Polytheism in Ancient Egypt Many Gods Beliefs
Discover how Ancient Egyptians practiced polytheism by worshiping many gods and goddesses each with unique powers shaping religion and daily life

🌟 Introduction
Religion was at the heart of Ancient Egyptian life, and it was polytheistic. This means Egyptians believed in many gods and goddesses, each controlling different parts of the world and human life. The sun god Ra brought daylight, the god Osiris ruled the afterlife, and the goddess Isis protected families. Egyptians built temples, made offerings, and held festivals to honor the gods. By worshiping many gods, Egyptians explained natural events like floods, sickness, and harvests, believing the gods controlled them all.
🔍 What was Polytheism in Ancient Egypt?
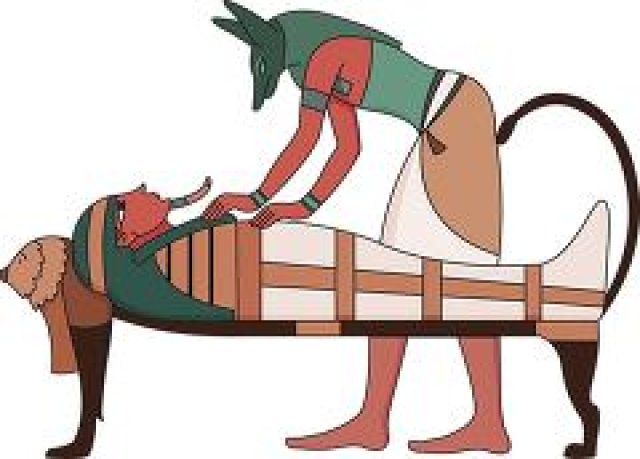
Polytheism in Ancient Egypt was the belief in many gods and goddesses. Egyptians believed their gods could take human or animal form, such as a man with a falcon head or a woman with cow horns. Some gods created the world, while others protected the dead or helped with farming. Over 2,000 different gods were worshiped, though some were more important than others.
🌍 Why was Polytheism Important in Ancient Egypt?
Polytheism was important because it shaped every part of Egyptian life. Religion explained how the world worked and why events happened. Pharaohs claimed to rule with the gods' blessing, temples were built as homes for the gods, and priests served as a bridge between people and the divine. Without polytheism, Egyptian art, temples, and even their ideas about the afterlife would not have existed.
🧪 Polytheism in Daily Life
Daily life in Egypt revolved around honoring the gods. Farmers prayed to Hapi, the god of the Nile, for good floods. Families prayed to Bes, the protector of children, to keep their homes safe. Festivals were held for Ra, Hathor, and Isis, where people sang, danced, and made offerings. Even in death, Egyptians relied on Anubis to guide them to the afterlife and Osiris to judge their souls.
📜 Major Egyptian Gods
-
Ra: The sun god, considered the most important deity, who sailed across the sky each day.
-
Osiris: God of the afterlife, resurrection, and fertility.
-
Isis: Goddess of magic, motherhood, and protection.
-
Horus: God of the sky, often shown as a falcon or a man with a falcon's head.
-
Anubis: God of mummification and the protector of the dead, shown with a jackal's head.
-
Hathor: Goddess of love, joy, and music, often depicted with cow horns.
-
Thoth: God of wisdom and writing, believed to have invented hieroglyphics.
✨ Fun Facts
-
Egyptians believed the gods lived in temples, and statues were treated as if they were alive.
-
Some gods merged together, like Amun-Ra, to show their combined power.
-
Cats were sacred animals linked to the goddess Bastet.
📌 Key Takeaways
-
Polytheism means belief in many gods.
-
Egyptians worshiped more than 2,000 gods and goddesses.
-
Religion shaped daily life, from farming to festivals to the afterlife.
🐾 Kid-Friendly Summary
Egyptians were polytheistic, which means they believed in many gods. Each god had a job, like bringing the sun, protecting families, or helping the dead. Egyptians prayed, built temples, and celebrated festivals to keep the gods happy.
📚 Vocabulary Words
-
Polytheism: Belief in many gods and goddesses.
-
Deity: Another word for god or goddess.
-
Temple: A sacred building where gods were worshiped.
-
Priest: A person who performed ceremonies for the gods.
Interactive Quiz: Polytheism in Ancient Egypt
-
What does polytheism mean?
A) Belief in one god
B) Belief in many gods
C) Belief in no gods
D) Belief in animals -
Who was the god of the afterlife?
A) Ra
B) Anubis
C) Osiris
D) Horus -
Which goddess protected families and motherhood?
A) Isis
B) Hathor
C) Bastet
D) Nephthys