What Is Buoyancy? Floating and Sinking Explained for Kids
Learn what buoyancy is and how it helps objects float in water. Easy science facts and fun experiments for kids about floating, sinking, and ships.
Summary:
Buoyancy is the force that allows objects to float in water (or other fluids). It's the reason why boats, ships—even rubber ducks—can stay on the surface instead of sinking. In this article, you’ll learn what buoyancy is, how it works, and why it’s so important in water transportation.
🌊 What Is Buoyancy?
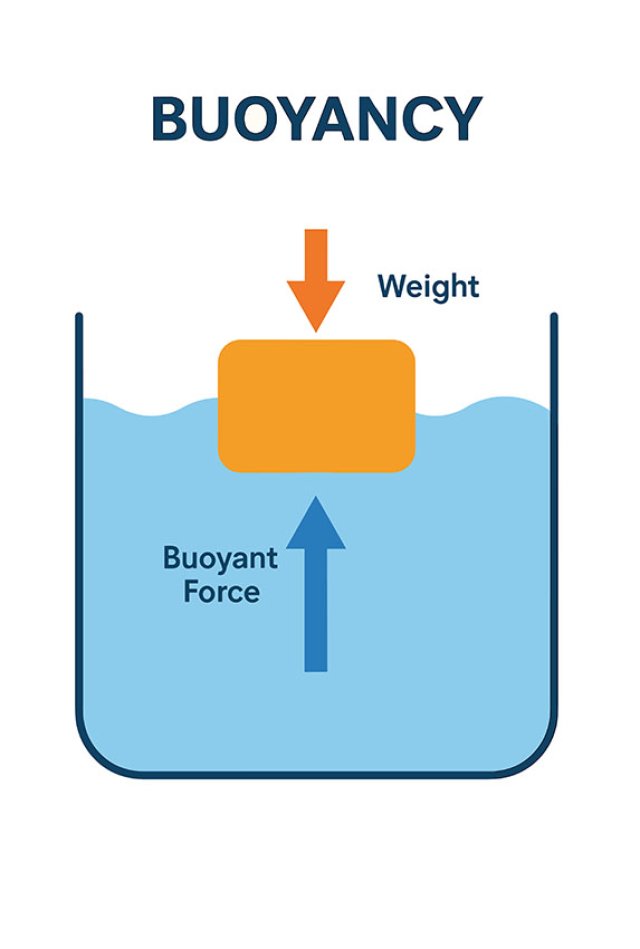
Buoyancy is the upward force that water (or any fluid) pushes on an object when that object is in the water. It works against gravity.
If the buoyant force is strong enough to push the object up and keep it there, the object floats. If not, it sinks.
💡 Simple Rule:
If an object weighs less than the water it pushes aside (displaces), it floats!
⚖️ How Does Buoyancy Work?
When you place something in water, it pushes water out of the way. This is called displacement. The more water an object pushes out of the way, the greater the buoyant force pushing back up.
What Affects Buoyancy:
- Weight of the object
- Shape (wide and flat shapes float better)
- Material (wood floats better than metal)
- Amount of water displaced
Even heavy ships float because their shape spreads out their weight and displaces a lot of water.
🛳️ Buoyancy in Boats and Ships
All watercraft—from tiny canoes to massive cargo ships—use buoyancy to stay afloat. That’s why:
- Ships are hollow and wide, not solid blocks of metal
- Submarines control their buoyancy using ballast tanks
- Life jackets help people float by increasing buoyancy with light, air-filled materials
Engineers and shipbuilders must carefully design boats to stay stable and safe using buoyant forces.
🧪 A Famous Experiment: Archimedes' Principle
The idea of buoyancy goes back over 2,000 years to a scientist named Archimedes. He discovered that:
An object placed in water is pushed up by a force equal to the weight of the water it displaces.
This idea is called Archimedes' Principle and it’s still used today in science and engineering.
🧁 Fun Float Test!
Try this at home:
- Fill a sink or bucket with water.
- Drop in a rock, a rubber ball, a sponge, and a plastic spoon.
- Which items float? Which ones sink? Why?
This test shows how size, shape, and material affect buoyancy.
📚 Vocabulary to Know
- Buoyancy – The upward force that helps objects float in water
- Displace – To push water out of the way
- Float – To stay on top of water
- Sink – To fall below the surface of water
- Archimedes' Principle – The science rule that explains buoyancy
🧠 Think About It!
How can a huge steel ship float, but a small coin made of metal sinks? (Hint: It’s all about shape and displacement!)
🧒 Kid-Friendly Summary
Buoyancy is what helps things float in water. When something pushes water out of the way, the water pushes back. If that force is strong enough, the object floats. That’s why boats stay on top—and why you don’t sink when wearing a life jacket!























































