Military of the United States
|
|
| United States armed forces | |
|---|---|
| Military manpower | |
| Military age | 18 years of age |
| Availability | males & females ages 15-49: 73,597,731 (2004 est.) |
| Reaching military age annually | males/females: 2,124,164 (2004 est.) |
| Active troops | 1,427,000 (Ranked 2nd) |
| Military expenditures | |
| Dollar figure | $400 billion (FY2005 est.) |
| Percent of GDP | 3.7% (FY2005 est.) |
The armed forces of the United States of America consist of the
- United States Army
- United States Marine Corps
- United States Navy
- United States Air Force
- United States Coast Guard[1] (https://academickids.com:443/encyclopedia/index.php/Military_of_the_United_States#fn_CoastGuard)
The combined United States armed forces consists of 1.4 million active duty personnel along with several hundred thousand each in the United States Army Reserve and United States National Guard. There is currently no conscription. The armed forces are also members of the United States Uniformed Services. The United States Armed Forces is the most powerful military in the world and their force projection capabilities are unrivaled by any other singular nation or organization (e.g. the European Union). The United States Department of Defense is the controlling organization for the U.S. military and is headquartered at The Pentagon. The Commander-in-Chief of the U.S. military is the President of the United States.
The United States military is a hierarchical military organization, with a system of military ranks to denote levels of authority within the organization. The military service is divided into a professional officer corps along with a greater number of enlisted personnel who perform day to day military operations. Unlike certain other countries, the United States officer corps is not restricted by society class, education, or nobility. United States military officers are appointed from a variety of sources, including the service academies, ROTC, and direct appointment from both civilian status and the enlisted ranks.
The U.S. military also maintains a number of military awards and badges to denote the qualifications and accomplishments of military personnel.
On July 26, 1948 U.S. President Harry S. Truman signed Executive Order 9981 which racially desegregated the military of the United States. Homosexuals, however, are still barred from serving openly (see Don't ask, don't tell.) By law, women may not be put into direct combat, however, assymmetrical warfare has put women into situations, which are not direct combat operations in name only. (approximately 9% of Army positions available; see [2] (http://www.goarmy.com/JobDetail.do?id=47) as an example).
Template:United States armed forces
| Contents |
Capabilities
- Our forces will be strong enough to dissuade potential adversaries from pursuing a military build-up in hopes of surpassing, or equalling, the power of the United States. — President George W. Bush, National Security Strategy, Chapter IX, September 2002.
The United States military is unique in the amount of power it can project globally. Although France and the United Kingdom are capable of projecting limited amounts of power overseas, the United States military is the only military capable of fighting a major regional war at a distance from its homeland. The U.S. is also one of the few nations in the world that has a sizable nuclear arsenal and maintains active doctrines for plausible nuclear attack operations.
As such, much of the U.S. military capabilities are tied up in logistics and transportation, which allow rapid buildup of forces as needed. The Air Force maintains a large fleet of C-5 Galaxy, C-17 Globemaster, and C-130 Hercules transportation aircraft. The Marine Corps maintains Marine Expeditionary Units at sea with the Navy's Atlantic and Pacific Fleets. The Navy's fleet of 12 aircraft carriers, combined with a military doctrine of power projection, enable a flexible response to potential threats.
The United States Army is not as portable as the Marine Corps, but Army Chief of Staff General Peter Schoomaker announced a reorganization of the Army's active-duty units into 48 brigade groups with an emphasis on power projection.
Organization
Under the United States Constitution, the President of the United States is the Commander-in-Chief of the armed forces. To coordinate military action with diplomatic action, the President has an advisory National Security Council.
Under the President is the United States Secretary of Defense, a Cabinet Secretary responsible for the Department of Defense.
Both the President and Secretary are advised by the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
In accordance with the Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1986 (which fundamentally changed the organisation of the Department) the 4 Service Chiefs together with the Chairman and Vice Chairman form the Joint Chiefs of Staff. However operational control flows from the President and Secretary of Defense to the Commanders of the Unified Combatant Commands. (see Goldwater-Nichols Act) Each service is responsible for providing military units to the commanders of the various Unified Commands.
National Command organizational chart
-------------------President--------------
| | | |
| | | |
| SECDEF ----------| |
| | | |
| | Chairman JCOS NSC
| | |
| | |
Regional Combatant JCOS
Commander or Commander
(functional command)
|
|
|
Army, Navy, Air Force,
Marine Corps commanding
officer
Joint Chiefs of Staff
The 4 Service Chiefs together with the Chairman and Vice Chairman form the Joint Chiefs of Staff.
Unified Combatant Commands
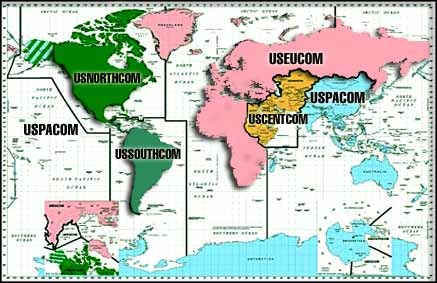
There are 9 Unified Combatant Commands- 5 geographic and 4 functional.
| Command | Commander | Home Base | Area of Responsibility |
| United States Northern Command (NORTHCOM) | Admiral Timothy J. Keating (USN) | Peterson Air Force Base, Colorado | North American homeland defense and coordinating homeland security with civilian forces. |
| United States Central Command (CENTCOM), | General John Abizaid (US Army) | Macdill Air Force Base, Florida | The Horn of Africa through the Persian Gulf region, into Central Asia. |
| U.S. European Command (EUCOM) | General James L. Jones (USMC) (also Supreme Allied Commander Europe(SACEUR)) | Stuttgart-Vaihingen, Germany | Europe and African and Middle Eastern nations not covered by CENTCOM. |
| U.S. Pacific Command (PACOM) | Admiral William J. Fallon (USN) | Honolulu, Hawaii | The Asia-Pacific region including Hawaii. |
| U.S. Southern Command (SOUTHCOM) | General James T. Hill (US Army) | Miami, Florida | South, Central America and the surrounding waters |
| The 5 Geographic Commands | |
|---|---|
 |
| U.S. Special Operations Command (SOCOM) | General Bryan D. Brown (USArmy) | MacDill Air Force Base, Florida | Provides special operations for the Army, Navy, Air Force and Marine Corps. |
| U.S. Joint Forces Command (JFCOM) | Admiral Edmund P. Giambastiani (USN) (also Supreme Allied Commander Transformation (SACT)) | Norfolk, Virginia | Supports other commands as a joint force provider. |
| United States Strategic Command (STRATCOM) | Admiral James O. Ellis Jr. (USN) | Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska | Covers the strategic deterrent force and coordinates the use of space assets. |
| U.S. Transportation Command (TRANSCOM) | General John W. Handy (USAF) | Scott Air Force Base, Illinois | Covers global mobility of all military assets for all regional commands. |
Personnel
Personnel in each service
As of the middle of 2004
| Service | Total Active Duty Personnel | Percentage Female | Enlisted | Officers |
| Army | 500,203 | 15.2% | 414,325 | 69,307 |
| Marine Corps | 176,202 | 6.0% | 157,150 | 19,052 |
| Navy | 375,521 | 14.5% | 319,929 | 55,592 |
| Air Force | 379,887 | 19.6% | ||
| Coast Guard | 40,151 | 10.7% | 31,286 | 7,835 |
Personnel deployed
As of April, 2004
Overseas
The United States has military personnel deployed in numerous countries around the world, with numbers ranging from merely a handful to tens of thousands. Some of the largest contingents are:
| Germany | 75,603 |
| South Korea | 40,258 |
| Japan | 40,045 |
| Italy | 13,354 |
| United Kingdom | 11,801 |
| Iraq | 148,000(2005.05) |
Within the United States
Including territories and ships afloat within territorial waters
A total of 1,168,195 personnel are within the United States including some deployments in:
| Continental U.S. | 1,168,195 |
| Hawaii | 35,810 |
| Alaska | 17,989 |
| Afloat | 120,666 |
Budget Comparison
WorldMilitarySpending.jpg
see main article US military budget
The military expenditure of the Department of Defence for 2004 was:
| Total | $437.111 Billion |
| Operations and maintenance | $174.081 Bil. |
| Military Personnel | $113.576 Bil. |
| Procurement | $76.217 Bil. |
| Research & Development | $60.756 Bil. |
| Military Construction | $6.310 Bil. |
The United States military budget is larger than the military budgets of the next twenty biggest spenders combined, and six times larger than China's, which places second. The United States and its close allies are responsible for approximately two-thirds of all military spending on Earth (of which, in turn, the U.S. is responsible for two-thirds), dollar for dollar. Military spending accounts for more than half of the United States' federal discretionary spending, which is all of the U.S. government's money not spoken for by pre-existing obligations. [3] (http://www.globalissues.org/Geopolitics/ArmsTrade/Spending.asp)
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, in 2003 the United States spent approximately 47% of the world's total military spending of US$956,000,000,000.
Notes
- Template:Anb The United States Coast Guard has both military and law enforcement functions. Title 14, United States Code, Section 1, states "The Coast Guard as established January 28, 1915, shall be a military service and a branch of the armed forces of the United States at all times." In peacetime it is part of the Department of Homeland Security, but in wartime becomes part of the Department of Defense. Coast Guard units have seen combat in every war of the United States, including the U.S. occupation of Iraq.
See also
- Military history of the United States
- List of U.S. military books
- U.S. military historical joint commands
External links
- United States Order of Battle (http://www.geocities.com/Pentagon/9059/usaob.html)
- kamouflage.net > US Military camouflage patterns (http://www.kamouflage.net/camouflage/00181/en_index.php)
de:US-Streitkräfte ja:アメリカ合衆国軍 no:Amerikas forente staters forsvar pl:Siły Zbrojne Stanów Zjednoczonych sl:Oborožene sile Združenih držav Amerike zh:美军
| North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) | 
|
|---|---|
| Belgium | Bulgaria | Canada | Czech Republic | Denmark | Estonia | France | Germany | Greece | Hungary | Iceland | Italy | Latvia | Lithuania | Luxembourg | The Netherlands | Norway | Poland | Portugal | Romania | Slovakia | Slovenia | Spain | Turkey | United Kingdom | United States of America | |
