Phi (letter)
|
|
| Greek alphabet | |
|---|---|
| Α α Alpha | Β β Beta |
| Γ γ Gamma | Δ δ Delta |
| Ε ε Epsilon | Ζ ζ Zeta |
| Η η Eta | Θ θ Theta |
| Ι ι Iota | Κ κ Kappa |
| Λ λ Lambda | Μ μ Mu |
| Ν ν Nu | Ξ ξ Xi |
| Ο ο Omicron | Π π Pi |
| Ρ ρ Rho | Σ σ Sigma |
| Τ τ Tau | Υ υ Upsilon |
| Φ φ Phi | Χ χ Chi |
| Ψ ψ Psi | Ω ω Omega |
| obsolete letters | |
| [[Digamma|Template:Polytonic Digamma]] | [[San (letter)|Template:Polytonic San]] |
| [[Qoppa|Template:Polytonic Qoppa]] | [[Sampi|Template:Polytonic Sampi]] |
Phi (upper case Φ, lower case φ or ϕ), pronounced fee or fie (depending on context and, often, personal inclination), is the 21st letter of the Greek alphabet. It is pronounced fee by modern Greeks. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 500.
The lower-case letter φ (or often its variant, ϕ) is used as a symbol for:
- The golden ratio 1.618... in mathematics, art, and architecture.
- Euler's totient function in number theory.
- The argument of a complex number in mathematics.
- The value of a plane angle in physics and mathematics.
- The work function in electronics.
- The phase of a wave in signal processing.
- In spherical coordinates phi is usually used to represent the angle to the z axis.
- In engineering, the diameter symbol
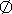 is often referred to as "phi". This symbol is used to indicate the diameter of a circular section, for example
is often referred to as "phi". This symbol is used to indicate the diameter of a circular section, for example  14 means the diameter of the circle is 14 inches or millimeters, depending on the context.
14 means the diameter of the circle is 14 inches or millimeters, depending on the context.
- Any function in mathematics.
The upper-case letter Φ is used as a symbol for:
- The magnetic flux in physics.
See also phi phenomenon. Template:Wiktionaryparda:Phi de:Phi el:Φι es:Fi fr:Φ ja:Φ nl:Phi (letter) pl:Fi pt:Φ fi:Fii zh:Φ
