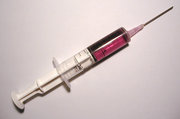
Syringe
|
|
A syringe consists of a plunger fitted to a tube, called the barrel, which has a small opening on one end. Syringes are used to transfer small amounts of liquids or gasses to or from otherwise inaccesible areas. It operates on the principle of suction by filling the barrel with the subtance at the opening when the plunger is drawn out, and expelling the substance when the plunger is depressed. The process of administering a substance with a syringe and needle is called an injection. The word syringe comes from the Greek syrinx, which means "tube".
Needle syringes
Syringes are used in conjunction with hypodermic needles for injections of liquid or gasses into body tissues, or for their removal from the body. They may also be used for injections across the rubber septum of a medical device, container, or scientific apparatus such as in certain types of chromatography. The injection of a air into an artery is undesireable, as it may cause a gas embolism. Prevention of embolisms by removing air from the syringe is the source of the familiar image of holding a syringe upside down, tapping it, and expelling a small amount of liquid before and injection into the bloodstream. However, some surgical techniques, such as laproscopy, sometimes involve injecting air into a body cavity.
The barrel of a syringe is made of either plastic or glass, and usually has graduated marks indicating the volume of fluid in the syringe. Glass syringes may be sterilized by the use of an autoclave, however, modern medical syringes are made from plastic because it is cost-effective to dispose of them, which further reduces the risk of spreading blood-borne diseases. The re-use of needles and syringes has been associated with the spread of diseases, especially HIV and Hepatitis among IV drug users.
In applications where transfer of pathogens is not an issue and a very high degree of precision is important (i.e. quantitative chemical analysis), glass syringes are still used because their tolerance is lower and the plunger moves more smoothly.
Syringes may also be used when cooking meat to enhance flavor and texture by injecting juices inside the meat, and in baking to inject filling inside a pastry
Rectal and vaginal syringes
For the administration of enemas or douches, there exist bulb syringes where a bulb is fitted with a nozzle, liquid is pumped into it, the nozzle is inserted into the rectum or vagina and the bulb is pressed upon for injection. There also exist fountain syringes where the liquid is in a bag or can and goes to the nozzle via a pipe. In earlier times, clyster syringes were used for that purpose.
External links
- Who invented the syringe (http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/blsyringe.htm)de:Spritze