Ancient Rome for Students: The Rise of the Republic and the Power of the Empire
Explore the fascinating world of Ancient Rome in this kid-friendly article for students. Learn about Roman government, daily life, the military, famous emperors, and lasting inventions. Includes vocabulary, fun facts, and a quiz!

🏛 Ancient Rome: The Rise of the Republic and the Power of the Empire
Introduction
From small beginnings, Ancient Rome grew into one of the most powerful civilizations in history. It gave us roads, aqueducts, amazing buildings, a legal system, and many words in modern languages. Ancient Rome wasn’t just an empire of soldiers and emperors—it was also home to poets, inventors, farmers, and families. This article will take you through the fascinating story of how Rome rose, ruled, and left a legacy that still lives on today.
📍 Location and Time Period
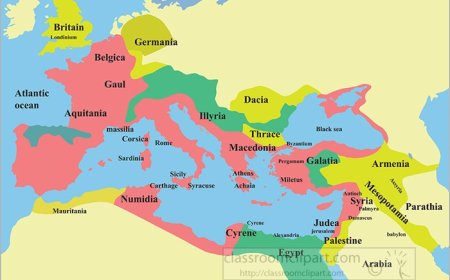
Ancient Rome began in central Italy, along the Tiber River, around 753 BCE. At first, it was a kingdom, then a republic, and finally an empire. It lasted for over 1,000 years until 476 CE, when the Western Roman Empire fell.
The Roman Empire stretched across Europe, North Africa, and parts of the Middle East, making it one of the largest empires in history.
🏛 Government: From Republic to Empire
The Roman Republic (509 BCE–27 BCE)
The Republic was a time when Rome was ruled by elected officials, not kings. Citizens could vote, but only free men had that right. Two leaders called consuls shared power, and the Senate made laws. The Republic taught people that laws should be written down and that everyone should follow them.
The Roman Empire (27 BCE–476 CE)
In 27 BCE, Augustus became the first emperor, turning Rome into an empire. Emperors had almost total power. Some, like Augustus and Trajan, were loved. Others, like Nero and Caligula, were known for being cruel or strange.
🧑🌾 Daily Life in Ancient Rome
Romans lived in either big, fancy houses or small apartment-style homes called insulae. Wealthy families had gardens, slaves, and lots of space. Poorer people lived in crowded buildings.
Roman meals included bread, cheese, olives, and fruits. The rich might eat peacock or stuffed dormice!
Children played with toys like wooden swords and marbles. Boys often went to school if their family could afford it.
🏛️ Religion and Gods
At first, the Romans believed in many gods (polytheism), similar to the Greeks. Some major Roman gods include:
- Jupiter – king of the gods (like Zeus)
- Mars – god of war
- Venus – goddess of love
- Neptune – god of the sea
Romans built temples and offered sacrifices to their gods. Later, in the 300s CE, Christianity spread through Rome, and Emperor Constantine made it the official religion of the empire.
🏟 Achievements and Inventions
Ancient Romans were amazing builders and thinkers. Some of their best-known inventions and contributions include:
- Aqueducts to carry water to cities
- Concrete, used to build long-lasting buildings
- Roman numerals, a number system still used on clocks
- The Julian calendar, the ancestor of our modern calendar
- Roman roads, over 50,000 miles of them, made travel and trade easier
They also developed a legal system where laws were written and justice was expected.
🎭 Art, Culture, and Entertainment
Romans loved entertainment. They went to gladiator games at the Colosseum, plays at theaters, and horse races at the Circus Maximus.
They made:
Statues of gods and leaders
Mosaics from tiny colored tiles
Frescoes, paintings on walls
Famous Roman writers include:
Virgil, who wrote the Aeneid
Ovid, who wrote about myths and love
Cicero, a great speaker and politician
🛡 Military and Expansion
Rome had one of the most powerful armies ever. Roman soldiers were called legionaries and were trained, disciplined, and well-equipped. With their strong military, Rome conquered:
- Greece
- Egypt
- Gaul (modern-day France)
- Britain
- Parts of the Middle East
They built forts, roads, and cities wherever they went, spreading Roman culture and law.
💰 Trade and Economy
Rome had a strong economy based on farming, mining, and trade. They grew crops like wheat, grapes, and olives, and mined metals like gold and silver. Roman coins were used all over the empire.
Markets called fora were where people shopped, shared news, and discussed politics.
🏛 Famous Landmarks and Structures
The Colosseum – A huge arena for gladiator battles and shows
The Roman Forum – The center of public life in Rome
The Pantheon – A temple with a large dome still standing today
Hadrian’s Wall – A wall in northern Britain built to keep out invaders
🏚 Decline and Legacy
The Roman Empire began to weaken in the 300s CE because of:
Invasions by barbarian tribes (like the Visigoths)
Bad rulers and civil wars
Economic troubles
The Western Roman Empire fell in 476 CE, but the Eastern Empire (Byzantine Empire) lasted another 1,000 years.
Legacy: Rome gave the world:
- Ideas of law and citizenship
- Languages (Latin is the root of Italian, French, Spanish, and more)
- Amazing architecture
- Roads, bridges, and cities
🎉 Fun Facts About Ancient Rome
- Roman soldiers marched about 20 miles a day carrying 60 pounds of gear!
- Julius Caesar was stabbed 23 times by his own senators.
- Romans brushed their teeth with crushed oyster shells and mint.
- Some public toilets had sponge sticks instead of toilet paper!
- The Roman Colosseum could seat more than 50,000 people.
🧠 Vocabulary List
- Republic – A type of government where people elect leaders
- Emperor – A ruler of an empire
- Consul – One of the two top leaders in the Roman Republic
- Senate – A group of officials who made laws in Rome
- Gladiator – A fighter who battled in public for entertainment
- Aqueduct – A structure that carried water from far away
- Forum – A central place in Roman cities for markets and meetings
- Legionary – A soldier in the Roman army
- Polytheism – Belief in many gods
- Colosseum – A huge arena in Rome for gladiator games
📚 Kid-Friendly Summary
Ancient Rome grew from a small city to a giant empire. Romans built roads, made laws, and invented cool things like aqueducts and concrete. They had emperors, gladiators, and amazing buildings. Even though the empire ended, Roman ideas are still part of our lives today—from the way we govern to the way we build cities!