Voltage divider
|
|
In electronics, a voltage divider or resistor divider is a design technique used to create a voltage (Vout) which is proportional to another voltage (Vin). This is also known as the voltage divider rule.
| Contents |
Resistor divider
Two resistors are connected as shown in the following diagram:
The output voltage Vout is related to Vin as follows:
- <math>
V_{out} = \frac{R_2}{R_1+R_2} \cdot V_{in} <math>
As a simple example, if R1 = R2 then
- <math>
V_{out} = \frac{1}{2} \cdot V_{in} <math>
Any ratio between 0 and 1 is possible.
Note that this rule only works if the divider is unloaded, i.e. the load resistance is infinite and all of the current flowing through R1 goes into R2. If current flows into a load resistance (through Vout), that resistance must be considered in parallel with R2 (see resistor) to determine the voltage at Vout.
Impedance divider
A voltage divider is usually thought of as two resistors, but capacitors, inductors, or any combined impedance can be used. For general impedances Z1 and Z2, the voltage becomes
- <math>
V_{out} = \frac{Z_2}{Z_1+Z_2} \cdot V_{in} <math>
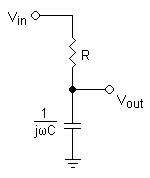
For instance, for a divider can be made with a resistor and capacitor:
Since the capacitor's impedance is
<math> Z_C = {1 \over j \omega C} <math>
(where j is the imaginary number, and ω is frequency in radians per second) and the resistor's impedance is simply
<math> Z_R = R <math>
this divider will have the voltage ratio:
<math>{V_{out} \over V_{in}} = {{1 \over j \omega C} \over {1 \over j \omega C} + R} = {1 \over 1 + R j \omega C}<math>
The ratio then depends on frequency, in this case decreasing as frequency increases. This circuit is, in fact, a basic lowpass filter, or, in the world of audio, a treble-cut filter.
See also
External links
- Calculator: voltage divider - loaded and open circuit (http://www.sengpielaudio.com/calculator-voltagedivider.htm)da:Spændingsdeler