Inductor
|
|
An inductor is a passive electrical device that stores energy in a magnetic field, typically by combining the effects of many loops of electric current.
| Contents |
Physics of the inductor
Construction
An inductor is usually constructed as a coil of conducting material, typically copper wire. A core of ferrous material is sometimes used, which increases the inductance. Inductors can also be built on integrated circuits using the same processes that are used to make computer chips. In these cases, aluminum is typically used as the conducting material. However, it is rare that actual inductors are built on ICs; they are bulky on a small scale, and practical constraints make it far more common to use a circuit called a "gyrator" which uses a capacitor to behave as if it were an inductor.
Smaller inductors used for very high frequencies are sometimes made with a wire passing through a ferrite cylinder or bead.
Inductance
Inductance is a physical characteristic of an inductor. See inductance.
Energy
The energy (measured in joules, in SI) stored in an inductor is equal to the amount of work required to establish the current flowing through the inductor, and therefore the magnetic field. This is given by:
- <math> E_\mathrm{stored} = {1 \over 2} L I^2 <math>
where I is the current flowing through the inductor.
In electric circuits
An inductor only resists changes in current. An ideal inductor does not offer any resistance to direct current, except when the current is switched on and off, in which case it makes the change more gradual. However, all real-world inductors are constructed from material with finite electrical resistance, which opposes even direct current.
In general, the relationship between the time-varying voltage v(t) across an inductor with inductance L and the time-varying current i(t) passing through it is described by the differential equation
- <math>v(t) = L \frac{di(t)}{dt}<math>
When a sinusoidal alternating current (AC) flows through an inductor, a sinusoidal alternating voltage (or electromotive force, abbr. emf) is induced. The amplitude of the emf is related to the amplitude of the current and to the frequency of the sinusoid by the following equation.
- <math>V = I \times \omega L<math>
where ω is the angular frequency of the sinusoid defined in terms of the frequency f as
- <math>\omega = 2 \pi f\,<math>
Inductive reactance is defined as:
- <math> X_L = \omega L = 2 \pi f L\, <math>
where XL is the inductive reactance, ω is the angular frequency, f is the frequency in Hertz, and L is the inductance.
Inductive reactance is the positive imaginary component of impedance.
The complex impedance of an inductor is then given by:
- <math> Z = j \omega L = j 2 \pi f L\ = j X_L, <math>
where j is the imaginary unit.
Inductor networks
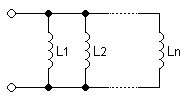
Inductors in a parallel configuration each have the same potential difference (voltage). To find their total equivalent inductance (Leq):
- <math> \frac{1}{L_\mathrm{eq}} = \frac{1}{L_1} + \frac{1}{L_2} + \cdots + \frac{1}{L_n}<math>
The current through inductors in series stays the same, but the voltage across each inductor can be different. The sum of the potential differences (voltage) is equal to the total voltage. To find their total inductance:
- Missing image
Inductorsseries.png
A diagram of several inductors, connected end to end, with the same amount of current going through each
- <math> L_\mathrm{eq} = L_1 + L_2 + \cdots + L_n \,\! <math>
Q Factor
The quality factor of an inductor can be found through this formula, where R is its internal electrical resistance
- <math>
Q = \frac{\omega{}L}{R} <math>
Applications
Inductors are closely related to electromagnets in structure, but used for a different purpose: to store energy in a magnetic field.
Because of their ability to alter AC signals, inductors are used extensively in analog circuits and signal processing, including radio reception and broadcasting. As the inductive reactance <math>X_L<math> changes with frequency, an electronic filter can use inductors in conjunction with capacitors and other components to filter out specific parts of the frequency spectrum.
Two (or more) coupled inductors form a transformer, which is a fundamental component of every national power grid.
An inductor is typically used at the output of a switching regulator power supply. The inductor is charged for a specific fraction of the regulator's switching frequency, and discharged for the remainder of the cycle. This charge/discharge ratio is what drops (or boosts) the input voltage to its new level.
Inductors are also employed in electrical transmission systems, where they are used to intentionally depress system voltages. In this field, they are more commonly referred to as reactors.
See also
- Capacitor
- Resistor
- Electricity
- Electronics
- Gyrator
- Inductance (including Mutual Inductance)
- Induction loop
- Saturable reactor
- Transformer
Synonyms
da:Elektrisk spole de:Spule (Elektrotechnik) es:Inductor fr:Self id:Induktor it:Induttore nl:Spoel ja:インダクタンス pl:Cewka fi:Kela (laite) sv:Spole