Coil
|
|
| Contents |
General applications
Ressort_de_compression.jpg
A coil is made of rigid materials which can fashioned into a spiral or helical shape. Flexible materials like wire, rope, hose, or cable can also be coiled into empty loops, or wound around a central drum or spindle.
Some common applications of coils include:
- A coil spring is the most common type of spring.
- A set of stairs fashioned in a coil shape, which are called spiral staircases.
- A Slinky is a coil-shaped toy.
- A coil stamp is a type of postage stamp sold as strips one stamp wide.
- A boiler coil is an element in a water heater.
- Evaporator coils are used in air conditioning and other refrigeration cycles.
- Coil is a colloquial term applied to contraceptive intrauterine devices.
See also: list of coil knots
Electromagnetic
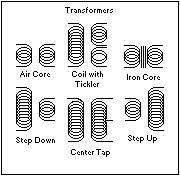
In electrical engineering, a electromagnetic coil is formed when a metallic or conductive wire is looped around a core to create an electronic inductor or electromagnet. A transformer coil has a primary coil and a secondary coil that transfers energy from one electrical circuit to another by magnetic coupling without moving parts. An extra coil (sometimes referred to as a tickler coil) is usually a third coil placed in relation to a primary coil and secondary coil.
Some common electromagnetic coils include:
- A bifilar coil is a coil that uses the effect of mutual relation self-induction.
- A Barker coil is used in low field NMR imaging.
- A Braunbeck coil is used in geomagnetic research.
- A degaussing coil is used in the process of removing permanent magnetism (magnetic hysteresis) from an object.
- A Garrett coil is used in metal detectors.
- A Helmholtz coil is a device for producing a region of nearly uniform magnetic field.
- A hybrid coil (or bridge transformer) is a single transformer that effectively has three windings.
- An induction coil (or ignition coil) is an electrical device in common use as the ignition system (ignition coil or spark coil) of internal-combustion engines.
- A loading coil is, in electronics, a coil (inductor) inserted in a circuit to increase its inductance. Archaically called Pupin coils.
- A multiple coil magnet is an electromagnet that has several coils of wire connected in parallel.
- A Maxwell coil is a device for producing almost a constant magnetic field.
- A Oudin coil is a disruptive discharge coil.
- The polyphase coils are connected together in a polyphase system such as a generator or motor.
- A relay coil is the copper winding part of a relay that produces a magnetic field that actuates the mechanism.
- A Rogowski coil is an electrical device for measuring alternating current.
- A single coil is a type of pickup for the electric guitar.
- A solenoid is a mechanical device, based around a coil of wire, that converts energy into linear motion.
- A Tesla coil is category of disruptive discharge coils, usually denoting a resonant transformer that generates very high voltages at radio frequencies.
- A voice coil which is mounted to the moving cone of a loudspeaker.
Further reading
- Querfurth, William, "Coil winding; a description of coil winding procedures, winding machines and associated equipment for the electronic industry" (2d ed.). Chicago, G. Stevens Mfg. Co., 1958.
- Weymouth, F. Marten, "Drum armatures and commutators (theory and practice) : a complete treatise on the theory and construction of drum winding, and of commutators for closed-coil armatures, together with a full résumé of some of the principal points involved in their design; and an exposition of armature reactions and sparking". London, "The Electrician" Printing and Publishing Co., 1893.
- "Coil winding proceedings". International Coil Winding Association.
- Chandler, R. H., "Coil coating review, 1970-76". Braintree, R. H. Chandler Ltd, 1977.
Chemistry
In the study of how molecules interact with each other, there are a few specific references to organic coils. During self-assembly, organic elements organize to form this structural pattern. Molecular self-assembly assembles the molecules, without guidance or management from an outside source, into these shapes.
Examples of these structural patterns include:
- A coiled coil is a structural motif found in many proteins.
- The DNA coil is a nucleic acid structure that contains the genetic instructions specifying the biological development of all cellular forms of life (and many viruses).
- A random coil is a polymer conformation where the monomers are arranged at random.
- The RNA coil is a nucleic acid structure consisting of a string of covalently-bound nucleotides.
As an acronym, COIL denotes the Chemical Oxygen Iodine Laser.
Other uses
Musician names
"Coil" is, or is part of, the name for some musicians or their albums.
Name
- Coil is a British experimental band.
- Icon of Coil is a Norwegian electronic body music band.
- Lacuna Coil is an Italian goth heavy metal band.
- This Mortal Coil is a British dark cover band.
Publication
- Coil is a 1997 album by American band Toad the Wet Sprocket.