What Is an Electric Vehicle (EV)? Battery-Powered Cars Explained for Kids
Learn how electric vehicles work and why they're good for the environment. A fun and educational EV guide for kids with facts, types, and safety tips.
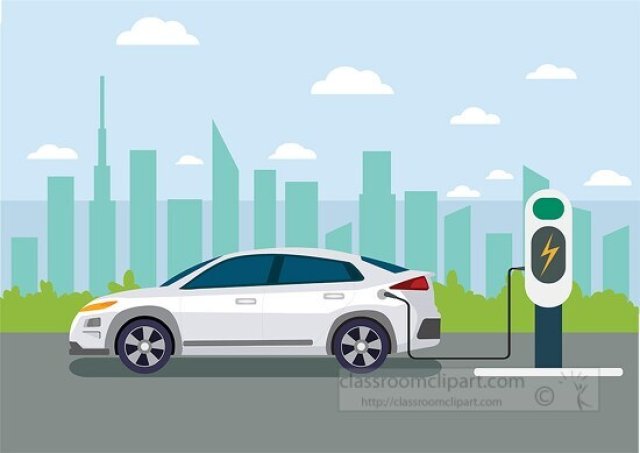

⚡ Electric Vehicles (EVs): Cars of the Future
Summary:
An electric vehicle (EV) is a type of car or truck that runs on electricity instead of gasoline. EVs are quiet, clean, and better for the environment. In this article, you’ll learn how electric vehicles work, why they’re important, and how they’re changing the future of transportation.
🚗 What Is an Electric Vehicle?
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that is powered by a battery and electric motor instead of a gas-powered engine. EVs don’t need fuel from a gas station—they plug in to charge, just like your phone or tablet!
Types of Electric Vehicles:
- Electric cars – The most common type of EV
- Electric buses – Used for city travel and school transportation
- Electric trucks – Haul goods with no engine noise or fumes
- Electric bikes and scooters – Used for quick trips and fun rides
💡 Did You Know? Some electric cars can drive over 300 miles on a single charge!
⚙️ How Do EVs Work?
EVs run on a battery pack that powers an electric motor. When you press the accelerator, electricity flows to the motor, which turns the wheels.
Key EV Parts:
- Battery – Stores electric energy (like a super-powerful phone battery)
- Electric motor – Moves the wheels
- Charger/Plug – Used to refill the battery
- Onboard computer – Controls power, braking, and speed
Most EVs can be charged at home, at public charging stations, or at fast chargers on the road.
🕰️ A Short History of Electric Vehicles
- 1830s – Early inventors built electric carriages and wagons
- Late 1800s – Electric cars became more popular than gas cars in some cities
- 1900s – Gasoline cars took over because they could travel farther
- 2000s – New battery technology brought EVs back
- Today – Companies like Tesla, Nissan, and Ford make electric cars around the world
🌍 Why Are EVs Important?
Electric vehicles help protect the environment by:
- Producing zero exhaust pollution
- Using clean energy (like wind or solar power)
- Reducing our need for fossil fuels
- Being quiet and better for city life
EVs are part of a movement toward greener, smarter transportation.
🔌 Where Can You Charge an EV?
Charging an EV is like charging a big electronic device.
| Charger Type | Where It's Found | Charging Time |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (slow) | Home outlets | 8–12 hours or more |
| Level 2 (medium) | Public charging stations | 3–8 hours |
| DC Fast Charger | Highways, EV stations | 30–60 minutes |
Many cities and schools now have EV charging stations in parking lots!
⚠️ Are EVs Safe?
Yes! Electric vehicles are tested for safety just like regular cars. Many EVs include:
- Automatic braking
- Touchscreen controls
- Backup cameras
- Lane-keeping systems
They also produce less heat, making them safer in some cases.
📚 Vocabulary to Know
- Electric vehicle (EV) – A car or truck that runs on electricity
- Battery – Stores and supplies electric power
- Charger – A device that recharges an EV battery
- Motor – Converts electric energy into movement
- Emissions – Pollution released by gas-powered vehicles (EVs have none!)
🧠 Think About It!
If every car in the world were electric, how would that change the air we breathe or the sounds we hear in cities?
🧒 Kid-Friendly Summary
An electric vehicle is a car or truck that uses a battery instead of gas. It’s quiet, clean, and better for the Earth. You can charge it at home or at stations, and it helps reduce air pollution. Electric vehicles are the future of travel!