Receptor antagonist
|
|
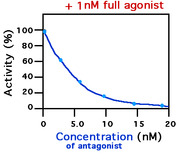
In medicine and biology, an antagonist is a substance that inhibits the normal physiological function of a receptor. Many drugs work by blocking the action of endogenous receptor agonists such as hormones and neurotransmitters. Antagonists that compete with an agonist for a receptor are competitive antagonists. Those that antagonize by other means are non-competitive antagonists.
Antagonists stop the agonists from acting on certain receptors by blocking it.