Non-linear control
|
|
Non-linear control is a sub-division of control engineering which deals with the control of non-linear systems. Non-linear systems are those systems whose input-output behaviour is very much unpredictable. For linear systems, we have a lot of well-established control techniques like root-locus, Bode plot, Nyquist criterion, state-feedback, pole-placement etc.
| Contents |
Properties of non-linear systems
- They do not follow the principle of superposition (linearity and homogeneity).
- They may have multiple isolated equilibrium points.
- They exhibit properties like limit-cycle, bifurcation, chaos.
- For a sinusoidal input, the output signal may contain many harmonics and sub-harmonics with various amplitudes and phase differences. While for a linear system, we know that for u= A sin(ωt), output y = B sin(ωt+ φ).
Analysis and control of non-linear systems
- Describing function method
- Phase plane method
- Lyapunov based methods
- Input-output stability
- Feedback linearization
- Back-stepping
- Sliding mode control
- Singular perturbation
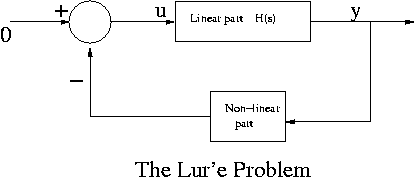
The Lur'e problem
In this section, we will study the stability of an important class of control systems namely feedback systems whose forward path contains a linear time-invariant subsystem and whose feedback path contains a memory-less and possibly time-varying non-linearity. This class of problem is named for A. I. Lur'e.
The linear part is characterized by four matrices (A,B,C,D). The non-linear part is Φ ∈ [a,b], a<b, is a sector non-linearity.
Absolute stability problem
Given that
- (A,B) is controllable and (C,A) is observable
- two real numbers a,b with a<b.
The problem is to derive conditions involving only the transfer matrix H(.) and the numbers a,b, such that x=0 is a globally uniformly asymptotically stable equilibrium of the system (1)-(3) for every function Φ ∈ [a,b]. This is also known as Lure's problem.
We will discuss two main theorems concerning Lure's problem.
- The Circle criterion
- The Popov criterion.
Popov criterion
The class of systems studied by Popov is described by
- <math>
\begin{matrix} \dot{x}&=&Ax+bu \\ \dot{\xi}&=&u \\ y&=&cx+d\xi \quad (1) \end{matrix} <math>
<math> u = -\phi (y) \quad (2) <math>
where x ∈ Rn, ξ,u,y are scalars and A,b,c,d have commensurate dimensions. The non-linear element Φ: R → R is a time-invariant nonlinearity belonging to open sector (0, ∞). This means that
Φ(0) = 0, y Φ(y) > 0, ∀ y ≠ 0; (3)
The transfer function from u to y is given by
- <math> h(s) = \frac{d}{s} + c(sI-A)^{-1}b \quad \quad (4)<math>
Things to be noted
- Popov criterion is applicable only to autonomous systems.
- The system studied by Popov has a pole at the origin and there is no throughput from input to output.
- Non-linearity Φ belongs to a open sector.
Theorem: Consider the system (1) and (2) and suppose
- A is Hurwitz
- (A,b) is controllable
- (A,c) is observable
- d>0 and
- Φ ∈ (0,∞)
then the above system is globally asymptotically stable if there exists a number r>0 such that
infω ∈ R Re[(1+jωr)h(jω)] > 0
References
- A. I. Lur'e and V. N. Postnikov, "On the theory of stability of control systems," Applied mathematics and mechanics, 8(3), 1944, (in Russian).
- M. Vidyasagar, Nonlinear Systems Analysis, second edition, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey 07632.