Ancient Greece: Democracy, Myths, and the Birth of Western Civilization
Discover Ancient Greece in this fun and educational article for students. Learn about Greek gods, democracy, famous thinkers, the Olympics, and more! Includes a vocabulary list, fun facts, and a quiz.
Introduction
Ancient Greece is one of the most fascinating civilizations in history. It was not just one big country, but a group of city-states like Athens and Sparta. The ancient Greeks gave us many things we still use today—like democracy, the Olympics, theater, philosophy, and amazing architecture. Whether it's myths about powerful gods or stories of brave warriors, Ancient Greece has left a lasting impact on the world.
📍 Location and Time Period
Ancient Greece was located in southeastern Europe, on a peninsula surrounded by the Aegean, Mediterranean, and Ionian Seas. It included mainland Greece and many islands. The civilization began around 800 BCE and lasted until about 146 BCE, when it was conquered by the Romans.
The mountainous landscape made travel and farming difficult, so Greeks built separate city-states (called polis) that had their own governments and armies but shared the same language and religion.
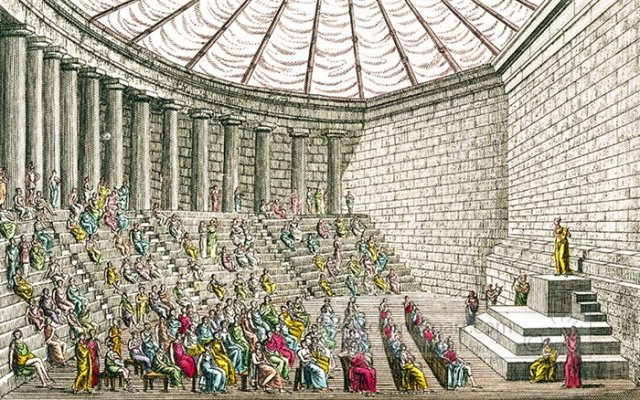
🏛️ Government and City-States
Ancient Greece is famous for creating democracy, a system where citizens vote to make decisions. This began in Athens, one of the most powerful city-states. Only free adult men born in Athens could vote, but the idea of citizens having a say was revolutionary.
Other city-states had different systems:
Sparta was a military state ruled by kings and focused on war and discipline.
Corinth and Delphi were wealthy cities known for trade and religion.
🧑🌾 Daily Life in Ancient Greece
Greek life was different depending on whether you lived in Athens, Sparta, or a village:
Men worked in government, farming, or trade.
Women managed the home and were not involved in politics.
Children played games, learned music and poetry, and some boys went to school.
Greek homes were simple, with courtyards for cooking and gathering. People wore clothes made of linen or wool, and sandals on their feet.
🕊️ Religion and Beliefs
The ancient Greeks believed in many gods and goddesses, making them polytheistic. Each god had a special power and personality. The Greeks built temples to honor them and held festivals and sacrifices.
Some major gods and goddesses include:
Zeus – king of the gods
Athena – goddess of wisdom and war
Poseidon – god of the sea
Apollo – god of music and the sun
Aphrodite – goddess of love
The Greeks also believed in myths—stories about the gods that explained nature, emotions, and life events.
🏟️ The Olympics and Entertainment
The Olympic Games began in 776 BCE in the city of Olympia. These athletic competitions were held every four years to honor Zeus. Only men could compete, and they did so in the nude!
Popular events included:
Running races
Wrestling
Discus and javelin
Chariot racing
Greeks also loved theater. They built outdoor amphitheaters where people watched tragedies and comedies written by famous playwrights like Sophocles and Aristophanes.
🧠 Achievements and Inventions
Ancient Greece was full of brilliant thinkers. People asked big questions about life, knowledge, and the universe.
Famous philosophers include:
- Socrates – asked questions to discover truth
- Plato – wrote about ideal government
- Aristotle – studied science, logic, and ethics
The Greeks also made great progress in:
- Mathematics – with Euclid and Pythagoras
- Medicine – led by Hippocrates, the “father of medicine”
- Architecture – using columns like Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian
- Art – creating life-like statues of gods and people
🛡️ Military and Conquests
Greece often had wars, both between its own city-states and with outside powers. Two major military events were:
The Persian Wars, where Greece defeated the powerful Persian Empire
The Peloponnesian War, a long battle between Athens and Sparta
Later, Alexander the Great, a ruler from Macedonia (north of Greece), conquered a huge empire stretching from Greece to Egypt and India. His empire spread Greek culture all over the ancient world.
💰 Trade and Economy
Ancient Greece had poor farmland, so trade was essential. The Greeks traded olive oil, wine, and pottery for goods like grain, metals, and spices. They used coins made of silver and gold.
Markets called agoras were the center of city life, where people bought goods, shared news, and discussed politics.
🏛️ Famous Landmarks and Structures
Greek architecture is still admired today. Their most famous buildings include:
The Parthenon – a temple to Athena in Athens
The Temple of Apollo at Delphi
The Theater of Epidaurus – known for amazing acoustics
Greeks used columns to support buildings, which inspired many modern government buildings and museums.
🏚️ Decline and Legacy
By 146 BCE, the Roman Empire had conquered Greece. Although Greek independence ended, its culture lived on. The Romans admired Greek art, ideas, and gods—and many of them became part of Roman life.
The legacy of Ancient Greece includes:
Democracy
Philosophy
Scientific thinking
Olympic Games
Theater and architecture
Even today, we still study Greek ideas in schools, use their myths in books and movies, and admire their achievements.
🎉 Fun Facts About Ancient Greece
Greek citizens voted by placing colored stones in jars!
Spartan boys began military training at age 7.
The word “school” comes from the Greek word scholē, which meant “free time.”
Greek statues were originally painted in bright colors.
The marathon race is based on a Greek legend about a soldier running 26 miles to announce a victory.
🧠 Vocabulary List
- City-state – A small independent area with its own laws and government
- Democracy – A form of government where citizens vote on decisions
- Philosopher – A person who asks questions about life, knowledge, and the universe
- Agora – A public market and meeting place in a Greek city
- Olympics – Athletic competitions held to honor Zeus
- Polytheistic – Belief in many gods
- Myth – A story that explains natural events or traditions, often involving gods
- Parthenon – A famous temple in Athens built to honor Athena
- Column – A tall support structure used in Greek architecture
- Empire – A group of countries or areas ruled by one power
📚 Kid-Friendly Summary
Ancient Greece was full of ideas, heroes, gods, and inventions. The Greeks created democracy, asked big questions, and started the Olympics. They told myths, built beautiful temples, and helped shape the world we know today. From amazing thinkers to powerful warriors, the legacy of Ancient Greece lives on in our schools, sports, and stories.