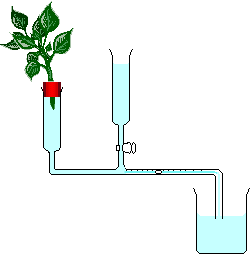
Potometer
|
|
A potometer is a device used for measuring the rate of water uptake of a leafy plant shoot. The main reason for water uptake by a cut shoot is transpiration.
By changing the surrounding atmospheric conditions, the effect on transpiration of wind, heat, and humidity can be measured. Potometers are notoriously difficult to set up, because air bubbles in the xylem of the plant or in the apparatus itself will prevent the device from working properly.
The basic design of a potometer
Potometers come in a variety of designs, but all follow the same basic principle. The device shown in the diagram is a Ganong's Potometer. It consists of:
- A length of capillary tube A bubble is introduced to the capillary. As water is taken up by the plant, the bubble moves. The distance the bubble travels in a given time is determined by the rate of water uptake by the plant.
- A reservoir. By turning the tap on the reservoir, the position of the bubble can be set at the start of the experiment. Some designs of potometer use a syringe instead of a funnel with a tap.
- A tube for holding the shoot. In the diagram the shoot is held in place by inserting a rubber bung in the tube. The hole in the bung through which the shoot passes must be thoroughly greased with petroleum jelly to keep it airtight.
Setting up
- Cut a leafy shoot from a plant (e.g. Pelargonium) and plunge its base into water {try not to get any water on the leaves}. This prevents the xylem from taking up any air.
- Back in the laboratory, put the stem into a large sink full of water and carefully trim the shoot again, by cutting off the bottom under water with a sharp razor blade. Keep the leaves out of the water.
- Immerse the whole of the potometer into the sink. Move it about until all the air bubbles come out.
- Put the shoot stem into the bung, grease the joint with plenty of petroleum jelly, then put the bung into the potometer.
- Make sure the tap is closed, then lift the whole ensemble out of the water.
- Leave the end of the capillary tube out of the water until an air bubble forms then put the end into a beaker of water.
Using a potometer
Allow the bubble time to round the corner and start at the beginning of the mm scale. Then time how far the bubble moves in a given period of time. Repeat under different conditions and compare. The usual conditions to try is placing the plant in a bright light, placing it by a fan, and placing it in a humid atmosphere.
See also: Transpiration, School Biology experiments and demonstrations, How-to's