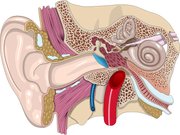
Vestibulocochlear nerve
|
|
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth of twelve cranial nerves, and also known as the auditory nerve. It is the nerve along which the sensory cells (the hair cells) of the inner ear transmit information to the brain. It consists of the cochlear nerve, carrying information about hearing, and the vestibular nerve, carrying information about balance. The auditory nerve is also known as the acoustic nerve.
It emerges from the medulla oblongata and enters the internal acoustic meatus in the temporal bone, along with the facial nerve. The cochlear nerve arises from cells in the spiral ganglion of the cochlea. The peripheral fibers pass on to the hair cells of the cochlea, and the central fibers course through the canal of the modiolus and continue to the internal auditory meatus.
Axons of the cochlear nerve synapse in the cochlear nucleus. Cells in the ventral cochlear nucleus then synapse on cells of the superior olives of the pons on the same side and on the opposite side. These cells compare the timing of impulses from the left and right ears, allowing for auditory localization. Superior olive cells' axons form part of a fibre tract, the lateral lemniscus, and go to the inferior colliculus in the tectum. Cells in the dorsal cochlear nucleus send axons directly via the trapezoid bodies and lateral lemniscus to the inferior colliculus. Dorsal cochlear nucleus cells carry information about the frequency of sounds. Axons of the inferior colliculus synapse on the medial geniculate nucleus of the thalamus on the same side and on the opposite side. Axons of medial geniculate neucleus cells project to the primary auditory cortex, also known as A1.
Some reflex fibers pass on to the motor nuclei of the eye musculature and other motor nerve nuclei of cranial and spinal nerves via the tectospinal and tectobulbar tracts.
Axons of the vestibular nerve synapse in the vestibular nucleus on the lateral floor and wall of the fourth ventricle in the pons and medulla. The vestibular nerve goes to the semicircular canals via the vestibular ganglion. It receives positional information.
Anatomy Clipart and Pictures
- Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Anatomy)
- Anatomy Clip Art (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Clipart/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Animations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Animations/Anatomy)
- Anatomy Illustrations (http://classroomclipart.com/cgi-bin/kids/imageFolio.cgi?direct=Illustrations/Anatomy)