Old English language
|
|
Old English (also called Anglo-Saxon) is an early form of the English language that was spoken in England and southern Scotland between the mid-fifth century and the mid-twelfth century. It is a West Germanic language and therefore is similar to Old Frisian and Old Saxon. It is also quite similar to Old Norse (and by extension, to modern Icelandic). Unlike modern English, Old English is a language rich with morphological diversity and is pronounced essentially as it is spelt. It maintains several distinct cases: the nominative, accusative, genitive, dative and instrumental, remnants of which survive only in a few pronouns in modern English.
Old English was not static, and its usage covered a period of some 700 years – from the Anglo-Saxon migrations into England of the fifth century to some time after the Norman invasion of 1066, when the language underwent a major and dramatic transition. During this period of time it assimilated some aspects of the languages that it came in contact with, such as the Celtic languages and the two variants of the Scandinavian languages from the invading Norsemen who were occupying and controlling the Danelaw in northern and eastern England.
The term Old English does not strictly refer to older varieties of Modern English such as are found in Shakespeare or the King James Bible, which are called Early Modern English by linguists. In some older works (such as the 1913 edition of Webster's Dictionary), Old English refers to Middle English, or also more specifically Middle English as used from 1150 to 1350, with the older form of the language referred to exclusively as Anglo-Saxon. [1] (http://machaut.uchicago.edu/?resource=Webster%27s&word=English)
| Contents |
Germanic origins
The most important shaping force on Old English was its Germanic heritage in vocabulary, sentence structure and grammar, that it shared with its sister languages in continental Europe. Some of these features were specific to the West Germanic language family to which Old English belongs, while some other features were inherited from the Proto-Germanic language from which all Germanic languages are believed to have been derived.
Though many of these links with the other Germanic languages have since been obscured by later linguistic influences, particularly Norman French, many remain even in modern English. Compare modern English 'Good day' with the Old English Gódne dæg, modern Dutch Goeden dag, or modern German Guten Tag.
Like other West Germanic languages of the period, Old English was fully inflected with five grammatical cases, which had dual plural forms for referring to groups of two objects, in addition to the usual singular and plural forms. It also assigned gender to all nouns, even to those that describe inanimate objects: for example, séo sunne (the Sun) was feminine, while se móna (the Moon) was masculine.
Latin influence
The influence of Latin on Old English should not be ignored. A large percentage of the educated and literate population (monks, clerics, etc.) were competent in Latin, which was then the prevalent lingua franca of Europe. It is sometimes possible to give approximate dates for the entry of individual Latin words into Old English based on which patterns of linguistic change they have undergone, though this is not always reliable. There were at least three notable periods of Latin influence. The first occurred before the ancestral Saxons left continental Europe for England. The second began when the Anglo-Saxons were converted to Christianity and Latin-speaking priests became widespread. However, the largest single transfer of Latin-based words occurred following the Norman invasion of 1066, after which an enormous number of Norman French words entered the language. Most of these Oïl language words were themselves derived ultimately from classical Latin, although a notable stock of Norse words were introduced, or re-introduced in Norman form. The Norman Conquest approximately marks the end of Old English and the advent of Middle English.
The language was further altered by the transition away from the runic alphabet (also known as futhorc) to the Latin alphabet, which was also a significant factor in the developmental pressures brought to bear on the language. Old English words were spelt as they were pronounced; the silent letters of Modern English therefore did not often exist in Old English. For example, the 'hard-c' sound in cniht, the Old English equivalent of 'knight' was pronounced. Another side-effect of spelling words phonetically was that spelling was extremely variable – the spelling of a word would reflect differences in the phonetics of the writer's regional dialect and also idiosyncratic spelling choices which varied from author to author. Thus, for example, the word "and" could be spelt either "and" or "ond".
Therefore, Old English spelling can be regarded as even more jumbled than modern English spelling, although it can at least claim to reflect some existing pronunciation, while modern English in many cases cannot. Most students of Old English in the present day learn the language using normalised versions and are only introduced to variant spellings after they have mastered the basics of the language.
Viking influence
Old_norse,_ca_900.PNG
The second major source of loanwords to Old English were the Scandinavian words introduced during the Viking raids of the ninth and tenth centuries. These tend to be everyday words, and those which are concerned with particular administrative aspects of the Danelaw (that is, the area of land under Viking control, which included extensive holdings all along the eastern coast of England and Scotland). The Vikings spoke Old Norse, a language which is related to English in that they both derive from the same ancestral Germanic language. It is very common for the intermixing of speakers of different dialects, such as occurs during times of political unrest, to result in a simplified koine, and one theory holds that exactly such a mixture of Old Norse and Old English helped accelerate the decline of case endings in Old English. Apparent confirmation of this is the fact that simplification of the case endings occurred earliest in the North and latest in the Southwest, the area farthest away from Viking influence.
Celtic influence
The number of Celtic loanwords is of a much lower order than either Latin or Scandinavian. As few as twelve loanwords have been identified as being entirely secure. Out of all the known and suspected Celtic loanwords, most are names of geographical features, and especially rivers.
Dialects
To further complicate matters, Old English was rich in dialect forms. The four main dialect forms of Old English were Kentish, Mercian, Northumbrian and West Saxon. Each of these dialects were associated with an independent kingdom on the island. Of these, all of Northumbria and most of Mercia were overrun by the Vikings during the 9th century. The portion of Mercia and all of Kent that were both successfully defended, were then integrated into Wessex.
After the process of unification of the diverse Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in 878 by Alfred the Great, there is a marked decline in the importance of regional dialects. This is not because they stopped existing: regional dialects continued even after that time to this day, as evidenced both by the existence of middle and modern English dialects later on, and by common sense – people do not spontaneously develop new accents when there is a sudden change of political power.
However, the bulk of the surviving documents from the Anglo-Saxon period are written in the dialect of Wessex, Alfred's kingdom. It seems likely that with consolidation of power, it became necessary to standardise the language of government to reduce the difficulty of administering the remoter areas of the kingdom. As a result, paperwork was written in the West Saxon dialect. Not only this, but Alfred was passionate about the spread of the vernacular, and brought many scribes to his region from Mercia in order that previously unwritten texts were recorded. The Church was likewise affected, especially since Alfred initiated an ambitious programme to translate religious materials into the vernacular. In order to retain his patronage and ensure the widest circulation of the translated materials, the monks and priests engaged in the programme worked in his dialect. Alfred himself seems to have translated books out of Latin and into English, notably Pope Gregory I's treatise on administration, "Pastoral Care".
Due at least partially to the centralisation of power and to the Viking invasions, there is little or no written evidence for the development of non-Wessex dialects after Alfred's unification.
Phonology and standardised orthography
Old English was at first written in runes (futhorc), but shifted to the Latin alphabet with some additions: the letter yogh, adopted from Irish; the letter eth and the runic letters thorn and wynn. Also used was a symbol for the conjunction 'and', a character similar to the number seven ('7'), and a symbol for the relative pronoun 'þæt', a thorn with a crossbar through the ascender ('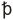 '). Also used occasionally were macrons over vowels, abbreviations for following 'm's or 'n's. All of the sound descriptions below are given using IPA symbols.
'). Also used occasionally were macrons over vowels, abbreviations for following 'm's or 'n's. All of the sound descriptions below are given using IPA symbols.
Consonants
- b:
- c: between or before front vowels: ; otherwise in all other positions except after an 's' (see sc) or before a 'g'. The 'soft-c' ) is sometimes written with a diacritic by modern speakers for the sake of pronunciation, like so: 'ċ' or 'č' or 'ç'.
- cg:
- d:
- ð/þ: initially, finally or between a vowel and a voiceless consonant: ; between two vowels or between a vowel and a voiced consonant: . In the modern orthography, all voiceless 'ð'/'þ's use the þ (thorn), while all voiced ones use the ð (eth).
- ðð/þþ:
- f: initially, finally or between a vowel and a voiceless consonant: ; between two vowels or between a vowel and a voiced consonant: .
- ff:
- g: between or before front vowels: ; after a front vowel and before a consonant: ; otherwise in all other positions. The 'soft-g' ) is sometimes written with a diacritic by modern speakers for the sake of pronunciation, represented as 'ġ' or the number three ('3') – representing yogh ), which is not to be confused with ezh ), a similar looking letter.
- h: initial or following a consonant: ; following a back vowel or a diphthong beginning with a back vowel: ; following a front vowel or a diphthong beginning with a front vowel: .
- hl: – a voiceless alveolar lateral fricative, like the Welsh letter 'll'.
- ': , replaced in modern print by hw' – a voiceless labial-velar fricative, like the Scots letter 'wh'.
- k: (rarely used)
- l:
- m:
- n: when before a 'g' or 'c': ; otherwise .
- p:
- q: – Used before a 'u' representing the consonant , but rarely used, being rather a feature of Middle English. Old English preferred or in modern print 'cw'.
- r: either or perhaps found in modern English.
- s: initially, finally or between a vowel and a voiceless consonant: ; between two vowels or between a vowel and a voiced consonant: .
- sc: or unpredictably , however is by far the more common, while is used only in a few words, the most common being 'ascian' ('to ask').
- ss:
- t:
- ' (wynn): , replaced in modern print by w'.
- x:
- z: rarely used as 'ts' was usually used instead, for example 'bezt' vs 'betst', said as meaning 'best'.
Doubled consonants have doubly long durations; 'ðð'/'þþ', 'ff' and 'ss' are shown above only to demonstrate that they cannot be voiced as their single constituents can be.
Vowels
Pure vowels and diphthongs in Old English have two degrees of length; though the distinction was originally unwritten, in our modern orthography we use acute accents (as in this article), macrons or following colons to denote long vowels and leave short ones unmarked.
Pure vowels
- a: or before in some cases (for example 'land', which was often said as )
- á: or
- æ:
- ǽ: or
- e: or
- é:
- i:
- í:
- o: or
- ó:
- u:
- ú:
- y:
- ý:
Diphthongs
- ea:
- éa:
- eo: or or or
- éo: or
- ie: or
- íe: or
Old English grammar
Syntax
As a West Germanic language, Old English syntax has a great deal of common ground with Dutch and German. Old English is not dependent upon S (subject), V (verb), O (object) or "SVO" word order in the way that Modern English is. The syntax of an Old English sentence can be in any of these shapes: SVO order, VSO order, and OVS order. The only constant rule, as in German and Dutch, is that the verb must come as the second concept. That is, in the sentence 'in the town, we ate some food', it could appear as 'in the town, ate we some food', or 'in the town, ate some food we'. This variable word order is especially common in poetry. Prose, while still displaying variable word order, is much more likely to use SVO ordering. Similarly, word order became less flexible as time went on: the older a text is, the less likely it is to have a fixed word order.
To further complicate the matter, prepositions may appear after their object, though they are not postpositions, as they may occur in front of the noun too, and usually do, for example:
God cwæð him þus tó (lit.) God said him thus to that is God said thus to him
Verbs
Verbs in Old English are divided into strong or weak verbs. For a fuller discussion of these, see Germanic weak verb and West Germanic strong verb.
Strong verbs
Strong verbs use the Germanic form of conjugation (known as Ablaut). In this form of conjugation, the stem of the word changes to indicate the tense. We still have verbs like this in modern English, for example "sing, sang, sung" is a strong verb, as are "swim, swam, swum" and "choose, chose, chosen." The root portion of the word changes rather than its ending. In Old English, there were seven major classes of strong verb; each class has its own pattern of stem changes. Learning these is a major challenge for students of the language.
The classes had the following distinguishing features to their infinitive stems:
- + 1 consonant.
- or + 1 consonant.
- Originally e + 2 consonants (This was no longer the case by the time of written Old English).
- e + 1 consonant (usually l or r, plus the verb brecan 'to break').
- e + 1 consonant (usually a stop or a fricative).
- a + 1 consonant.
- No specific rule – first and second have identical stems or ), and the infinitive and the past participle also have the same stem.
| Stem Changes in Strong Verbs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Infinitive | First Preterite | Second Preterite | Past Participle |
| I | í | á | i | i |
| II | éo or ú | éa | u | o |
| III | see table below | |||
| IV | e | æ | ǽ | o |
| V | e | æ | ǽ | e |
| VI | a | ó | ó | a |
| VII | – | é or éo | é or éo | – |
The first preterite stem is used in the preterite tense, for the first and third persons singular. The second preterite stem is used for second person singular, and all persons in the plural (as well as the preterite subjunctive).
The third class went through so many sound changes that it was barely recognisable as a single class. The first was a process called 'breaking'. Before <h>, and <r> + another consonant, <æ> turned into <ea>, and <e> to <eo>. Also, before <l> + another consonant, the same happened to <æ>, but <e> remained unchanged (except before combination <lh>).
The second sound-change to affect it was the influence of palatal sounds <g>, <c>, and <sc>. These turned anteceding <e> and <æ> to <ie> and <ea>, respectively.
The third sound change turned <e> to <i>, <æ> to <a>, and <o> to <u> before nasals.
Altogether, this split the third class into five sub-classes:
- e + two consonants (apart from clusters beginning with l).
- eo + r or h + another consonant.
- e + l + another consonant.
- g, c, or sc + ie + two consonants.
- i + nasal + another consonant.
| Stem Changes in Class III | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-class | Infinitive | First Preterite | Second Preterite | Past Participle |
| a | e | æ | u | o |
| b | eo | ea | u | o |
| c | e | ea | u | o |
| d | ie | ea | u | o |
| e | i | a | u | u |
Regular strong verbs were all declined roughly the same, with the main differences being in the stem vowel.
Weak verbs
Weak verbs are formed principally by adding endings to past and participles. An example is "walk, walked" or "look, looked". There are only three different classes of weak verb.
Linguistic trends have greatly favoured weak verbs over the last 1200 years. In Old English, especially early on, strong verbs were the dominant form of verb. Today, there are many more weak verbs than strong verbs. Some verbs that were originally strong have become weak; most foreign verbs are adopted as weak verbs; and when verbs are made from nouns (for example "to scroll" or "to water") the resulting verb is weak. Additionally, weak verbs are easier to conjugate, since there are fewer different classes of them. In combination, these factors have drastically reduced the number of strong verbs, so that in modern English weak verbs are the dominant form (although occasionally a weak verb may turn into a strong verb through the process of analogy, such as "to spit" or "to sneak").
Atypical verbs
Additionally there is a further group of four verbs which are anomalous, the verbs "will", "do", "go" and "be". These four have their own conjugation schemes which differ significantly from all the other classes of verb. This is not especially unusual: "will", "do", "go", and "be" are the most commonly used verbs in the language, and are very important to the meaning of the sentences they are used in. They have their own conjugation schemes to make them as distinct as possible, to reduce the possibility that a listener will mis-hear the word.
Dón 'to do', gán 'to go', and willan 'will' are conjugated alike:
| Conjugation | Pronoun | 'do' | 'go' | 'will' |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infinitive | – | dón | gán | willan |
| Present Indicative | ||||
| ic | dó | gá | wille | |
| þú | dést | gǽst | wilt | |
| hé/hit/hé | déð | gǽð | wile | |
| wé/gé/híe | dóð | gáð | willað | |
| Past Indicative | ||||
| ic/hé/hit/héo | dyde | éode | wolde | |
| þú | dydest | éodest | woldest | |
| wé/gé/híe | dydon | éodon | woldon | |
| Present Subjunctive | (all persons) | dó | gá | wille |
| Past Subjunctive | (all persons) | dyde | éode | wolde |
| Present Participle | dónde | – | willende | |
| Past Participle | gedón | gegán | – | |
The verb 'to be' is actually composed of three different stems:
| Conjugation | Pronoun | Present | Future | Past |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infinitive | – | sindon | béon | wesan |
| Present Indicative | ||||
| ic | eom | béo | wese | |
| þú | eart | bist | wesst | |
| hé/hit/héo | is | bið | wes(t) | |
| wé/gé/híe | sind(on) | béoð | wesað | |
| Past Indicative | ||||
| ic | – | – | wæs | |
| þú | – | – | wǽre | |
| hé/hit/héo | – | – | wæs | |
| wé/gé/híe | – | – | wǽron | |
| Present Subjunctive | ||||
| ic/þú/hé/hit/héo | síe | béo | wese | |
| wé/gé/híe | síen | béon | wesen | |
| Past Subjunctive | ||||
| ic/þú/hé/hit/héo | – | – | wǽre | |
| wé/gé/híe | – | – | wǽren | |
| Imperative | ||||
| (singular) | – | béo | wes | |
| (plural) | – | béoð | wesað | |
| Present Participle | – | béonde | wesende | |
| Past Participle | – | gebéon | – | |
The present forms of wesan are almost never used. The béon forms are usually used in reference to future actions. The modern verb 'to be' takes its present indicative forms from sindon, its past indicative forms from wesan, its present subjunctive forms from béon, its past subjunctive forms from wesan, and its imperative and particicple forms from béon.
Nouns
Old English nouns were declined – that is, the ending of the noun changed to reflect its function in the sentence. There were five major cases: nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, and instrumental.
- The nominative case indicated the subject of the sentence, for example cyning means 'king'. It was also used for direct address. Adjectives in the predicate (qualifying a noun on the other side of 'to be') were also in the nominative.
- The accusative indicated the direct object of the sentence, for example "Æþelbald lufode cyning" means "Æþelbald loved the king", where Æþelbald is the subject and the king is the object. Already the accusative had begun to merge with the nominative; it was never distinguished in the plural, or in a neuter noun.
- The genitive case indicated possession, for example the "cyninges scip" is "the ship of the king" or "the king's ship". It also indicated partitive nouns.
- The dative case indicated the indirect object of the sentence, for example "hringas cyninge" means "rings for the king" or "rings to the king". There were also several verbs which took direct objects in the dative.
- The instrumental case indicated an instrument used to achieve something, for example "lifde sweorde", "he lived by the sword", where sweorde is the instrumental form of 'sweord'. During the Old English period, the instrumental was falling out of use, having largely merged with the dative. Only pronouns and strong adjectives retained separate forms for the instrumental.
There were different endings depending on whether the noun was in the singular (for example, hring 'one ring') or plural (for example, hringas 'many rings').
Nouns are also categorised by grammatical gender – masculine, feminine, or neuter. Masculine and neuter words generally share their endings. Feminine words have their own subset of endings. The plural does not distinguish between genders.
Furthermore, Old English nouns are divided as either strong or weak. Weak nouns have their own endings. In general, weak nouns are easier than strong nouns, since they had begun to lose their declensional system. However, there is a great deal of overlap between the various classes of noun: they are not totally distinct from one another. There are only a couple dozen endings in practice, so it's a lot easier than it sounds at first.
Here are the strong declensional endings and examples for each gender:
| The Strong Noun Declension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | – | -as | – | -u/– | -u/– | -a |
| Accusative | – | -as | – | -u/– | -e | -a, -e |
| Genitive | -es | -a | -es | -a | -e | -a |
| Dative | -e | -um | -e | -um | -e | -um |
For the '-u/–' forms above, the '-u' is used with a root consisting of a single short syllable or ending in a long syllable followed by a short syllable, while roots ending in long a syllable or two short syllables are not inflected. (A long syllable contains a long vowel or is followed by two consonants. Note also that there are some exceptions; for example, feminine nouns ending in -þu such as strengþu 'strength'.)
| Example of the Strong Noun Declension for each Gender | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine engel 'angel' | Neuter scip 'ship' | Feminine sorg 'sorrow' | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | engel | englas | scip | scipu | sorg | sorga |
| Accusative | engel | englas | scip | scipu | sorge | sorga/sorge |
| Genitive | engles | engla | scipes | scipa | sorge | sorga |
| Dative | engle | englum | scipe | scipum | sorge | sorgum |
Note the syncopation of the second e in engel when an ending follows. This syncopation of the vowel in the second syllable occurs with two-syllable strong nouns which have a long vowel in the first syllable and a second syllable consisting of a short vowel and single consonant (for example, engel, wuldor 'glory', and héafod 'head'). However, this syncopation is not always present, so forms such as engelas may be seen.
Here are the weak declensional endings and examples for each gender:
| The Weak Noun Declension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | -a | -an | -e | -an | -e | -an |
| Accusative | -an | -an | -e | -an | -an | -an |
| Genitive | -an | -ena | -an | -ena | -an | -ena |
| Dative | -an | -um | -an | -um | -an | -um |
| Example of the Weak Noun Declension for each Gender | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine nama 'name' | Neuter éage 'eye' | Feminine tunge 'tongue' | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | nama | naman | éage | éagan | tunge | tungan |
| Accusative | naman | naman | éage | éagan | tungan | tungan |
| Genitive | naman | namena | éagan | éagena | tungan | tungena |
| Dative | naman | namum | éagan | éagum | tungan | tungum |
In addition, nouns which end in '-or' are unchanged as per usual in the uninflected forms, but the '-or' is removed and '-r' suffixed to the root for all suffixed forms. Also masculine and neuter nouns whose main vowel is short 'æ' and end with a single consonant change the vowel to 'a' in the plural. Here are a couple of examples of such declensions:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Some masculine and neuter nouns end in -e in their base form. These drop the -e and add normal endings. Note that neuter nouns in -e always have -u in the plural, even with a long vowel:
| Example of the Strong Noun Declensions ending in -e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine ende 'end' | Neuter stýle 'steel' | ||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |||
| Nominative | ende | endas | stýle | stýlu | ||
| Accusative | ende | endas | stýle | stýlu | ||
| Genitive | endes | enda | stýles | stýla | ||
| Dative | ende | endum | stýle | stýlum | ||
Nouns ending in -h lose this when an ending is added, and lengthen the vowel in compensation (this can result in compression of the ending as well):
| Example of the Strong Noun Declensions ending in -h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine mearh 'horse' | Neuter feorh 'life' | Masculine scóh 'shoe' | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | mearh | méares | feorh | feorh | scóh | scós |
| Accusative | mearh | méares | feorh | feorh | scóh | scós |
| Genitive | méares | méara | féores | féora | scós | scóna |
| Dative | méare | méarum | féores | féorum | scó | scóm |
Nouns whose stem ends in -w change this to -u or drop it in the nominative singular. (Note that this '-u/–' distinction depends on syllable weight, as for strong nouns, above.)
| Example of the Strong Noun Declensions ending in -w | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Neuter smeoru 'grease' | Feminine sinu 'sinew' | Feminine lǽs 'pasture' | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | smeoru | smeoru | sinu | sinwa | lǽs | lǽswa |
| Accusative | smeoru | smeoru | sinwe | sinwa, -e | lǽswe | lǽswa, -e |
| Genitive | smeorwes | smeorwa | sinwe | sinwa | lǽswe | lǽswa |
| Dative | smeorwe | smeorwum | sinwe | sinwum | lǽswe | lǽswum |
A few nouns follow the -u declension, with an entirely different set of endings. The following examples are both masculine, although feminines also exist, with the same endings (for example duru 'door' and hand 'hand'). Note that the '-u/–' distinction in the singular depends on syllable weight, as for strong nouns, above.
| Example of the -u Declension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine sunu 'son' | Masculine feld 'field' | ||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |||
| Nominative | sunu | suna | feld | felda | ||
| Accusative | sunu | suna | feld | felda | ||
| Genitive | suna | suna | felda | felda | ||
| Dative | suna | sunum | felda | feldum | ||
There are also some nouns of the consonant declension, which show i-umlaut in some forms.
| Example of the Strong Noun Declensions ending in -w | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine fót 'foot' | Feminine hnutu 'nut' | Feminine bóc 'book' | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | fót | fét | hnutu | hnyte | bóc | béc |
| Accusative | fót | fét | hnutu | hnyte | bóc | béc |
| Genitive | fótes | fóta | hnyte, hnute | hnuta | béc, bóce | bóca |
| Dative | fóte | fótum | hnyte, hnute | hnutum | béc, bóc | bócum |
Other such nouns include (with singular and plural nominative forms given):
Masculine: tóþ, téþ 'tooth'; mann, menn 'man'; fréond, fríend 'friend'; féond, fíend 'enemy' (cf. 'fiend')
Feminine: studu, styde 'post' (cf. 'stud'); hnitu, hnite 'nit'; ác, ǽc 'oak'; gát, gǽt 'goat'; bróc, bréc 'leg covering' (cf. 'breeches'); gós, gés 'goose'; burg, byrg 'city' (cf. German cities in -burg); dung, ding 'prison' (cf. 'dungeon' by way of French and Frankish); turf, tyrf 'turf'; grút, grýt 'meal' (cf. 'grout'); lús, lýs 'louse'; mús, mýs 'mouse'; neaht, niht 'night' Feminine with loss of -h in some forms: furh, fyrh 'furrow' or 'fir'; sulh, sylh 'plough'; þrúh, þrýh 'trough'; wlóh, wléh 'fringe'. Feminine with compression of endings: cú, cý 'cow' (cf. dialectal plural 'kine')
Nouns of relationship:
| Nouns of Relationship | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine fæder 'father' | Masculine bróðor 'brother' | Feminine módor 'mother' | Feminine sweostor 'sister' | Feminine dohtor 'daughter' | |||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | fæder | fæd(e)ras | bróðor | (ge)bróðor | módor | módra/módru | sweostor | (ge)sweostor, -tru, -tra | dohtor | dohtor |
| Accusative | fæder | fæd(e)ras | bróðor | (ge)bróðor | módor | módra/módru | sweostor | (ge)sweostor, -tru, -tra | dohtor | dohtor |
| Genitive | fæder | fæd(e)ra | bróðor | (ge)bróðra | módor | módra | sweostor | (ge)sweostra | dohtor | dohtra |
| Dative | fæder | fæderum | bréðer | (ge)bróðrum | méder | módrum | sweostor | (ge)sweostrum | dehter | dohtrum |
Neuter nouns with -r in plural:
| Lamb 'lamb' n. | ||||
| Case | Singular | Plural | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | lamb | lambru | ||
| Accusative | lamb | lambru | ||
| Genitive | lambes | lambra | ||
| Dative | lambe | lambrum | ||
Other such nouns: cealf, cealfru 'calf'; ǽg, ǽru 'egg' (the form 'egg' is a borrowing from Old Norse); cild 'child' has either the normal plural cild or cildru (cf. 'children', with -en from the weak nouns).
Adjectives
Adjectives in Old English are declined using the same categories as nouns: five cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three genders (masculine, feminine, neuter), and two numbers (singular, plural). In addition, they can be declined either strong or weak. The weak forms are used in the presence of a definite or possessive determiner, while the strong ones are used in other situations. The weak forms are identical to those for nouns, while the strong forms use a combination of noun and pronoun endings:
| The Strong Adjective Declension | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | – | -e | – | -u/– | -u/– | -e, -a |
| Accusative | -ne | -e | – | -u/– | -e | -e, -a |
| Genitive | -es | -ra | -es | -ra | -re | -ra |
| Dative | -um | -um | -um | -um | -re | -um |
| Instrumental | -e | -um | -e | -um | -re | -um |
For the '-u/–' forms above, the distinction is the same as for strong nouns.
| Example of the Strong Adjective Declension: gód 'good' | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | gód | góde | gód | gód | gód | góde, -a |
| Accusative | gódne | góde | gód | gód | góde | góde, -a |
| Genitive | gódes | gódra | gódes | gódra | gódre | gódra |
| Dative | gódum | gódum | gódum | gódum | gódre | gódum |
| Instrumental | góde | gódum | góde | gódum | gódre | gódum |
| Example of the Weak Adjective Declension: gód 'good' | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | góda | gódan | góde | gódan | góde | gódan |
| Accusative | gódan | gódan | góde | gódan | gódan | gódan |
| Genitive | gódan | gódena | gódan | gódena | gódan | gódena |
| Dative | gódan | gódum | gódan | gódum | gódan | gódum |
| Instrumental | gódan | gódum | gódan | gódum | gódan | gódum |
Note that the same variants described above for nouns also exist for adjectives. The following example shows both the æ/a variation and the -u forms in the feminine singular and neuter plural:
| Example of the Strong Adjective Declension: glæd 'glad' | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | glæd | glade | glæd | gladu | gladu | glade |
| Accusative | glædne | glade | glæd | gladu | glade | glade |
| Genitive | glades | glædra | glades | glædra | glædre | glædra |
| Dative | gladum | gladum | gladum | gladum | glædre | gladum |
| Instrumental | glade | gladum | glade | gladum | glædre | gladum |
The following shows an example of an adjective ending with -h:
| Example of the Strong Adjective Declension: héah 'high' | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | héah | héa | héah | héa | héa | héa |
| Accusative | héane | héa | héah | héa | héa | héa |
| Genitive | héas | héara | héas | héara | héare | héara |
| Dative | héam | héam | héam | héam | héare | héam |
| Instrumental | héa | héam | héa | héam | héare | héam |
The following shows an example of an adjective ending with -w:
| Example of the Strong Adjective Declension: gearu 'ready' | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Masculine | Neuter | Feminine | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nominative | gearu | gearwe | gearu | gearu | gearu | gearwe |
| Accusative | gearone | gearwe | gearu | gearu | gearwe | gearwe |
| Genitive | gearwes | gearora | gearwes | gearora | gearore | gearora |
| Dative | gearwum | gearwum | gearwum | gearwum | gearore | gearwum |
| Instrumental | gearwe | gearwum | gearwe | gearwum | gearore | gearwum |
Pronouns
Most pronouns are declined by number, case and gender; in the plural form most pronouns have only one form for all genders. Additionally, Old English pronouns reserve the dual form (which is specifically for talking about groups of two things, for example "we two" or "you two" or "they two"). These were uncommon even then, but remained in use throughout the period.
Personal pronouns
| First Person | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Singular | Plural | Dual |
| Nominative | ic, íc | wé | wit |
| Accusative | mec, mé | úsic, ús | uncit, unc |
| Genitive | mín | úre | uncer |
| Dative | mé | ús | unc |
| Second Person | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Singular | Plural | Dual |
| Nominative | þú | gé | git |
| Accusative | þéc, þé | éowic, éow | incit, inc |
| Genitive | þin | éower | incer |
| Dative | þe | éow | inc |
| Third Person | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Case | Singular | Plural | Dual |
| Nominative | hé m., héo f., hit n. | hié m., héo f. | – |
| Accusative | hine m., híe f., hit n. | hié m., hío f. | – |
| Genitive | his m., hire f., his n. | hiera m., heora f. | – |
| Dative | him m., hire f., him n. | him | – |
Many of the forms above bear strong resemblances to their contemporary English language equivalents: for instance in the genitive case éower became "your", úre became "our", mín became "mine".
Prepositions
Prepositions (like our words by, for, with, because) often follow the word which they govern, in which case they are called postpositions. They are not declined.
See also Old English language (list of prepositions)
Example
This text is from the epic poem Beowulf.
| Line Count | Original | Translation |
| [332] | oretmecgas æfter æþelum frægn: | ...asked the warriors of their lineage: |
| [333] | "Hwanon ferigeað ge fætte scyldas, | "Whence do you carry ornate shields, |
| [334] | græge syrcan ond grimhelmas, | Grey mail-shirts and masked helms, |
| [335] | heresceafta heap? Ic eom Hroðgares | A multitude of spears? I am Hrothgar's |
| [336] | ar ond ombiht. Ne seah ic elþeodige | herald and officer. I have never seen, of foreigners, |
| [337] | þus manige men modiglicran, | So many men, of braver bearing, |
| [338] | Wen ic þæt ge for wlenco, nalles for wræcsiðum, | I know that out of daring, by no means in exile, |
| [339] | ac for higeþrymmum Hroðgar sohton." | But for greatness of heart, you have sought Hrothgar." |
| [340] | Him þa ellenrof andswarode, | To him, thus, bravely, it was answered, |
| [341] | wlanc Wedera leod, word æfter spræc, | By the proud Geatish chief, who these words thereafter spoke, |
| [342] | heard under helme: "We synt Higelaces | Hard under helm: "We are Hygelac's |
| [343] | beodgeneatas; Beowulf is min nama. | Table-companions. Beowulf is my name. |
| [344] | Wille ic asecgan sunu Healfdenes, | I wish to declare to the son of Healfdene |
| [345] | mærum þeodne, min ærende, | To the renowned prince, my mission, |
| [346] | aldre þinum, gif he us geunnan wile | To your lord, if he will grant us |
| [347] | þæt we hine swa godne gretan moton." | that we might be allowed to address him, he who is so good." |
| [348] | Wulfgar maþelode (þæt wæs Wendla leod; | Wulfgar Spoke – that was a Vendel chief; |
| [349] | his modsefa manegum gecyðed, | His character was to many known |
| [350] | wig ond wisdom): "Ic þæs wine Deniga, | His war-prowess and wisdom – "I, of him, friend of Danes, |
| [351] | frean Scildinga, frinan wille, | the Scyldings' lord, will ask, |
| [352] | beaga bryttan, swa þu bena eart, | Of the ring bestower, as you request, |
| [353] | þeoden mærne, ymb þinne sið, | Of that renowned prince, concerning your venture, |
| [354] | ond þe þa ondsware ædre gecyðan | And will swiftly provide you the answer |
| [355] | ðe me se goda agifan þenceð." | That the great one sees fit to give me." |
See also
- Anglo-Frisian nasal spirant law
- Anglo-Saxon literature
- Beowulf
- Declension in English
- Exeter Book
- Go (verb)
- History of the English language
- History of the Scots language
- I-mutation
- List of Germanic and Latinate equivalents
Old English might also refer to Old English (Ireland), or Olde English.
External links
- The Electronic Introduction to Old English (http://www.wmich.edu/medieval/research/rawl/IOE/index.html)
- First steps in Old English - a course for absolute beginners (http://www.kami.demon.co.uk/gesithas/OEsteps/)
- Old English - Anglo-Saxon alphabet (http://www.omniglot.com/writing/oldenglish.htm)
- The Origins of Old English (http://lonestar.texas.net/~jebbo/learn-as/origins.htm)
- Guide to using Old English computer characters (http://tlt.its.psu.edu/suggestions/international/bylanguage/oegermanic.html) (Unicode, HTML entities, etc.)
- Dictionary of Old English Project at the University of Toronto (http://www.doe.utoronto.ca)
- The Germanic Lexicon Project (http://www.ling.upenn.edu/~kurisuto/germanic/language_resources.html)
- Text Collections - Texts and Translations (http://www.georgetown.edu/faculty/ballc/oe/oe-texts.html)
- Links relating to Old English, including learning resources (http://wandership.ca/collect/links/oe.php)ang:Englisc sprǽc
de:Altenglische Sprache es:Inglés antiguo eo:Anglosaksa lingvo fr:Langue anglo-saxonne ja:古英語 no:Gammelengelsk språk pl:Język staroangielski sco:Auld Inglis leid simple:Old English language zh:古英语
