Agonist
|
|
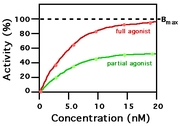
An agonist is a substance that binds to a receptor and triggers a response in the cell. An agonist is the opposite of an antagonist in the sense that while an antagonist also binds to the receptor, it fails to activate the receptor and actually blocks it from activation by agonists. A partial agonist activates a receptor but does not cause as much of a physiological change as does a full agonist. The receptors of the human body work by being stimulated or inhibited by natural (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or synthetic (such as drugs) agonists and antagonists. Recently a novel theory called functional selectivity has been proposed that broadens the conventional definition of pharmacology.
Etymology
Stems from the Late Latin word agnista, 'contender', from the Greek agnists, 'contestant', from agn, 'contest'. An agonist is a chemical contestant or contender.ja:アゴニスト sr:Агониста