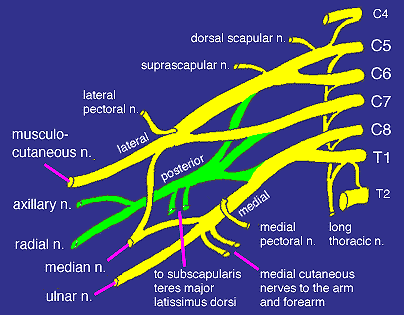
Brachial plexus
|
|
The brachial plexus is an arrangement of nerve fibres (a plexus) running from the spine (vertebrae C5-T1), through the neck, the axilla (armpit region), and into the arm. All nerves of the arm stem from the brachial plexus (with the exception of the intercostobrachialis nerve which supplies an area of skin near the axilla). Therefore, lesions of the plexus can lead to severe functional impairment.
The brachial plexus starts from the five ventral rami of the spinal nerves, these are the five roots. These roots merge to form three trunks.
Each trunk then splits to form an anterior and a posterior division. These six divisions will regroup to become the cords. The cords are named by their position in respect to the axillary artery.
- The posterior cord is formed from the three posterior divisions of the trunks.
- The lateral cord is the anterior divisions from the upper and middle trunks.
- The medial cord is simply a continuation of the lower trunk.
From the cords come the nerves of the arm.
- The axillary nerve is a branch off the posterior cord, the rest of the cord becomes the radial nerve.
- Branches from the lateral and medial cord merge to form the median nerve.
- The musculocutaneous nerve is formed from the rest of the lateral cord.
- The ulnar nerve arises from the rest of the medial cord.de:Plexus brachialis
Anesthesia of the Brachial Plexus<P> The fact that the nerves of the brachial plexus are grouped together acts as a benefit as well. Local anesthetics such as lidocaine or bupivacaine can be injected in close proximity to these nerves, rendering an entire arm insensate and immobile. The process of injecting local anesthetic for this purpose is called regional nerve blockade or more simply, a nerve block, and it is a common procedure in anesthesia. After an onset time of approximately 10 to 15 minutes, the targeted arm will be fully anesthetized and ready for surgery. The patient can remain awake during the ensuing surgical procedure, or he can be sedated with medications or fully anesthetized with general anesthesia as the situation requires. The use of peripheral nerve blockade (in this case, a "brachial plexus nerve block") offers several advantages when compared to general anesthesia or local anesthesia:
- The patient can remain awake and breathing on their own, thus protecting themselves from aspiration of stomach contents into the lungs. By avoiding general anesthesia, patients with adverse reactions to general anesthetics (viz. malignant hyperthermia, severe post-operative nausea and vomiting, known hypersensitivity to agents) can be successfully treated. Similarly, patients who experience nuisance side effects from general anesthesia such as nausea, vomiting, or excessive sleepiness can minimize these symptoms.
- There is no need to perform an endotracheal intubation, the procedure of inserting a breathing tube into the trachea. Occasionally, such intubation is unexpectedly difficult to perform, causing injury to the patient.
- The affected limb's sympathetic nerves are anesthetized, leading to vasodilation. This improves blood flow to the affected limb and makes microvascular surgical procedures technically simpler.
- The limb can remain numb for several hours after surgery, providing excellent pain relief.
- Deep and superficial structures of the limb are similarly anesthetized, allowing extensive surgical exploration and correction to occur. This is in contrast to locally injected local anesthetics, which tend only to numb superficial structures in the immediate vicinity of the injection.
- Surgery is expected to be limited either to a region between the midpoint of the humerus and the fingers (in which case the brachial plexus block should be either a supra-clavicular, infra-clavicular, subcoracoid, or axillary block), OR surgery is expected to be limited to a region between the midpoint of the humerus and the shoulder (in which case the brachial plexus block should be an interscalene block). Because of the distribution of the local anesthetics on the various portions of the brachial plexus, surgeries crossing the midpoint of the humerus often reveal patchy, unanesthetized portions of the arm. Such procedures probably should not be performed under regional nerve block alone.
- There are no contra-indications to a block such as infection at the intended injection site, significant anti-coagulation, allergy or hypersensitivity to local anesthetic medications, or disproportionate risk in the event of a local anesthetic toxic reaction (seizure) such as gastric aspiration in a patient who has not adequately fasted,
- There will not be a need to perform a neurologic exam immediately following the surgical procedure,
- Patient prefers this technique over other available and reasonable approaches.