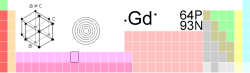
Gadolinium
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name, Symbol, Number | Gadolinium, Gd, 64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical series | Lanthanides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group, Period, Block | _ , 6, f | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density, Hardness | 7901 kg/m3, no data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | silvery white Missing image Gd,64.jpg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic weight | 157.25(3) amu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic radius (calc.) | 188 (233) pm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | no data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| van der Waals radius | no data | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Xe]6s25d14f7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| e-s per energy level | 2, 8, 18, 25, 9, 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states (Oxide) | 3 (mildly basic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State of matter | solid (ferromagnetic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 1585 K (2394 ?F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 3523 K (5882 ?F) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar volume | 19.90 ×10-6 m3/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 359.4 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 10.05 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure | 24400 Pa at 1585 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Velocity of sound | 2680 m/s at 293.15 K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | 1.20 (Pauling scale) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specific heat capacity | 230 J/(kg*K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical conductivity | 0.736 106/m ohm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 10.6 W/(m*K) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1st ionization potential | 593.4 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2nd ionization potential | 1170 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3rd ionization potential | 1990 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4th ionization potential | 4250 kJ/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Most stable isotopes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI units & STP are used except where noted. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gadolinium is a chemical element in the periodic table that has the symbol Gd and atomic number 64.
| Contents |
Notable characteristics
Gadolinium is a silvery white, malleable and ductile rare earth metal with a metallic luster. It crystallizes in hexagonal, close-packed alpha form at room temperature; when heated to 1508 K, it transforms into its beta form, which has a body-centered cubic structure.
Unlike other rare earth elements, gadolinium is relatively stable in dry air; however, it tarnishes quickly in moist air and forms a loosely adhering oxide that spalls off and exposes more surface to oxidation. Gadolinium reacts slowly with water and is soluble in dilute acid.
Gadolinium has the highest thermal neutron capture cross-section of any (known) element, 49,000 barns, but it also has a fast burn-out rate, limiting its usefulness as a nuclear control rod material.
Gadolinium becomes superconductive below a critical temperature of 1.083 K. It is strongly magnetic at room temperature, and is in fact the only metal to exhibit ferromagnetic properties except for fourth period transition metals.
Applications
Gadolinium is used for making gadolinium yttrium garnets, which have microwave applications; gadolinium compounds also are used for making phosphors for colour TV tubes, and solutions of compounds are used as intravenous contrast to enhance images in patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Gadolinium is also used for manufacturing compact discs and computer memory. Gadolinium is also used as a secondary, emergency shut-down measure in some nuclear reactors, particularly of the CANDU type.
Gadolinium also possesses unusual metallurgic properties, with as little as 1% of gadolinium improving the workability and resistance of iron, chromium and related alloys to high temperatures and oxidation.
In the future, gadolinium ethyl sulfate, which has extremely low noise characteristics, may be used in masers. Furthermore, gadolinium's high magnetic movement and low Curie temperature (which lies just at room temperature) suggest applications as a magnetic component for sensing hot and cold.
History
In 1880, Swiss chemist Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac observed spectroscopic lines due to gadolinium in samples of didymium and gadolinite; French chemist Paul Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran separated gadolinia, the oxide of Gadolinium, from Mosander's yttria in 1886. The element itself was isolated only recently for the first time.
Gadolinium, like the mineral gadolinite, is named after Finnish chemist and geologist Johan Gadolin.
Biological role
Gadolinium has no known biological role, but is said to stimulate the metabolism.
Occurrence
Gadolinium is never found in nature as the free element, but is contained in many minerals such as gadolinite, monazite and bastnasite. Today, it is prepared by ion exchange and solvent extraction technique, or by the reduction of its anhydrous fluoride with metallic Calcium.
Compounds
Compounds of gadolinium include:
Isotopes
Naturally occurring gadolinium is composed of 5 stable isotopes, 154-Gd, 155-Gd, 156-Gd, 157-Gd and 158-Gd, and 2 radioisotopes, 152-Gd and 160-Gd, with 158-Gd being the most abundant (24.84% natural abundance). 30 radioisotopes have been characterized with the most stable being 160-Gd with a half-life of 1.3E+21 years, 152-Gd with a half-life of 1.08E+14 years, and 150-Gd with a half-life of 1.79E+6 years. All of the remaining radioactive isotopes have half-lifes that are less than 74.7 years, and the majority of these have half lifes that are less than 24.6 seconds. This element also has 4 meta states with the most stable being 143m-Gd (t? 110 seconds), 145m-Gd (t? 85 seconds) and 141m-Gd (t? 24.5).
The primary decay mode before the most abundant stable isotope, 158-Gd, is electron capture and the primary mode after is beta minus decay. The primary decay products before 158-Gd are element Eu (Europium) isotopes and the primary products after are element Tb (Terbium) isotopes.
Precautions
As with the other lanthanides, gadolinium compounds are of low to moderate toxicity, although their toxicity has not been investigated in detail.
References
- Los Alamos National Laboratory – Gadolinium (http://periodic.lanl.gov/elements/64.html)
External links
- WebElements.com – Gadolinium (http://www.webelements.com/webelements/elements/text/Gd/index.html)
- EnvironmentalChemistry.com – Gadolinium (http://environmentalchemistry.com/yogi/periodic/Gd.html)
- It's Elemental – Gadolinium (http://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele064.html)