Patroclus, Alexander honouring Achilles, and Hephaestion, Patroclus. As Aelian in his Varia Historia (12.7) claims, "He thus intimated that he was the object of Alexander's love, as Patroclus was of Achilles." Many discussed his ambiguous sexuality. Letter 24 of those ascribed to Diogenes of Sinope, thought to be written in either the 1st century or the 2nd century, and probably reflecting the gossip of Alexander's day, exhorts him: "If you want to be beautiful and good (kalos k'agathos), throw away the rag you have on your head and come to us. But you won't be able to, for you are ruled by Hephaestion's thighs." And Curtius reports that "He scorned [feminine] sensual pleasures to such an extent that his mother was anxious lest he be unable to beget offspring." To whet his appetite for the fairer sex, King Philip and Olympias brought in a high-priced Thessalian courtesan named Callixena.
Later in life Alexander married several princesses of former Persian territories: Roxana of Bactria; Statira, daughter of Darius III; and Parysatis, daughter of Ochus. He fathered at least two children, Heracles born in 327 BC by his mistress Barsine the daughter of Satrap Artabazus of Phrygia, and Alexander IV of Macedon by Roxana in 323 BC. This would be in keeping with the ancient omnivorous approach to sexuality.
Curtius maintains that Alexander also took as a lover "... Bagoas, a eunuch exceptional in beauty and in the very flower of boyhood, with whom Darius was intimate and with whom Alexander would later be intimate," (VI.5.23). Eumenes writes that, previous to venturing further east, Alexander installed Bagoas in a villa outside of Babylon and required all his officers and courtesans, both Greek and Persian, to render him honours (i.e. to present him with rich gifts). Alexander's favor to Bagoas is also apparent in his subsequent appointment of Bagoas as one of the trierarchs, men of substance who oversaw and funded the construction of the navy for the journey homeward. Their relationship seems to have been well known among the troops, as Plutarch recounts an episode (also mentioned by Athenaios and Dicaearchus) during some festivities on the way back from India, in which his men clamor for him to openly kiss the young man. "Bagoas [...] sat down close by him, which so pleased the Macedonians, that they made loud acclamations for him to kiss Bagoas, and never stopped clapping their hands and shouting till Alexander put his arms round him and kissed him." (Plutarch, The Lives). Whatever his relationship with Bagoas, it was no impediment to relations with his queen: six months after Alexander's death Roxana gave birth to his son and heir Alexander IV. Besides Bagoas, Curtius mentions yet another lover of Alexander, Euxenippos, "whose youthful grace filled him with enthusiasm." (VII.9.19)
The suggestion that Alexander was homosexual or bisexual remains highly controversial and excite passions in some quarters in Greece, (former Yugoslav) Republic of Macedonia and diasporas thereof. People of various national, ethnic and cultural origins regard him as a national hero. They argue that historical accounts describing Alexander's relations with Hephaestion and Bagoas as sexual were written centuries after the fact, and thus it can never be established what the 'real' relationship between Alexander and his male companions were. Others argue that the same can be said about all our information regarding Alexander. Such debates, however, are considered anachronistic by scholars of the period, who point out that the concept of homosexuality did not exist in Greco-Roman Antiquity: sexual attraction between males was seen as a normal and universal part of human nature since it was believed that men were attracted to beauty, an attribute of the young, regardless of gender. If Alexander's love life was transgressive it was not for his love of beautiful youths but for his involvement with a man his own age, in a time when the standard model of male love was pederastic. See History of Homosexuality for more information.
It has been proposed that Alexander was also a "cross-dresser," on the grounds that he was known to wear the "silvery dress" of Athena, which he received from priests at Troy. This idea, however, subsists upon a misunderstanding of "dress," used in the sense of "attire." In fact, it was Athena who was the cross-dresser, wearing armor when Greek women and other female gods did not.
The army of Alexander the Great before the Battle of Gaugamela
The army of Alexander the Great was, for the most part, that of his father Philip. It was composed of light and heavy troops and some engineers, medical and staff units. About one third of the army was composed of his Greek allies from the Hellenic League.
Infantry
The main infantry corps was the phalanx, composed of six regiments (taxies) numbering about 1,500 phalangites each. Each soldier had a long pike called a sarissa, which was up to 18 feet long, and a short sword. For protection the soldier wore a Phygrian-style helmet and a shield. Arrian mentions large shields (the aspis) but this is disputed; it is difficult to wield both a large pike and a large shield at the same time. Many modern historians claim the phalanx used a smaller shield, called a pelta, the shield used by peltasts. It is unclear whether the phalanx used body armor, but heavy body armor is mentioned in Arrian (1.28.7) and other ancient sources. Modern historians believe most of the phalangites did not wear heavy body armor at the time of Alexander the Great
Another important unit were the Hypaspists (shield bearers), arranged into three battalions (lochoi) of 1,000 men each. One of the battalions was named the "Agema" and served as the King's bodyguards. Their armament is unknown; it is difficult to to get a clear picture from ancient sources. Sometimes hypaspists are mentioned in the front line of the battle just between the phalanx and the heavy cavalry and seem to have acted as heavy infantry, but they also accompanied Alexander on flanking marches and were capable of fighting on rough terrain like light troops.
In addition to the units mentioned above, the army included some 6,000 Greek allied and mercenary hoplites, also arranged in phalanxes. They carried a shorter spear, a dora, which was six or seven feet long and a large aspis, shield.
Alexander also had light infantry units composed of peltasts, psiloi and others. Peltasts are considered to be light infantry, although they had a helmet and a small shield and were heavier then the psiloi. The best peltasts were the Agrianians from Thrace.
Cavalry
The heavy cavalry included the "Campanion cavalry," raised from the Macedonian nobility, and the Thessalian cavalry. The Companion cavalry (hetairoi, friends) was divided into eight squadrons called "ile," 200 strong, except the Royal Squadron of 300. They were equipped with a 12-14 foot lance, the xyston, and heavy body armor. The horses were partially clad in armor as well. The riders did not carry shields. The organization of the Thessalian cavalry was similar to the Companion Cavalry, but they had a shorter spear and fought in a looser formation.
Of light cavalry, the prodomoi (runners) secured the wings of the army during battle and went on reconaissance missions. Several hundred allied horse rounded out the cavalry, but were inferior to the rest.
Death

In the afternoon of June 10, 323 BC, Alexander died of a mysterious illness in the palace of Nebuchadrezzar II of Babylon. He was only 33 years old. Various theories have been proposed for the cause of his death which includes poisoning by the sons of Antipater, murder by his wife Roxane [1] (http://news.independent.co.uk/world/science_technology/story.jsp?story=568501), and sickness due to a relapse of malaria he had contracted in 336 BC.
In 1998, in an article titled "A Mysterious Death" in the New England Journal of Medicine, volume 338:1764-1769, David W. Oldach, M.D. (a professor of pathology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine), and others (including eminent Alexander historian Eugene N. Borza), analyzed Alexander's symptoms as described in Arrian, Diodorus and Plutarch. Oldach dismissed the poisoning theory and diagnosed the king's final illness as typhoid, perhaps complicated by peritonitis and Guillain-Barr頳yndrome, leading to the possibility that a helplessly paralyzed Alexander might actually have been killed by his embalmers.
Peter Green, in his biography on Alexander the Great, speculated that there was more than just a grain of truth in the traditional story, universally held in antiquity, of how Alexander the Great died - that Aristotle, tired of Alexander's pretentions and perhaps fearful for his life after Alexander executed his nephew, mixed the poison, that Cassander, son of Antipater, viceroy of Greece, brought it in a mule's hoof, and that his royal cupbearer administered it to the king. The reasoning, Green believes, is that enough was now seen as enough by the generals and Macedonian nobility, who felt they were being slowly but surely phased out of power by Alexander's "one world" policies. Alexander, who planned an invasion of Arabia after he'd assembled a force in Babylon, did not consider himself finished with his plans for world conquest by any means, and many Macedonians feared he'd become little more than an Oriental despot if given enough time. The fact that he was hugely unpopular in nearly every country he passed through simply made it permissible to strike down the tyrant. When after Alexander's death it was necessary to establish a "legitimate" heir to the throne, every general and would-be king felt it impossible to admit to the murder without losing whatever moral claim they might have on the empire. But, as Green notes, motive does not necessarily make a murder, and the general feeling is that the affair is too murky to ever see clearly through, pending, perhaps, the find of Alexander's body hidden away somewhere.
That Alexander's body failed to decompose for, it is said, six days supports the theory that he was suffering from typhoid induced paralysis but it also points to poison as many poisons act as a preservative. Graham Phillips in 'Alexander the Great: Death in Babylon' is skeptical that Alexander could have really lasted long in a state of paralysis, presumed dead in hot Babylon. He gives other reasons for doubting typhoid pointing out that Alexander is not described as suffering from diarrhea. He suggests a plant based poison is more likely and favors Belladonna in particular. Belladonna may produce paralysis of the vocal cords which fits the description of how Alexander though conscious was unable to speak.
According to legend, Alexander was preserved in a clay vessel full of honey (which acts as a preservative) and interred in a glass coffin. According to Aelian (Varia Historia 12.64), Ptolemy stole away the body and brought it to Alexandria, where it was on display until Late Antiquity. Its current whereabouts are unknown.
The so-called "Alexander Sarcophagus," discovered near Sidon and now in the Instanbul Archaeological Museum, is now generally thought to be that of Abdylonymus, whom Hephaestion appointed as the king of Sidon by Alexander's order. The sarcophagus depicts Alexander and his companions hunting and in battle with the Persians.
Legacy and division of the Empire
Main article: Diadochi
After Alexander's death his empire was divided among his officers, first mostly with the pretense of preserving a united kingdom, later with the explicit formation of rival monarchies and territorial states.
Ultimately, the conflict was settled after the Battle of Ipsus in Phrygia in 301 BC. Alexander's empire was divided at first into four major portions: Cassander ruled in Greece, Lysimachus in Thrace, Seleucus I Nicator ("the winner") in Mesopotamia and Iran, and Ptolemy I in the Levant and Egypt. Antigonus I ruled for a while in Asia Minor and Syria, but was soon defeated by the other four generals. Control over Indian territory was short-lived, ending when Seleucus I was defeated by Chandragupta Maurya, the first Mauryan emperor.
By 270 BC, Hellenistic states consolidated, with:
- The Antigonid Empire, centered on Greece
- The Seleucid Empire in Asia
- The Ptolemaic kingdom in Egypt and Cyrenaica
By the 1st century BC though, most of the Hellenistic territories in the West had been absorbed by the Roman Republic. In the East, they had been dramatically reduced by the expansion of the Parthian Empire and the secession of the Greco-Bactrian kingdom.
Alexander's conquests also had long term cultural effects, with the flourishing of the Hellenistic civilization throughout the Middle-East and Central Asia, and the development of Greco-Buddhist art in the Indian subcontinent.
Timeline
Alexander's character
Modern opinion on Alexander has run the gamut from the idea that he believed he was on a divinely-inspired mission to unite the human race, to the view that he was the ancient world's equivalent of Napoleon I of France or Adolf Hitler, a megalomaniac bent on world domination. Such views tend to be anachronistic, however, and the sources allow a variety of interpretations. Much about Alexander's personality and aims remains enigmatic.
Alexander is remembered as a legendary hero in Europe and much of both Southwest Asia and Central Asia, where he is known as Iskander. To Zoroastrians, on the other hand, he is remembered as the destroyer of their first great empire and as the leveller of Persepolis. Ancient sources are generally written with an agenda of either glorifying or denigrating the man, making it difficult to evaluate his actual character. Most refer to a growing instability and megalomania in the years following Gaugamela, but it has been suggested that this simply reflects the Greek stereotype of a medizing king. The murder of his friend Cleitus, which Alexander deeply and immediately regretted, is often pointed to, as is his execution of Philotas and his general Parmenion for failure to pass along details of a plot against him, though this last may have been prudence rather than paranoia.
Modern Alexandrists continue to debate these same issues and others in modern times. One unresolved topic involves whether Alexander was actually attempting to better the world by his conquests, or whether his purpose was primarily to rule the world.
Partially in response to the ubiquity of positive portrayals of Alexander, an alternate character is sometimes presented which emphasizes some of Alexander's negative aspects. Some proponents of this view cite the destructions of Thebes, Tyre, Persepolis and Gaza as examples of atrocities, and argue that Alexander preferred to fight rather than negotiate. It is further claimed, in response to the view that Alexander was generally tolerant of the cultures of those whom he conquered, that his attempts at cultural fusion were severely practical and that he never actually admired Persian art or culture. To this way of thinking, Alexander was, first and foremost, a general rather than a statesman.
Alexander's character also suffers from the interpretation of historians who themselves are subject to the bias and idealisms of their own time. Good examples are W. W. Tarn, who wrote during the late 19th century and early 20th century, and who saw Alexander in an extremely good light, and Peter Green, who wrote after World War II and for whom Alexander did little that was not inherently selfish or ambition-driven. Tarn wrote in an age where world conquest and warrior-heroes were acceptable, even encouraged, whereas Green wrote with the backdrop of the Holocaust and nuclear weapons. As a result, Alexander's character is skewed depending on which way the historian's own culture is, and further muddles the debate of who he truly was.
Stories/Legends
According to one story, the philosopher Anaxarchus checked the vainglory of Alexander, when he aspired to the honours of divinity, by pointing to Alexander's wound, saying, "See the blood of a mortal, not the ichor of a god." In another version Alexander himself pointed out the difference in response to a sycophantic soldier.
Alexander had a legendary horse named Bucephalus (meaning "ox-headed"), supposedly descended from the Mares of Diomedes.
Ancient sources
The ancient sources for Alexander's life are, from the perspective of ancient history, relatively numerous. Alexander himself left only a few inscriptions and some letter-fragments of dubious authenticity, but a large number of his contemporaries wrote full accounts. These included his court historian Callisthenes, his general Ptolemy, and a camp engineer Aristoboulus. Another early and influential account was penned by Cleitarchus. Unfortunately, these works were lost. Instead, the modern historian must rely on authors who used these and other early sources.
The five main accounts are by Arrian, Curtius, Plutarch, Diodorus, and Justin.
- Anabasis Alexandri ("The Campaigns of Alexander" in Greek) by the Greek historian Arrian of Nicomedia;
- Historiae Alexandri Magni, a biography of Alexander in ten books, of which the last eight survive, by the Roman historian Quintus Curtius Rufus;
- Life of Alexander (see Parallel Lives) and two orations On the Fortune or the Virtue of Alexander the Great (see Plutarch#Other_Works), by the Greek historian and biographer Plutarch of Chaeronea;
- Bibliotheca historia ("Library of world history"), written in Greek by the Sicilian historian Diodorus Siculus, from which Book 17 relates the conquests of Alexander. The books immediately before and after, on Philip and Alexander's "Successors," throw light on Alexander's reign.
- The Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus by Junianus Justinus, which contains factual errors and is highly compressed.
Much is recounted incidentally in other authors, including Strabo, Athenaeus, Polyaenus, and others.
The "problem of the sources" is the main concern (and chief delight) of Alexander-historians. In effect, each presents a different "Alexander," with details to suit. Arrian presents a flattering portrait, Curtius a darker one. Plutarch can't resist a good story, light or dark. All include a considerable level of fantasy, prompting Strabo (2.1.9) to remark, "All who wrote about Alexander preferred the marvellous to the true." Nevertheless, the sources tell us much, and leave much to our interpretation and imagination.
Alexander's legend
Alexander was a legend in his own time. His court historian Callisthenes portrayed the sea in Cilicia as drawing back from him in proskynesis. Writing after Alexander's death, another participant, Onesicritus, went so far as to invent a tryst between Alexander and Thalestris, queen of the mythical Amazons. (When Onesicritus read this passage to his patron, Alexander's general and later King Lysimachus, Lysimachus quipped "I wonder where I was at the time.")
In the first centuries after Alexander's death, probably in Alexandria, a quantity of the more legendary material coalesced into a text known as the "Alexander Romance," later falsely ascribed to the historian Callisthenes and therefore known as Pseudo-Callisthenes. This text underwent numerous expansions and revisions throughout Antiquity and the Middle Ages, exhibiting a plasticity unseen in "higher" literary forms. Latin and Syriac translations were made in Late Antiquity. From these, versions were developed in all the major languages of Europe and the Middle East, including Armenian, Georgian, Persian, Arabic, Turkish, Hebrew, Serbian, Slavonic, Romanian, Hungarian, German, English, Italian, and French. The "Romance" is regarded by most Western scholars as the source of the account of Alexander given in the Koran (Sura "The Cave"). It is the source of many incidents in Ferdowsi's "Shahnama". A Mongol version is extant.
Some believe that, excepting certain religious texts, it is the most widely-read work of pre-modern times.
Alexander's legend in non-Western sources
Alexander was often identified in Persian and Arabic-language sources as "Dh?Qarnayn", Arabic for "The Horned One", probably a reference to the appearance of his hair on later coins. Islamic accounts of the Alexander legend, particularly in Persia combined the Pseudo-Callisthenes material with indigenous Sasanid Persian ideas about Alexander.
Pahlavi sources on the Alexander legend devised a mythical genealogy for him whereby his mother was a concubine of Darius II, making him the half-brother of the last Achaemenid shah, Darius III, probably in order to justify his domination of the old Persian Empire. Alexander is also blamed for ending the golden age of Zoroastrianism by seizing and destroying the original golden text of the Zend Avesta by throwing it into the sea.
Despite his supposed sins, by the Islamic period the adoption of Pseudo-Callisthenes' accounts meant that the image of Alexander was on balance positive. By the 12th century CE such important writers as Nezami Ganjavi were making him the subject of their epic poems, and holding him up as the model of the ideal statesman or philosopher-king, an idea adopted from the Greeks and elaborated on by Muslim philosophers like al-Farabi.
The traditional non-Western accounts differ from what we now know about the life of Alexander on a number of points. For example, he is held to be the companion of Aristotle and the direct student of Plato.
Main towns founded by Alexander
Around 70 towns or outposts are claimed to have been founded by Alexander. Some of the main ones are:
- Alexandria, Egypt
- Alexandria Asiana, Iran
- Alexandria in Ariana, Afghanistan
- Alexandria of the Caucasus, Afghanistan
- Alexandria on the Oxus, Afghanistan
- Alexandria of the Arachosians, Afghanistan
- Alexandria on the Indus, Pakistan
- Alexandria Eschate, "The furthest", Tajikistan
- Kandahar (Alexandropolis), Afghanistan
Alexander in popular media
- A 1956 movie starring Richard Burton titled Alexander the Great was produced by MGM
- Oliver Stone's film Alexander, starring Colin Farrell, was released on November 24, 2004.
- Baz Luhrmann had been planning to make a very different film about Alexander, starring Leonardo DiCaprio, but the release of Stone's film eventually persuaded him to abandon the project. [2] (http://www.imdb.com/news/wenn/2004-11-01#2)
- Numerous television series about Alexander have been created.
- The British heavy metal band Iron Maiden had a song entitled "Alexander the Great" on their album Somewhere in Time (1986). The song describes Alexander's life, but contains one inaccuracy: in the song it is stated that Alexander's army would not follow him into India.
- Brazilian musician Caetano Veloso's 1998 album Livro includes an epic song about Alexander called "Alexandre."
- From 1969 to 1981, Mary Renault wrote a historical fiction trilogy, speculating on the life of Alexander: Fire from Heaven (about his early life), The Persian Boy (about his conquest of Persia, his expedition to India, and his death, seen from the viewpoint of a Persian eunuch), and Funeral Games (about the events following his death).
- A further trilogy of novels about Alexander was written in Italian by Valerio Massimo Manfredi and subsequently published in an English translation, entitled The Son of the Dream, The Sands of Ammon and The Ends Of The Earth.
- Steven Pressfield's 2004 book The Virtues of War is told from the first-person perspective of Alexander.
- An epic sci-fi animated retelling of the story called Reign: The Conquerer by Peter Chung of Aeon Flux fame debuted on the Cartoon Network's Adult Swim block variety show in 2003.
External links
Primary Sources
- Alexander the Great: An annotated list of primary sources (http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander_z1b.html) from Livius.org
- Wiki Classical Dictionary, extant sources (http://www.ancientlibrary.com/wcd/Alexander_the_Great%2C_extant_sources) and fragmentary and lost sources (http://www.ancientlibrary.com/wcd/Alexander_the_Great%2C_Fragmentary_and_lost_sources)
- Plutarch, Life of Alexander (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Plutarch/Lives/Alexander*/home.html) (in English)
- Justin, Epitome of the Philippic History of Pompeius Trogus (http://www.forumromanum.org/literature/justin/english/index.html) (in English)
- Plutarch, Of the Fortune or Virtue of Alexander the Great (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Plutarch/Moralia/Fortuna_Alexandri*/home.html) (in English)
- Quintus Curtius Rufus, Histories of Alexander (http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Curtius/home.html) (in Latin)
Projects
- Alexander the Great on the Web (http://www.isidore-of-seville.com/Alexanderama.html), a comprehensive directory of some 1,000 sites
- Livius Project (http://www.livius.org/aj-al/alexander/alexander00.html) articles on Alexander by Jona Lendering
- Pothos.org: Alexander's Home on the Web (http://www.pothos.org)
- Wiki Classical Dictionary: Category Alexander the Great (http://www.ancientlibrary.com/wcd/Category:Alexander_the_Great), a Mediawiki based project, with stricter guidelines and editors
Narratives
- Alexander the Great of Macedon (http://www.1stmuse.com/frames/), a project by John J. Popovic
- The loves of Alexander III of Macedon (http://www.androphile.org/preview/Library/Biographies/Alexander/Alexander.htm)
Discussion
- Pothos Forum (http://www.pothos.org/forum)
Bibliography
- PDF: A Bibliography of Alexander the Great (http://hum.ucalgary.ca/wheckel/bibl/alex-bibl.pdf) by Waldemar Heckel