Norwalk virus group
|
|
| Norwalk virus | |
|---|---|
 Template:Taxobox begin placement virus Template:Taxobox group iv entry | |
| Family: | Caliciviridae |
| Genus: | Norovirus |
| Species: | Norwalk virus |
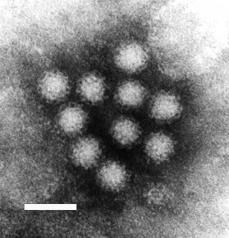
|} Norwalk virus is the prototype virus of the genus norovirus of the family Caliciviridae. Noroviruses contain a positive strand RNA genome of approximately 7.5 kb, encoding a major structural protein (VP1) of about 60 kDa and a minor capsid protein VP2. The 27-35 nm viral particles have a buoyant density of 1.39-1.40 g/ml in CsCl. Viruses within this genus consists of several serologically distinct groups of viruses that have been named after the places where the outbreaks occurred. In the U.S., the Norwalk, Ohio and Montgomery County strains are serologically related but distinct from the Hawaii and Snow Mountain strains. The Taunton, Moorcroft, Barnett, and Amulree strains were identified in the U.K., and the Sapporo and Otofuke strains in Japan. Their serological relationships remain to be determined.
| Contents |
Nature of Acute Disease
Common names of the illness caused by the Norwalk and Norwalk-like viruses are viral gastroenteritis, acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis, (incorrectly) food poisoning, and (most commonly in American English) stomach flu.
Nature of Disease
The disease is self-limiting, mild, and characterized by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Headache and low-grade fever may occur. The infectious dose is unknown but presumed to be low.
Diagnosis of Human Illness
Specific diagnosis of the disease can only be made by a few laboratories possessing reagents from human volunteer studies. Identification of the virus can be made on early stool specimens using immune electron microscopy and various immunoassays. Confirmation often requires demonstration of seroconversion, the presence of specific IgM antibody, or a four-fold rise in antibody titer to Norwalk virus on paired acute-convalescent sera.
Associated Foods
Norwalk gastroenteritis is transmitted by the fecal-oral route via contaminated water and foods. Secondary person-to-person transmission has been documented. Water is the most common source of outbreaks and may include water from municipal supplies, well, recreational lakes, and swimming pools. (Outbreak investigations by the U. S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have shown that transmission among cruise ship passengers is almost wholly person-to-person. Cruise ship water supplies have never been implicated.)
Shellfish and salad ingredients are the foods most often implicated in Norwalk outbreaks. Ingestion of raw or insufficiently steamed clams and oysters poses a high risk for infection with Norwalk virus. Foods other than shellfish are contaminated by ill food handlers.
Relative Frequency of Disease
Only the common cold is reported more frequently than viral gastroenteritis as a cause of illness in the U.S. Although viral gastroenteritis is caused by a number of viruses, it is estimated that Norwalk viruses are responsible for about 1/3 of the cases not involving the 6-to-24-month age group. In developing countries the percentage of individuals who have developed immunity is very high at an early age. In the U.S. the percentage increases gradually with age, reaching 50% in the population over 18 years of age. Immunity, however, is not permanent and reinfection can occur.
Course of Disease and Complications
A mild and brief illness usually develops 24-48 h after contaminated food or water is consumed and lasts for 24-60 hours. Severe illness or hospitalization is very rare.
Target Populations
All individuals who ingest the virus and who have not (within 24 months) had an infection with the same or related strain, are susceptible to infection and can develop the symptoms of gastroenteritis. Disease is more frequent in adults and older children than in the very young.
Food Analysis
The virus has been identified in clams and oysters by radioimmunoassay. The genome of Norwalk virus has been cloned and development of gene probes and PCR amplification techniques to detect the virus in clinical specimens and possibly in food are under way.
Selected Outbreaks
Literature references can be found at the links below.
MMWR 48(11):1999 During August 27-September 1, 1998, 99 (12%) of 835 soldiers in one unit at a U.S. Army training center in El Paso, Texas, were hospitalized for acute gastroenteritis (AGE). Their symptoms included acute onset of vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fever. Review of medical center admission records for AGE during the previous year indicated that fewer than five cases occurred each month.
MMWR 44(2):1995 A report on the multistate outbreak of viral gastroenteritis associated with consumption of oysters from Apalachicola Bay, Florida, December 1994-January 1995.
MMWR 43(24):1994 During November 20-30, 1993, four county public health units (CPHUs) of the Florida Department of Health and Rehabilitative Services (HRS) in northwestern Florida conducted preliminary investigations of seven separate outbreaks of foodborne illness following consumption of raw oysters. On December 1, the HRS State Health Office initiated an investigation to characterize the illness, examine risk factors for oyster-associated gastroenteritis, and quantify the dose-response relation. In four specimens, small round-structured viruses were detected by EM; in one specimen, a Norwalk-like genome was confirmed by RT-PCR.
MMWR 42(49):1993 On November 17, 1993, the state health departments of Louisiana, Maryland, and Mississippi notified CDC of several outbreaks of gastroenteritis occurring in their states since November 12. Preliminary epidemiologic investigations identified consumption of oysters as the primary risk factor for illness. On November 16, the Louisiana Department of Health and Hospitals (LDHH) had identified the Grand Pass and Cabbage Reef harvesting areas off the Louisiana coast as the source of oysters associated with outbreaks in Louisiana and Mississippi. Tagged oysters associated with outbreaks in Maryland were traced to the same oyster beds. Small round structured viruses or Norwalk-like viruses were detected by EM and confirmed by RT-PCR in 13 of 26 stool specimens from ill persons in Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, and North Carolina.
MMWR 37(5):1988 An outbreak of diarrhea occurred among the 331 participants in an outing held at a South Dakota campground on August 30 and 31, 1986. A biotin-avidin immunoassay performed at CDC yielded a fourfold rise in antibody titer to Norwalk virus in seven of 11 paired human serum specimens. No pathogenic bacterial or parasitic agents were identified from stool samples. Illness was strongly associated with the consumption of water or the reconstituted powdered soft drink made with water.
Snow Mountain virus was implicated in an outbreak in a retirement community in California (1988) which resulted in two deaths. Illness was associated with consumption of shrimp probably contaminated by food handlers.
Preliminary evidence suggests that large outbreaks of gastroenteritis which occurred in Pennsylvania and Delaware in September, 1987, were caused by Norwalk virus. The source of both outbreaks was traced to ice made with water from a contaminated well. In Pennsylvania, the ice was consumed at a football game, and in Delaware, at a cocktail party. Norwalk virus is also suspected to have caused an outbreak aboard a cruise ship in Hawaii in 1990. Fresh fruits were the probable vehicle of contamination.
MMWR 35(23):1986 Three outbreaks of gastroenteritis occurred on two Caribbean cruise ships between April 26, and May 10, 1986. More than 1,200 persons developed gastrointestinal illness; no deaths were reported. At least one of the outbreaks appears to be associated with Norwalk virus. An outbreak of gastroenteritis caused by the Norwalk virus recently occurred in Tate, a rural community in north Georgia. An investigation implicated the community water system as the source of infection. (MMWR 31(30):1982 Aug 06)
Foodborne outbreaks of gastroenteritis caused by Norwalk virus are often related to consumption of raw shellfish. Frequent and widespread outbreaks, reaching epidemic proportions, occurred in Australia (1978) and in the state of New York (1982) among consumers of raw clams and oysters. From 1983 to 1987, ten well documented outbreaks caused by Norwalk virus were reported in the U.S., involving a variety of foods: fruits, salads, eggs, clams, and bakery items. For more information on recent outbreaks see the CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports.
External links
- CDC Viral Gastroenteritis FAQs (http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvrd/gastro.htm): Center for Disease Control and Prevention of Food Illness Fact Sheet
- Loci index for genome Norwalk virus (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=95340). Available from the GenBank Taxonomy database, which contains the names of all organisms that are represented in the genetic databases with at least one nucleotide or protein sequence.
The above was originally based on a page from the public domain Bad Bug Bookja:ノロウイルス de:Noro-Virus
