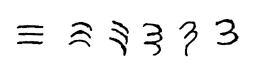3 (number)
|
|
| Template:Numbers (digits) | |
| Cardinal | 3 three |
| Ordinal | 3rd third |
| Numeral system | ternary |
| Factorization | prime |
| Divisors | 1, 3 |
| Roman numeral | III |
| Unicode representation of Roman numeral | Ⅲ, ⅲ |
| prefixes | tri- (from Greek) |
| Binary | 11 |
| Octal | 3 |
| Duodecimal | 3 |
| Hexadecimal | 3 |
3 (three) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4.
| Contents |
Evolution of the glyph
Three is often the largest number written with as many lines as the number represents. The Romans tired of writing 4 as IIII, but to this day 3 is written as three lines in Roman and Chinese numerals. This was the way the Brahmin Indians wrote it, and the Gupta made the three lines more curved. The Nagari started rotating the lines clockwise and ending each line with a slight downward stroke on the right. Eventually they made these strokes connect with the lines below, and evolved it to a character that looks very much like a modern 3 with an extra stroke at the bottom. It was the Western Ghubar Arabs who finally eliminated the extra stroke and created our modern 3. (The "extra" stroke, however, was very important to the Eastern Arabs, and they made it much larger, while rotating the strokes above to lie along a horizontal axis, and to this day Eastern Arabs write a 3 that looks like a mirrored 7 with ridges on its top line).
In fonts with text figures, 3 usually has a descender, for example, Missing image
TextFigs036.png
Image:TextFigs036.png
, though in some French fonts it has an ascender instead of a descender.
In mathematics
Three is the second smallest prime number (after two; the next prime number is five). Three is the first Fermat prime (220 + 1) as well as the first Mersenne prime (22 - 1). Three is the second Sophie Germain prime and the second Mersenne prime exponent. Three is also the first lucky prime, the second factorial prime (2! + 1), and the first unique prime due to the properties of its reciprocal.
Three is the second triangular number.
Three points form a plane (unless they are collinear).
Three is the fourth Fibonacci number and the third that is unique. It is also a Lucas number.
Three is the fourth open meandric number.
Vulgar fractions with 3 in the denominator have a single digit repeating sequences in their decimal expansions, (.000..., .333..., .666..., .999...)
A natural number is divisible by three if the sum of its digits in base 10 is divisible by 3. For example, the number 21 is divisible by three (3 times 7) and the sum of its digits is 2 + 1 = 3. Because of this, the reverse of any number that is divisible by three (or indeed, any permutation of its digits) is also divisible by three. For instance, 1368 and its reverse 8631 are both divisible by three (and so are 1386, 3168, 3186, 3618, etc..).
A triangle is the most durable shape possible, the only "perfect" figure which if all endpoints have hinges will never change it's shape unless the sides themselves are bent.
In human culture
Many human cultures have given the concept of three-ness symbolic meanings. The Holy Trinity in Christian doctrine (or trinity in general), is God both a single entity and three entities, the Father, the Son and the Spirit.
The process of synthesis in Hegelian dialectic creates three-ness from two-ness.
The three Doshas (weaknesses) and their antidotes are the basis of Ayurvedic medicine in India. The three Gunas underlie action, in the Vedic system of knowledge. There is also the concept of Trimurti in Hindu tradition.
Three (三, formal writing: 叁, pinyin san1) is considered a good number in Chinese culture because it sounds like the word "alive" (生 pinyin sheng1), compared to four.
In other fields
For other uses and related terms, see also 3 (disambiguation)
Three' is:
- The title of:
- The "third way" is a political term applied to a variety of "third choice" options that some offer as an alternative to dichotomous situations which may otherwise appear polarized.
- The number of stars in "Pacific's triple star" in the NZ National Anthem
- In Astrology, Gemini is the 3rd astrological sign of the Zodiac.
- The TV VHF channel most often used for hooking up VCRs, since it is rarely used by broadcasters. (If it is, then channel 4 is used instead.)
- "In Memory of 3" - a phrase about NASCAR driver Dale Earnhardt, who drove the number 3 car. It can also refer to a 2004 ESPN television movie about Earnhardt's life called, 3: The Dale Earnhardt Story.
- The designation of the Crowsnest Highway in Alberta and British Columbia.
- No. 3 - 1997 Korean gangster comedy written and directed by Neung-han Song
- In music,
- the roman numeral iii is the mediant scale degree, chord, or diatonic function, when distinguished III = major and iii = minor.
- 3 (band) - a rock band formed by Keith Emerson, Robert Berry and Carl Palmer
- important to popular American rock group, The White Stripes, and has become one of the trademarks of their style.
- 3 (telecommunications) - a 3G operator in Europe, Australia and Hong Kong
- threedegrees - an instant messaging software created by Microsoft
- Three Gorges
- Three Kingdoms
- The Three Stooges
- Three-letter abbreviations and acronyms (TLA)
- Three Links
- Three of a kind - a term used in poker, and also a pop/rap group based in the UK (see Three of a kind (rap group))
- Three Principles of the People
- Three Represents
- Three's Company - an American sitcom
- Three Years of Natural Disasters
- In rugby union, three is the number of the tighthead prop.
- In baseball, three represents the first baseman's position.
- Historical years: 3 A.D., 3 B.C., or 1903ca:Tres
da:3 (tal) de:Drei es:Tres eo:Tri fr:3 (nombre) ia:3 it:Tre ko:3 he:3 (מספר) la:3 nah:Ei nl:Drie ja:3 no:3 (tall) nn:Talet tre ru:Три sl:3 (število) sv:3 (tal) th:3 (จำนวน) zh:3