Spinal cord
|
|
The spinal cord is a part of the vertebrate nervous system that is enclosed in and protected by the vertebral column (it passes through the spinal canal). It consists of nerve cells. The cord conveys the 31 spinal nerve pairs of the peripheral nervous system, as well as central nervous system pathways that innervate skeletal muscles.
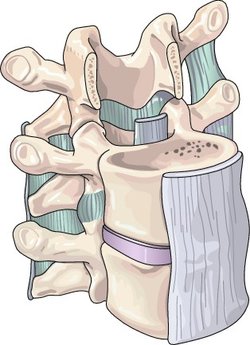
The vertebral column consists of vertebrae described as belonging to 5 groups (called segments). These segments are (in order from top to bottom): the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, and the sacrum and coccyx.
| Contents |
Embryology
In the human fetus, the spinal cord extends all the way down to the sacral vertebrae. As a person matures, the spinal cord shortens relative to the rest of the body, so at adulthood, the spinal cord only reaches down to around the level of L1 (the first, i.e. highest, lumbar vertebra), where it terminates and the cauda equina begin - this is why lumbar punctures are usually carried out on an adult at the (lower) level of L3/L4.
Anatomy
The spinal cord originates inside the brain at the inferior end of the medulla oblongata, exiting the skull via the foramen magnum. It is wrapped in three layers of membranes, called meninges.
The spinal cord carries sensory signals and motor innervation to most of the skeletal muscles in the body. Just about every voluntary muscle in the body below the head depends on the spinal cord for control. Similarly, most cutaneous sensation below the neck is transmitted via the spinal cord. Most of the sympathetic pathways and the lower (i.e. non-vagal) parasympathetic pathways also go through the spinal cord.
A cross-section through the spinal cord reveals that there is a central canal (carrying cerebrospinal fluid - CSF) surrounded by grey matter on the inside, and this is surrounded by white matter. (This is the opposite to the brain's cerebral cortex.) A section of the cord can be divided into neat symmeterical halves by the dorsal median sulcus and ventral median fissure.
The dorsal (towards the back) side of the spinal cord carries sensory information. The neurons that bring somatosensory information to the spinal cord reside in the dorsal root ganglion. Sensation from the lower body travels up the gracile tract, sensation from the upper body and arms travels up the cuneate tract, which lies lateral to the gracile tract. There is no cuneate tract in the lumbar part of the spinal cord as sensory information from the arms would not travel through this area.
Motor information (signals coming from the brain to move the muscles) travels down the ventral (close to the belly) half of the spinal cord. Motor neurons are located in the anterior (this means close to the front, in humans it means the same as ventral) horn of the grey matter. There are two main columns of neurons in the anterior horn, the medial and lateral motor columns.
The actual cord is approxiamately cylindrical in shape, but the diameter varies at different vetebral levels. There are two enlargements, cervical and lumbar. The cervical enlargement is due to the cord segments from C3 to T1 which innervates the upper limb via the brachial plexus. The lumbar enlargement arise from segments L1 to S3 and innervates the lower limbs via the lumbar and sacral plexuses.
The spinal cord proper ends at the level of L1. It terminates at a conical point known as the conus medullaris, from which a strand of connective tissue, the filum terminale extends caudally and attaches to the dorsal surface of the first cocygeal vertebra.
There is a higher proportion of white matter in the cervical (neck) part of the spinal cord. This is because it information to and from the whole body (such as the feet) must pass through here. In contrast, the lumbar and sacral areas do not carry information from anywhere above them, so have less white matter.
Pathology
- Damage in the spinal cord, called myelopathy, can result in paraplegia or quadriplegia, depending on the level within the spinal cord of the damage.
- spinal tumor
- syringomyelia
Anatomy Clipart and Pictures
- Clip Art (https://classroomclipart.com)
- Anatomy Illustrations (https://classroomclipart.com/clipart/Illustrations/Anatomy.htm)
- Anatomy Clipart (https://classroomclipart.com/clipart/Anatomy.htm)
- Anatomy Animations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Animations/Anatomy)