New Hampshire
|
|
| |||||
| State nickname: The Granite State | |||||
| |||||
| Other U.S. States | |||||
| Capital | Concord | ||||
| Largest city | Manchester | ||||
| Governor | John Lynch | ||||
| Official languages | English | ||||
| Area | 24,239 km² (46th) | ||||
| - Land | 23,249 km² | ||||
| - Water | 814 km² (3.4%) | ||||
| Population (2000) | |||||
| - Population | 1,235,786 (41st) | ||||
| - Density | 53.20 /km² (20th) | ||||
| Admission into Union | |||||
| - Date | June 21, 1788 | ||||
| - Order | 9th | ||||
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC-5/-4 | ||||
| Latitude | 42?40'N to 45?18'N | ||||
| Longitude | 70?37'W to 72?37'W | ||||
| Width | 110 km | ||||
| Length | 305 km | ||||
| Elevation | |||||
| - Highest | 1,917 m | ||||
| - Mean | 305 m | ||||
| - Lowest | 0 m | ||||
| Abbreviations | |||||
| - USPS | NH | ||||
| - ISO 3166-2 | US-NH | ||||
| Web site | www.state.nh.us | ||||
New Hampshire is a small U.S. state in northern New England. It is located east of Vermont, north of Massachusetts, south of Quebec, Canada, and west of Maine and the North Atlantic Ocean. The state ranks 46th of the 50 states in land area (23,249 km2) and 41st in population (around 1.3 million by a 2003 U.S. Census Bureau estimate). It is the site of the New Hampshire primary, the first primary in the U.S. presidential elections, and has probably the most famous of all state mottos: "Live free or die".
New Hampshire's state nickname is "the Granite State" because it has numerous granite quarries, although that industry has declined greatly in recent decades. The nickname has also been embraced for reflecting the state's attachment to tradition and limited government. Its state flower is the purple lilac. Its state bird is the purple finch. Its state tree is the American white birch, also called paper birch or canoe birch.
New Hampshire is home to the highest winds ever recorded on Earth: 231 mph in 1934 at the Mount Washington weather observatory in the Presidential Range.
In 2003 it gained international attention for having the first openly gay bishop, Gene Robinson, within the Anglican Communion (the Episcopal Church in the USA).
New Hampshire's recreational attractions include skiing and other winter sports; observing the fall foliage; the Lakes Region; and the New Hampshire International Speedway (formerly Loudon Racetrack), home of the Loudon Classic, the longest-running motorcycle race in the United States.
USS New Hampshire was named in honor of this state.
| Contents |
History
New Hampshire was founded by Captain John Mason and first settled in 1623, just three years after the Pilgrims landed in Massachusetts and it was one of the thirteen colonies that revolted against British rule in the American Revolution. It was the first state to declare its independence, and the historic attack on Fort William and Mary (now Fort Constitution) helped supply the cannon and ammunition needed for the Battle of Bunker Hill that took place north of Boston a few months later.
In the 1830s, NH saw two major news stories: the founding of the Republic of Indian Stream on its northern border with Canada over the unresolved post-revolutionary war border issue, and the founding of the modern Republican Party by Amos Tuck and friends. New Hampshire grew as a hotbed of Abolitionist sentiment up to the Civil War, participating in the Underground Railroad in providing safe routes into Canada, primarily via the Connecticut River waterway.
In the 20th Century, NH gained political renown for its First in the Nation political primaries which tended to accurately predict who would be elected President of the United States.
Law and Government
Main article: Government of New Hampshire
The New Hampshire state capital is Concord, which has also been known over time by the names Rumford and Penacook. The governor of New Hampshire is John Lynch (Democrat). New Hampshire's two U.S. senators are Judd Gregg (Republican) and John E. Sununu (Republican), whose father John H. Sununu was governor of the state from 1983–1988. List of New Hampshire Governors.
Unlike most states, New Hampshire does not have a Lieutenant Governor; the Senate President fills that role. However, New Hampshire has a bifurcated executive branch consisting of the Governor and a five-person Executive Council that is a holdover from the Governor's Council of the Colonial era. The Executive Council's duties include voting on state contracts worth more than $5,000, on nominations made by the governor to major state positions such as department heads, and all judgeships.
The New Hampshire state legislature, called the General Court, has 400 members in the House and 24 in the Senate. It claims to be the third-largest legislative body in the English-speaking world, behind only the United States House of Representatives and the British House of Commons. Based on 2000 Census data, this averages out to about one Representative for every 3090 people.
State representatives and state senators are paid just $100 a year, plus mileage, effectively meaning that state laws are written by volunteers. Because of this pay scale, many New Hampshire lawmakers are either wealthy or retired.
New Hampshire's government has earned the positive attention of residents in neighboring states: Killington, Vermont voted on March 2, 2004 to secede from Vermont and join New Hampshire—a largely symbolic act, since actual secession would require the agreement of both states' legislatures and the U.S. Congress. Supporters note that almost all Vermont towns were first chartered by New Hampshire, and point out that these two states already have unusual cross-border links, with the only two interstate school districts in the United States.
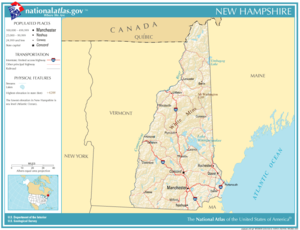
Geography
See List of New Hampshire counties
New Hampshire is part of the New England region. It is bounded by Quebec, Canada to the north, Maine and the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Massachusetts to the south, and Vermont to the west. New Hampshire's major regions are the Great North Woods, the White Mountains region, the Lakes region the Seacoast region, the Merrimack Valley region, the Monadnock region, and the Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee area.
See List of mountains in New Hampshire
New Hampshire was home to the famous geological formation called the Old Man of the Mountain, a face-like profile in Franconia Notch, until May 2–3, 2003, when the symbol of New Hampshire collapsed.
The Presidential Range in New Hampshire spans the central portion of the state, with Mount Washington being the tallest, and other mountains like Mount Madison and Mount Quincy Adams surrounding it. With hurricane force winds every third day on the average, 100 recorded deaths among visitors, and conspicous krummholz (dwarf, matted trees much like a carpet of bonsai), the upper reaches Mount Washington claim the distinction of the " worst weather on earth". In consequence, a non-profit observatory is located on the peak for the purposes of observing harsh environmental conditions.
In the flatter southwest corner of New Hampshire another feature, the prominent landmark and tourist attraction of Mount Monadnock, has given its name to a general class of earth-forms, a monadnock signifying in geomorphology any isolated resistant peak rising from a less resistant eroded plain.
See List of New Hampshire rivers
Major rivers include the 116 mile (187 km) Merrimack River, which bisects the state north-south and ends up in Massachusetts. Its major tributaries include the Souhegan River. The 410 mile (670 km) Connecticut River, which starts at New Hampshire's Connecticut Lakes and flows south to Connecticut, forms the western border of New Hampshire. Oddly, the state border is not in the center of that river, as is usually the case, but lies at the low-water mark on the Vermont side, so New Hampshire actually owns the whole river. The Piscataqua River and its several tributaries form the state's only significant ocean port where they flow into the Atlantic at Portsmouth.
The largest lake is Lake Winnipesaukee, which covers 72 square miles (186 km²) in the central part of New Hampshire.
New Hampshire has the shortest ocean coastline of any coastal state, 18 miles (29 km) by state figures. (Under some federal definitions, Pennsylvania's coast is shorter: See Footnote in "Miscellaneous"). Hampton Beach is a popular local summer destination. About 10 miles (16 km) offshore are the Isles of Shoals, nine small islands best known as the site of a 19th-century art colony founded by poet Celia Thaxter, as well as the alleged location of one of the buried treasures of the pirate Blackbeard.
There is an ongoing boundary dispute with Maine in the area of Portsmouth Harbor, with NH claiming dominion over several islands (now known as Seavey Island) that include the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard as well as to the Maine towns of Kittery and Berwick, which NH asserts were granted to it by Massachusetts prior to Maine becoming a state of its own rather than just the northern part of Massachusetts, in the Missouri Compromise of 1820. This claim is also bolstered by British records of captured American POWs during the Revolutionary period, held in England, who claimed "Berwick, NH", "York, NH", and "Kittery, NH" as their home towns.
A dramatic change in the visual landscape of New Hampshire occurred about a century ago when its changed from an open landscape of fields and small farms: It is now the second-most-forested state in the country, after Maine, in terms of percentage of land covered by woods. This change was caused by the abandonment of farms by owners seeking wage jobs in urban areas or bank seizure of unproductive farms, with farming families moving west. The reversion forms the subject of many poems by Robert Frost, while the emigration is consistent with the results of NH native and newspaper legend Horace Greeley imploring, "Go West, Young Man."
Economy
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/) estimates that New Hampshire's total state product in 2003 was $49 billion. Per capital personal income in 2003 was $35,140, 7th in the nation. Its agricultural outputs are dairy products, nursery stock, cattle, apples, and eggs. Its industrial outputs are machinery, electric equipment, rubber and plastic products, and tourism.
New Hampshire experienced a significant shift in its economic base during the last century. Historically, the base was composed of the traditional New England manufactures of textiles, shoe-making, and small machining shops drawing upon low wage labor from nearby small farms and from Quebec. Today, these sectors contribute only 2% for textiles, 2% for leather goods, and 9% for machining of the state's total manufacturing dollar value (Source: US Economic Census for 1997, Manufacturing, New Hampshire). These traditional sectors experienced their sharp decline during the Twentieth Century due to increasingly obsolete plants and increasingly cheaper wages available in the US South.
The current New Hampshire economy is largely driven by fiscal policy. The state has no personal income tax and advocates a frugal budget, thereby attracting commuters, light industry, specialty horticulture, and service firms from other jurisdictions with high tax policies, notably from neighboring Massachusetts. This is a viable fiscal policy for a small, high-income state with limited social service demands, but it has not been one hundred per cent successful, and pockets of depressed manufacturing activity still remain. Additionally, New Hampshire's lack of a broad based tax system (aside from the controversial state-wide property tax which former Governor Benson cut nearly in half in two years) has resulted in the state's local communities having some of the nation's highest property taxes, yet overall NH remains ranked 49th in combined average state and local tax burden, due to its lack of income or sales taxes.
Demographics
According to the Census Bureau, as of 2003, the population of New Hampshire was 1,287,687.
The racial makeup of the state is:
- 95.1% Caucasian (making New Hampshire number three in the highest caucasian percentage in the US, trailing Maine and Vermont)
- 1.7% Hispanic
- 1.3% Asian
- 0.7% African American
- 0.2% American Indian
- 1.1% mixed race.
The 5 largest ancestry groups in New Hampshire are: Irish (19.4%), English (18%), French (14.6%), French Canadian (10.6%), German (8.6%).
Religion
The religious affiliations of the citizens of New Hampshire are:
- Protestant – 41%
- Roman Catholic – 41%
- Other Christian – 3%
- Other Religions – 2%
- Non-Religious – 9%
The three largest Protestant denominations in New Hampshire are: Methodist (11% of the total state population), Baptist (9%), Presbyterian & Episcopalian (tied 2%).
Important cities and towns
- Manchester, the largest city in the state and known as the "Queen City", Manchester, has a main street (Elm Street) which is a dead-end at both ends. The Merrimack River runs through the city and once provided water power to a textile mill industry.
- Keene is still called "The Elm City" despite the fact that Dutch elm disease destroyed most of the city's elm trees in the 1930s. Keene is the home to Keene State College.
- Salem contains The Mall at Rockingham Park, frequented by Massachusetts residents to avoid paying sales tax; Canobie Lake Park, an amusement; and Rockingham Park, New England's first racetrack for horses.
- Peterborough is the inspiration for the town of Grover's Corners portrayed in Thornton Wilder's play Our Town.
- Lebanon known as "The City of Fountains" is the least-populated community in NH organized as a city. It contains Lebanon College and the Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center and is the location of many malls along the Connecticut River that draw Vermont shoppers avoiding that state's sales tax.
10 Largest Towns/Cities in New Hampshire According to 2000 Census
| Manchester | 107,006 | |
| Nashua | 86,605 | |
| Concord | 40,687 | |
| Derry | 34,021* | |
| Rochester | 28,461 | |
| Salem | 28,112 | |
| Dover | 26,884 | |
| Merrimack | 25,119* | |
| Londonderry | 23,236* | |
| Hudson | 22,928 |
* While Census records may seem to indicate that two separate Census Districts exist for this community, in fact one district is contained entirely within the other.
Education
Colleges and universities
Professional sport teams
Minor league baseball teams:
Hockey teams:
Arena football teams:
Miscellaneous information
See List of New Hampshire-related topics
- New Hampshire was the last of the New England states to observe Fast Day, a day of prayer for a bountiful harvest. Traditionally observed on the 4th Thursday in April, from 1949 was observed as a legal holiday on the 4th Monday in April until 1991 when it was replaced by Civil Rights Day. [1] (http://www.state.nh.us/nhinfo/fast.html)
- In 1999 New Hampshire changed the name of Civil Rights Day to Martin Luther King Day. [2] (http://www.factmonster.com/spot/mlkhistory1.html)
- There are no general sales or individual income taxes in New Hampshire, though the state does have meals, lodging, and other taxes. (List of other states without personal income taxes)
- New Hampshire is the only state that does not mandate public kindergarten, partly out of frugality and lack of funding, and partly out of belief in local control, a philosophy under which towns and cities, not the state, make as many decisions as possible. As of 2003, all but about two dozen communities in the state provided public kindergarten with local property-tax money.
- Like several states, New Hampshire requires all hard liquor to be sold in state-owned, state-run stores. This system generates millions of dollars annually for the state and results in liquor being so cheap that it attracts many out-of-state customers. Many liquor stores are located near state lines, often on interstate highways (with their own exits).
- New Hampshire is host to the New Hampshire Highland Games, formerly the Scottish Games. New Hampshire has also registered an official tartan with the proper authorities in Scotland; this tartan is used to make kilts worn by the State Police while they serve during the games.
- New Hampshire has the only piece of Interstate highway that is two-lane (i.e. a single northbound lane and a single southbound lane) with a cobblestone median. This was done to preserve Franconia Notch, the site of the Old Man of the Mountain, a rock formation visible from Interstate 93 in Franconia. The formation, the state symbol, fell apart due to natural erosion on May 3, 2003.
- In northern New Hampshire the town of Dixville Notch is traditionally the first city or town in the U.S. to vote in presidential primaries and the presidential election. The few dozen residents of Dixville Notch all stay awake until after midnight to vote. State law grants that a town where all registered citizens have voted may close early and announce their results.
- New Hampshire is the only state with no mandatory seatbelt law for adults, no motorcycle helmet law for adults nor mandatory vehicle insurance for automobiles.
- New Hampshire is the destination of the Free State Project.
- EXTENDED FOOTNOTE on coastline. Official figures recognize two coastal concepts, the coastline and the shoreline. The coastline is a generalized measurement of the shore configuration, whereas the shoreline is the most detailed measurement practical and includes measurements for offshore islands and other features such as inlets and rivers to the head of a narrow tidewater. Based on these concepts, Pennsylvania has a saltwater coastline of 0 miles , so it cannot be considered for ranking in a discussion of saltwater coastlines, but when the more detailed measurement of shoreline is used, Pennsylvania has a saltwater shoreline of 89 miles versus 131 for New Hampshire, giving Pennsylvania a shorter ocean shore. Pennsylvania's number apparently comes because a portion of the Delaware River on its s eastern border is tidal. Source: US Dept of Commerce, "US Coastline by States" cited on Page 606 of the 2003 "World Almanac".
Daily newspapers
|
|
Other publications
- The New Hampshire Gazette Portsmouth alternative biweekly, arguably the oldest paper in America (although other publications also make that claim)
- New Hampshire Business Review (statewide)
- Hippo Press (Manchester and Nashua editions)
- The New Hampshire (University of New Hampshire's student-run newspaper since 1911)
Clip Art and Pictures
- Free Clipart (http://classroomclipart.com)
State Maps
- US State Maps (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Clipart/US_State_Maps)
State Flags
- US State Flags (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Clipart/State_Flags)
Lesson Plans, Resources and Activites
- Lesson Plan Central (http://lessonplancentral.com)
External links
- Official State Website (http://www.state.nh.us)
- The New Hampshire Almanac (http://www.state.nh.us/nhinfo/)

|
State of New Hampshire
|
|---|---|
| Capital: | Concord |
| Regions: | Dartmouth Sunapee | Great North Woods | Lakes Region | Merrimack Valley | Monadnock | Seacoast |White Mountains |
| Major Metros: | Manchester | Nashua |
| Smaller Cities: | Berlin | Claremont | Concord | Dover | Franklin | Keene | Laconia | Lebanon | Portsmouth | Rochester | Somersworth |
| Counties: | Belknap | Carroll | Cheshire | Coos | Grafton | Hillsborough | Merrimack | Rockingham | Strafford | Sullivan |
| Political divisions of the United States | 
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||