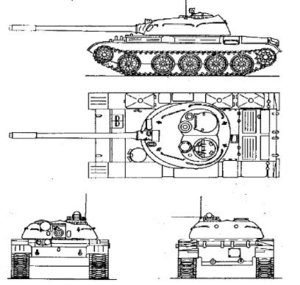
T-55
|
|
| Missing image T-55_skos_RB.jpg Museal Polish T-55 | |
| T-54/55 general characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Crew | 4 (commander, gunner, loader, driver) |
| Length | 6.20 m |
| Width | 3.60 m |
| Height | 2.32 m |
| Weight | 40.5 t |
| Armour | Up to 250 mm. Some late models have appliqué and reactive armour. |
| Base armour | Turret and Hull Front: ~200mm (sloped to equivalent) |
| Primary armament | 100 mm D10 rifled gun. Some late models can fire AT-10 Stabber ATGM) |
| Secondary armament | 7.62 mm PKMT coaxial machine gun, sometimes DShK 12.7 mm antiaircraft machine gun atop turret. |
| Power plant | 462-516 kW (620-690 hp) diesel, sometimes upgraded with a more powerful and reliable engine. |
| Speed | 35 km/h (off-road) |
| Range | 390 km |
The T-54 and T-55 main battle tanks were the Soviet Union's replacements for the World War II era T-34 tank. The T-54/55 tank series is the most produced in the world, and very widely employed, especially by former client states of the Soviet Union.
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are very similar and difficult to distinguish visually. Many T-54s were updated to T-55 standards. Soviet tanks were factory overhauled every 7,000 km, and often given minor technology updates. Many states have added or modified tank equipment (India affixed fake fume extractors to its T-54s and T-55s, so that Indian gunners wouldn't confuse them with Pakistani Type 59s).
T-54 can sometimes be distinguished by a dome-shaped ventilator on the turret front-right, and an SMGT 7.62 mm machine gun in a ball mount in the front of the hull, operated by the driver. Very early T-54s lacked a gun fume extractor, had an undercut at the turret rear, and a distinctive "pig-snout" gun mantlet. The T-55's new turret has large D-shaped panels, visible from above.
| Contents |
|
|
Production history
The first T-54 succeeded the T-44 in production from 1947 as a result of a WWII project. At the time it was better armed and armoured than its Western counterparts, the British Centurion and the American M26 Pershing.
The T-54 was redesigned in 1958 as the T-55, with a thicker turret casting, more powerful engine, and NBC protection. Production continued until 1981 in the Soviet Union. It was also produced in Czechoslovakia, Poland and in China as the Type 59, later redesigned as the Type 69; the Type 69 is still manufactured in China for export today. The Chinese sold thousands of the Type 69 to both Iran and Iraq during their war in the 1980s.
Tens of thousands of T-55 tanks were manufactured in the Soviet Union between 1958 and 1981. It and the T-62 were the two most common tanks in Russian inventory - in the mid-1970s the two types together comprised approximately 85% of the Russian army's tanks. The T-62 and T-55 are now mostly in reserve status; the active-duty units mainly use the T-64 and T-72, with a smaller number of T-80 and T-90 tanks in service (the T-90 in a few units only).
The Israelis captured over a thousand T-55s from the Syrians and Egyptians in the 1967 Six-Day War and the 1973 Yom Kippur War and kept many of them in service. They were upgraded with a 105 mm/L68 NATO-standard main gun replacing the old Soviet 100 mm D10, and a General Motors diesel replacing the original Soviet diesel engine. The Israelis designated these Tiran-5 medium tanks, and were used by reserve units until the early 1990's. Most of them were then sold to assorted Third World countries, some of them in Latin America, and the rest were heavily modified, converted into heavy armoured personnel carriers designated the IDF Achzarit.
The T-55 is considered to be the single most common tank type in the world today. Although it is completely outdated, it remains the tank of choice for many Third World nations who find it fits nicely within their limited budgets. A wide array of upgrades in different price ranges are provided by many manufacturers in different countries, including new engines, Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour, new main armament such as 120 mm or 125 mm guns, active protection suites, laser range-finders, and thermal sights such as the French AGAVA. These improvements make it a potent main battle tank (MBT) for the low-end budget, even to this day.
The T54/55 has been employed by Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Angola, Bangladesh, Central African Republic, China, Congo (Type 59), Cuba, Cyprus, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Finland, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, India, Iraq, Israel, North Korea (Type 59), Libya, Mali, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Pakistan (Type 59), Peru, Somalia, Syria, Uruguay,Yemen, South Yemen, Yugoslavia, Vietnam, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
Variants
- T-54
- T-54A - (early 1950s) added vertical-plane gun stabilizer. Originally had a small counter-weight on the muzzle, but was replaced with a fume extractor in 1955.
- T-54AK - command version with extra communications equipment.
- T-54B - (1957) 2-plane stabilization, IR night-fighting equipment.
- T-54C - temporarily removed AA machine gun and replaced loader's cupola with a flush hatch.
- T-54M - upgraded to T-55M standard (below)
- T-55 - (late 1950s) new turret with floor, over-pressure NBC protection, gamma ray detector, improved engine and power-assisted clutch, greater fuel and ammunition load. Early units had flush loader's hatch.
- T-55A - (1963-1979) anti-radiation protection (leading to visibly protruding turret hatches), dispensed with bow machine gun. T-55A model 1970 restored a 12.7 mm AA machine gun (sometimes called T-55AM).
- T-55 flame-thrower tank.
- MT-55A - bridge-layer tank (mostny tank).
- T-54-T armoured recovery vehicle.
- VT-55A - armoured recovery vehicle
- ZSU-57-2 - self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG); significant changes from T-54 such as much thinner armour and one less road wheel, with a new turret
Modernization
- T-55M - Modernization with ATGM launcher and new fire control system, improved gun stabilization, engine, increased armour. Visual differences include side skirts, smoke grenade launchers, and appliqué armour.
- T-55AM - T-55M with "bra armour" band around turret front.
- T-55AMD - T-55M with Drozd APS.
- T-55AM2 - T-55AM with "bra armour" but no new ATGM and fire control.
- T-55AD Drozd - T-55AM with with Drozd APS.
- T-55AMV - T-55AM with explosive reactive armour (ERA) instead of bra armour.
- T-55AMV-1 - T-55AMV with V-46 engine as T-72.
- T-55AM2PB - mostly made in USSR for East Germany, reactive armour and ATGM, most sold back to Russia in 1992, other T-55 tanks in Russian army upgraded to T-55AM2PB standards during 1992-2000.
International derivatives
Israel
- Tiran-5 - upgraded Israeli version built on tanks captured in 1967 and 1973, no longer in service in Israel but many were sold off.
China
- Type 59 - copy of T-55
- Type 69 - redesigned Type 59
Iraq
- T-55 Enigma - T-55, Type-59, and Type-69 tanks used by Iraqi Brigade commanders had appliqué armour on turrets and hulls composed of steel filled with concrete. Intended to, and in many cases successful at defeating shaped charge warheads (one example is reported to have survived several hits form Milan missiles before being dispatched by a helicopter).
- T-55QM - had NATO-standard 105 mm/L68 gun installed replacing the old 100 mm gun, along with a French laser range-finder), upgrades done in mid to late 1980s.
- T-55QM2 - T-55 upgraded by Russian technicians with a Russian 125 mm/L80 smoothbore gun and French laser range-finder, 1986-1991.
- Type 69-QM - Type 69 upgraded with NATO standard 105 mm gun and laser range-finder, 1984-1988.
- Type 69-QM2 - Type 69 upgraded with Warsaw Pact standard 125 mm/L80 smoothbore gun and laser rangefinder, 1986-1991.
Romania
- TR-77, or M-77 - (1977-1991) unlicensed redesign exported very widely
Combat history
- Hungary in 1956.
- Czechoslovakia in 1968.
- Israel-Arab wars in 1967 and 1973.
- Southeast Asia. (Vietnam, Cambodia)
- "Brushfire Wars" (Angola, Congo)
- Afghan Wars
- Chechen Wars
- Iran-Iraq War
- Gulf War.
See also
- List of tanks
- List of Soviet tanks
- T-64, T-80, T-84
- T-72, T-90, T-95
- Kharkiv Morozov Machine Building Design Bureau
de:T-54 de:T-55 fr:Char T-54 he:T-54 ja:T-55 pl:T-55 fi:T-55