Paraguay
|
|
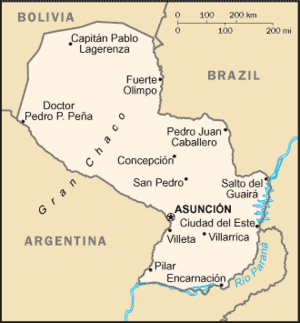
The Republic of Paraguay is a landlocked republic in South America. Lying on both banks of the Paraguay River, it borders Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the northeast and Bolivia to the northwest. The name "Paraguay" is derived from the Guarani words "parᦱuot;, meaning "this side" and "guay", meaning "river". The expression in Guarani is thought to refer solely to Asuncibut in Spanish refers to the entire country.
| ||||
| National motto: Paz y justicia (Spanish: Peace and justice)</font> | ||||
| ||||
| Official languages | Spanish and Guarani | |||
| Capital | [[Asunci | |||
| President | Nicanor Duarte Frutos | |||
| Area - Total - % water | Ranked 58th 406,750 km² 2.3% | |||
| Population - Total (07/2004) - Density | Ranked 100th 6,191,368 15/km² | |||
| Independence - Date | From Spain May 15, 1811 | |||
| Currency | [[Guaran�currency)|Guaran흝 | |||
| Time zone | UTC -4 | |||
| National anthem | Paraguayos, Rep?a o Muerte | |||
| Internet TLD | .py | |||
| Calling code | 595 | |||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of Paraguay
Europeans first arrived in the area in the early 16th century and the settlement of [[Asunci was founded in 1537. The city eventually became the centre of a Spanish colonial province, as well as a primary site of the Jesuit missions and settlements in South America in the 18th century. Paraguay declared its independence by overthrowing the local Spanish authorities on May 15, 1811.
In the disastrous War of the Triple Alliance (1865-1870), Paraguay lost two-thirds of all adult males and much of its territory. It stagnated economically for the next half century. In the Chaco War of 1932-1935 invading Bolivian troops, trying to gain a port on the Paraguay river for their landlocked country, were expelled by the Paraguayan Armed Forces from most of the Chaco region. The Chaco had been claimed by both countries, but the settlements in the region were mostly Paraguayan. The 35-year military dictatorship of Alfredo Stroessner was overthrown in 1989, and, despite a marked increase in political infighting in recent years, relatively free and regular presidential elections have been held since then. However, the democracy that exists in the country, while a great improvement on the 'stronato' is very limited. It is hampered by the widespread corruption and lack of any democratic political culture.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Paraguay
Paraguay's highly centralised and often dictatorial government was fundamentally changed by the 1992 constitution, which provides for a division of powers. The president and vice president are elected on the same ticket by popular vote for five-year terms, after which the president appoints a cabinet. The president functions as both head of state and head of government.
The bicameral parliament, the Congress or Congreso, consists of an 80-member Chamber of Deputies (C᭡ra de Diputados) and a 45-member Senate (C᭡ra de Senadores), elected concurrently with the president through a proportional representation system. Deputies are elected by department and senators nationwide on a list system, both for five-year terms. Each of Paraguay's 17 departments is headed by a popularly elected governor.
Paraguay's highest court is the Supreme Court. The Senate and the president select its nine members on the basis of recommendations from a constitutionally created Magistrates Council. A Paraguayan peculiarity is its flag, which features a slightly different design on the reverse side than on the front. The three stripes on the flag (red, white, and blue) come from the French flag. The front side contains the National Seal of Paraguay and the reverse contains the words "Paz y Justicia"(Peace and Justice) along with a lion and a Phyrgian Cap on a pole.
Departments
Main article: Departments of Paraguay
Paraguay consists of 18 departments (departamentos, singular - departamento):
- Alto Paraguay
- [[Alto Paran
- Amambay
- [[Asunciepartment|Asunci
- [[Boquer
- [[Caaguaz?artment|Caaguaz? [[Caazap᠄epartment|Caazap
- [[Canindey? Central
- [[Concepciepartment|Concepci
- Cordillera
- [[Guair
- [[Itap?* Misiones
- [[ѥembuc? [[Paraguar�epartment|Paraguar흝
- Presidente Hayes
- San Pedro
The (Gran) Chaco features mostly low, marshy plains near the river and dry forest and thorny scrub further west. The highest point is the Cerro Pero (Cerro Tres Kandu) at 842 m. The southeastern border is formed by the Parana River, containing the impressive Itaipu dam it shares with Brazil. It is currently the largest hydroelectric power plant in the world, generating nearly all of Paraguay's electricity.
The local climate ranges from subtropical to temperate, with substantial rainfall in the eastern portions, though becoming semi-arid in the far west.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Paraguay
Economy
Main article: Economy of Paraguay
Paraguay has a market economy marked by a large informal sector. The informal sector features both re-export of imported consumer goods to neighbouring countries as well as the activities of thousands of microenterprises and urban street vendors. Because of the importance of the informal sector, accurate economic measures are difficult to obtain. A large percentage of the population derive their living from agricultural activity, often on a subsistence basis.
Paraguay's economy is very dependent on Brazil, its neighbour in the east. Most of the country's imports come through the Brazilian port of [[Paranagu by railway. Ciudad del Este is the third largest free-tax commerce zone of the world, only behind Hong Kong and Miami. The country holds the impressive Itaipu dam which used to be the largest concrete structure, the largest dam and the largest power plant of the world. Itaipu's energy supplies about 20% of the current Brazilian needs and is the most important export good of Paraguay. The selling of cheaper goods is another important source of revenue and it is still a common habit in Brazil to go to Paraguay and buy electronics, like TV sets and sound systems there. About 60% of the country's GDP comes from commerce with Brazil. Nearly all the rest comes from commerce with Argentina with which the country shares another major power plant: [[Yaciret.
The formal economy grew by an average of about 3% annually in 1995-1997, but its GDP declined slightly in 1998, 1999, and 2000. Despite difficulties arising from political instability, corruption, slow structural reforms, high internal and external debts and deficient infrastructure; it is believed that the factor that most contributed to the stagnation of Paraguayan economy was the devaluation of the Brazilian currency, the Real, in 1998; which caused Paraguayan shops to lose their attractiveness (as prices there are mostly dollarised).
Since 1995 Paraguay has been a member of the free trade bloc MERCOSUR.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Paraguay
Ethnically, culturally, and socially, Paraguay has one of the most homogeneous populations in Latin America. About 95% of the people are mestizos of mixed Spanish and Guarani Indian descent. Little trace is left of the original Guarani culture except the language, which is understood by 90% of the population. About 75% of all Paraguayans speak Spanish. Guarani and Spanish are official languages. Germans, Japanese, Koreans, ethnic Chinese, Arabs, Brazilians, and Argentines are among those who have settled in Paraguay and they have to an extent retained their respective languages.
Paraguay's population is distributed unevenly throughout the country. The vast majority of the people live in the eastern region, most within 160 kilometers of [[Asunci, the capital and largest city. The Chaco, which accounts for about 60% of the territory, is home to less than 2% of the population. The country is predominantly Roman Catholic, with some Mennonite and other Protestant minorities.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Paraguay
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Paraguay
- Transportation in Paraguay
- Military of Paraguay
- Foreign relations of Paraguay
- Public holidays in Paraguay
- Reporters without borders World-wide press freedom index 2002: Rank 32 out of 139 countries
External links
- Portal del Gobierno Electro (http://www.paraguaygobierno.gov.py/) - Official governmental portal
- Recipes for Chipas (http://laca.com.au/telelatina/chipas.html), a cheese and cornmeal bread
- The American School of Asuncion (http://www.asa.edu.py/)
- Living in Paraguay (http://www.thowra.com/paraguay.html) A point of view: Asuncion and Paraguay
- Paraguay de Antes (http://www.meucat.com/album.html) Old pictures and postcards from Paraguay
| Countries in South America |
|---|
| Argentina | Bolivia | Brazil | Chile | Colombia | Ecuador | Guyana | Panama | Paraguay | Peru | Suriname | Trinidad and Tobago | Uruguay | Venezuela |
| Dependencies: Falkland Islands | French Guiana |