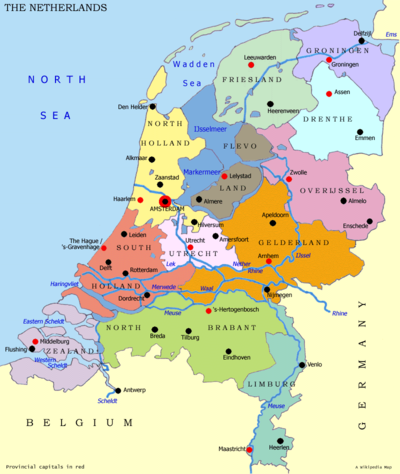
Provinces of the Netherlands
|
|
The modern day Netherlands are divided into twelve provinces (provincies in Dutch), listed below with their capital city:
See also the ranked list of Dutch provinces
| Contents |
Structure
A Dutch province represents the administrative layer in between the national government and the local municipalities, having the responsibility for matters of subnational or regional importance. The government of each province consists of three major parts: the Provinciale Staten which is the provincial parliament elected every four years. Elected from its members are the Gedeputeerde Staten, a college charged with most executive tasks, presided by the Commissaris van de Koningin or royal commissioner, appointed by the Crown.
Historical background
Nearly all Dutch provinces can trace their origin to a mediaeval state such as a county or a duchy, as can the provinces of Belgium. Their status changed when they came under a single ruler who centralised their administration, somewhat relegating the separate states to provinces, 17 in total. From these unified Netherlands, seven northern provinces would form the Republic of the Seven United Provinces in the 16th century, namely Holland, Zeeland, Gelderland, Utrecht, Friesland, Overijssel and Groningen. The Republic's lands also included Drenthe (one of the 17, but without the autonomous status of the others), and parts of Brabant, Limburg and Flanders, which were considered to be "conquered lands" and were governed directly by the Staten-Generaal, the parliament, hence their name Generality Lands. They were called Staats-Brabant, Staats-Limburg and Staats-Vlaanderen, meaning "of the state". Each of these "Netherlands" had a high degree of autonomy, co-operating with each other mainly on defense and on the international level in general, but keeping to their own affairs elsewhere.
On January 1, 1796, during the Batavian Republic, Drenthe and Staats-Brabant became the eighth and ninth provinces of the Netherlands; the latter known as Bataafs Brabant, Batavian Brabant, changing its name to Noord Brabant, North Brabant, in 1815 when it became part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, which also contained (then) South Brabant, a province in Belgium. This new unified state featured the provinces in their modern form, as non-autonomous subdivisions of the national state, and again numbering 17 provinces, though not all the same as the 16th century ones. In 1839, with the independence of Belgium, the original single province of Limburg was divided amongst the two countries, each now having a province called Limburg. A year later, Holland, the largest and most populous of the Dutch provinces, was also split into two provinces for a total of 11. The 12th member was to be Flevoland, a province consisting almost entirely of reclaimed land, established on January 1, 1986.
The Departments of the French Period
During the Batavian Republic, the Netherlands were from 1798 to 1801 completely reorganised into 8 new departments, most named after rivers, inspired by the French revolutionary example, in an attempt to do away with the old autonomous provincial status. They are listed below, with their capitals and the territory of the former provinces they mostly incorporated:
| English name | Dutch name | Capital | Contained the territory of |
|---|---|---|---|
| Department of the Ems | Departement van de Eems | Leeuwarden | Northern Friesland, Groningen |
| Department of the Old IJssel | Departement van de Oude IJssel | Zwolle | Southern Friesland, Drenthe, Overijssel, northern Gelderland |
| Department of the Rhine | Departement van de Rijn | Arnhem | Central Gelderland, eastern Utrecht |
| Department of the Amstel | Departement van de Amstel | Amsterdam | The area around Amsterdam |
| Department of Texel | Departement van Texel | Alkmaar | Northern Holland minus Amsterdam, northwestern Utrecht |
| Department of the Delf | Departement van de Delf | Delft | Southern Holland up to the Meuse, southwestern Utrecht |
| Department of the Dommel | Departement van de Dommel | 's-Hertogenbosch | The eastern part of Batavian Brabant, southern Gelderland |
| Department of the Scheldt and Meuse | Departement van de Schelde en Maas | Middelburg | Zeeland, Holland south of the Meuse and the western part of Batavian Brabant |
After only three years, following a coup d'etat, the borders of the former provinces were restored, though not their autonomous status. They were now also called "departments" and Drenthe was added to Overijssel. In 1806 the Kingdom of Holland replaced the republic to further French interests. It was during this administration that Holland was first split in two, with the department of Amstelland to the north and that of Maasland to the south. East-Frisia, then as now in Germany, was added to the kingdom as a department in 1807 and Drenthe split off again making a total of 11 departments.
When the Netherlands finally did become fully part of France in 1810, the departments of the kingdom and their borders were largely maintained, with some joined together. They were however nearly all renamed, again mainly after rivers, though the names differed from their Batavian counterparts. Following are their names and the modern day province they corresponded for the most part to:
| English name | French name | Dutch name | Modern province(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Department of the Zuiderzee | Département du Zuyderzée | Departement van de Zuiderzee | North Holland & Utrecht |
| Department of the Mouths of the Meuse | Département des Bouches-de-la-Meuse | Departement van de Monden van de Maas | South Holland |
| Department of the Mouths of the Scheldt | Département des Bouches-de-l'Escaut | Departement van de Monden van de Schelde | Zeeland |
| Department of the Two Nethes | Département des Deux-Nèthes | Departement van de Twee Nethen | Western North Brabant & Antwerp |
| Department of the Mouths of the Rhine | Département des Bouches-du-Rhin | Departement van de Monden van de Rijn | Eastern North Brabant & southern Gelderland |
| Department of the Upper IJssel | Département de l'Yssel-Supérieur | Departement van de Boven IJssel | Northern Gelderland |
| Department of the Mouths of the IJssel | Département des Bouches-de-l'Yssel | Departement van de Monden van de IJssel | Overijssel |
| Department of Frisia | Département de la Frise | Departement Friesland | Friesland |
| Department of the Western Ems | Département de l'Ems-Occidental | Departement van de Wester Eems | Groningen & Drenthe |
| Department of the Eastern Ems | Département de l'Ems-Oriental | Departement van de Ooster Eems | (East-Frisia) |
With the defeat and withdrawal of the French in 1813, the old provinces and their names were re-established, Holland was reunited and East-Frisia went its separate way. The 17 provinces of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands were for a significant part based on the former French departments and their borders, in particular in what would later become Belgium.
See also
External links
- Population and area figures (http://www.world-gazetteer.com/r/r_nl.htm)
- Basic data for each province, with links to official province sites (http://www.sdu.nl/staatscourant/scdata/prov/provincies.htm)
- http://www.statoids.com/unl.html
Template:Footer Provinces of the Netherlandsde:Provinzen der Niederlande fr:Provinces des Pays-Bas it:Province dei Paesi Bassi nl:Nederlandse provincies id:Daftar Provinsi Belanda