Falkland Islands
|
|
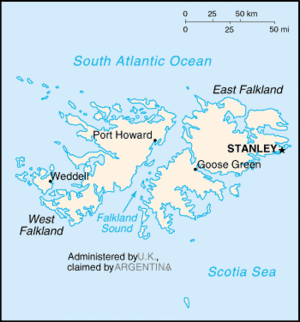
The Falkland Islands are an archipelago in the South Atlantic consisting of two main islands, East Falkland and West Falkland, and a number of smaller islands. They are administered as a largely self-governing overseas territory of the United Kingdom (UK) from Port Stanley, the capital and largest city, on East Falkland. Argentina, however, claims the islands, calling them by their Spanish name, Islas Malvinas (and the derived Malvinas Islands in English) and considers them part of the Tierra del Fuego Province.
Argentina invaded the islands in 1982, leading to the Falklands War in which they were retaken by the UK. The Argentines accuse the British of colonialism and emphasise decolonisation, whereas the British emphasise the right of the islanders, who consider themselves to be British, to self-determination. Although still a touchy diplomatic issue, international relations have improved in recent years.
The United Nations Committee on Decolonization includes the Falkland Islands on the United Nations list of Non-Self-Governing Territories.
| |||||
| Motto: Desire the right | |||||
| |||||
| Official language | English | ||||
| Capital | Port Stanley | ||||
| Governor | Howard Pearce | ||||
| Chief Executive | Chris Simpkins | ||||
| Area - Total - % water | not ranked 12,173 km² - | ||||
| Population - Total (2003 E) - Density | not ranked 2,967 0.24/km² | ||||
| Currency | Falkland pound (FKP; fixed to GBP) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC -4 (DST -3) | ||||
| National anthem | God Save the Queen | ||||
| Internet TLD | .fk | ||||
| Calling Code | 500 | ||||
| Contents |
History
Main article: History of the Falkland Islands
The Dutch sailor Sebald de Weert is usually credited with first sighting the Falklands in 1600, though both the British and Spanish maintain their own explorers discovered the islands earlier. Some older maps, particularly Dutch ones, used the name 'Sebald Islands' for a while. The history of exploration is as follows:
- 1504: Amerigo Vespucci (Florence/Spain)
- 1540: Ferdinand Camargo (Spain)
- 1592: John Davis (England)
- 1593: Richard Hawkins (England)
- 1600: Sebald de Weert (Netherlands)
- 1684: Cowley & Dampier (England) discovered Pepys Island, renamed South Georgia by James Cook in 1775.
- 1690: John Strong (England)
- 1701: Gouin de Beauchesne (France)
- 1708: Roger Woodes (Great Britain)
- 1740: George Anson (Great Britain)
In 1764, Louis de Bougainville (France) founded a naval base at Port Louis, East Falkland. The French named them the Îles Malouines, so-called from when the islands were briefly occupied by fishermen from St Malo. Ignorant of de Bougainville's presence, John Byron (Great Britain) established a base at Port Egmont, West Falkland in 1765. In 1766, France sold its base to Spain. Spain declared war on Great Britain in 1770 in a fight over the islands but the dispute was settled the following year, with Spain retaining East Falkland and Great Britain West Falkland (until 1774).
FalklandIslands.jpg
They remained practically unsettled until the 19th century. Argentina set up a penal colony in the islands in 1820, and in 1829 named Luis Vernet as the islands' governor, in order to colonise them. The United Kingdom invaded the islands in 1833, but Argentina maintained its claim. Various tensions led to an Argentine invasion in 1982. The islands were later retaken by the UK. See: Falklands War.
No native people lived in the islands when the Europeans arrived, although there is some disputed evidence for earlier human visits. The most convincing is the Falkland Island fox, or Warrah, possibly descended from South American culpeo used as hunting dogs by Yaghan people of Tierra del Fuego. It is unlikely that it reached the islands by itself. Abundant when the islands were settled by Europeans, it was considered a nuisance to livestock and hunted to extinction.
Politics
Main article: Politics of the Falkland Islands
Executive authority comes from the Queen and is exercised by the Governor on her behalf. Defence is the responsibility of the UK. There is a constitution, which was put into force in 1985.
Under the constitution, there is an Executive Council, and a Legislative Council. The Executive Council, which advises the Governor, is also chaired by the Governor. It consists of the Chief Executive, Financial Secretary and three Legislative Councillors, who are elected by the other Legislative Councillors. The Legislative Council consists of the Chief Executive, Financial Secretary and the eight Legislative Councillors, of whom five are elected from Stanley and three from Camp, for four year terms. It is presided over by the Speaker, currently Mr L.G Blake.
The loss of the war against Britain over control of the islands led to the collapse of the Argentine military dictatorship in 1983. Disputes over control of the islands still continue. In 2001, British Prime Minister Tony Blair was the first to visit Argentina since the war. On the 22nd anniversary of the war, Argentina’s President Néstor Kirchner gave a speech insisting that the islands would once again be part of Argentina. Kirchner, campaigning for president in 2003, regarded the islands a top priority. In June 2003 the issue was brought before a United Nations committee, and attempts have been made to open talks with Britain to resolve the issue of the islands. The Falkland Islanders themselves are almost entirely British, and maintain their allegiance to the United Kingdom.
Geography
Main article: Geography of the Falkland Islands
The islands are 300 miles (483 km) from the South American mainland.There are two main islands, East Falkland (Soledad) and West Falkland (Gran Malvina) and about 700 small islands. The total land area is 12,173 km².
Islanders themselves talk about two main areas of the islands, namely Stanley and the rest which they nickname "the Camp", from the Spanish "campo" meaning "countryside".
Economy
Main article: Economy of the Falkland Islands
The largest industries are fishing and agriculture. The islands have oil reserves that are believed to be quite substantial, but have yet to be exploited.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of the Falkland Islands
The population is 2,967 (July 2003 estimated).
Islanders call themselves "Islanders". Outsiders often call Islanders "Kelpers", from the kelp, which grows profusely around the islands, but the name is not used in the Islands any more. The word kelper is used in Argentina with the meaning of second-class citizens as a reflection on the legal status of the islanders within the UK prior to the passing of the Nationality Act of 1983.
Culture
Main article: Culture of the Falkland Islands
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in the Falkland Islands
- Transport in the Falkland Islands
- Military of the Falkland Islands
- Stamps and postal history of the Falkland Islands
See also
- Battle of the Falkland Islands - naval engagement of the First World War
- British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act 1983
- Falklands War - conflict between Argentina and United Kingdom
- Major Samuel Stransham
- Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey
- List of settlements in the Falkland Islands
Reference
External links
- Template:Wikitravel
- Falkland Islands government (http://www.falklands.gov.fk/) official website, including a detailed map (http://www.falklands.gov.fk/coastal-shipping/falkland-islands-map.jpg)
- Falkland Islands portal (http://www.falklandislands.com/), from the Falkland Islands Development Corporation
- BBC Focus on the Islands (http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/americas/country_profiles/4087743.stm)
- Penguin News (http://www.penguin-news.com/), a weekly newspaper since 1979 (membership required for access)
- Falkland Islands News Network (http://www.falklandnews.com/), privately maintained
- Falkland Islands Tourism (http://www.tourism.org.fk/), from a company by that name
- Satellite photograph of the islands (http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2005-05-03) taken April 28, 2005, hosted by a NASA website
- Falklands History (http://www.naval-history.net/F13history.htm)
| Countries in South America |
|---|
| Argentina | Bolivia | Brazil | Chile | Colombia | Ecuador | Guyana | Panama | Paraguay | Peru | Suriname | Trinidad and Tobago | Uruguay | Venezuela |
| Dependencies: Falkland Islands | French Guiana |
cs:Falklandy da:Falklandsøerne de:Falklandinseln et:Falklandi saared es:Islas Malvinas eo:Falklandoj fr:Îles Malouines id:Kepulauan Falkland it:Isole Falkland he:איי פוקלנד zh-min-nan:Falkland Kûn-tó nl:Falklandeilanden ja:フォークランド諸島 no:Falklandsøyene pl:Falklandy pt:Malvinas ru:Фолклендские острова sk:Falklandy sl:Falklandski otoki fi:Falklandinsaaret sv:Falklandsöarna zh:福克兰群岛