Moesia
|
|
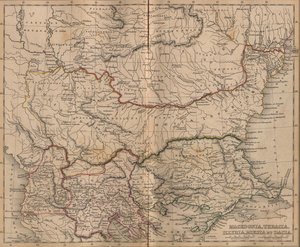
In ancient geography, Moesia was a district inhabited by a Thracian people. It was bounded on the south by the mountain ranges of Haemus and Scardus (Scordus, Scodrus), on the west by the Drinus, on the north by the Danube and on the east by the Euxine. It thus corresponded in the main to the modern Serbia and Bulgaria.
REmpire-Moesia.png
In 75 BC, C. Scribonius Curio, proconsul of Macedonia, penetrated as far as the Danube, and gained a victory over the inhabitants, who were finally subdued by M. Licinius Crassus, grandson of the triumvir and also proconsul of Macedonia, during the reign of Augustus c. 29 BC. The country, however, was not organized as a province until the last years of the reign; in AD 6 mention is made of its governor, Caecina Severus (Dio Cassius lv. 29).
Originally one province, under an imperial consular legate (who probably also had control of Achaea and Macedonia), it was divided by Domitian into Upper (superior) and Lower (inferior, also called Ripa Thracia) Moesia, the western and eastern portions respectively, divided from each other by the river Cebrus (Ciabrus; mod. Cibritza or Zibru). Some, however, place the boundary further west. Each was governed by an imperial consular legate and a procurator. As a frontier province, Moesia was strengthened by stations and fortresses erected along the southern bank of the Danube, and a wall was built from Axiopolis to Tomi as a protection against the Scythians and Sarmatians.
After the abandonment of Dacia to the Goths by Aurelian (270—275) and the transference of the Roman citizens from the former province to the south of the Danube, the central portion of Moesia took the name of Dacia Aureliani (again divided into Dacia ripensis and interior). The district called Dardania (in Upper Moesia), was formed into a special province by Diocletian, with the capital at Naissus or Nissa (modern Niš), the birthplace of Constantine the Great (in 272).
Since 238 Moesia was constantly invaded or raided by the Carpi, and the Goths, who had already invaded Moesia in 250, hard pressed by the Huns, again crossed the Danube during the reign of Valens (376), and with his permission settled in Moesia.
But quarrels soon took place, and the Goths under Fritigern defeated Valens in a great battle near Adrianople. These Goths are known as Moeso-Goths, for whom Ulfilas made the Gothic translation of the Bible. In the 7th century, Slavs and Bulgars entered the country and founded Serbia and Bulgaria.
The chief towns of Upper Moesia were: Singidunum (Belgrade), Viminacium (sometimes called municipium Aelium; Kostolac), Bononia (Widdin, Vidin), Ratiaria (Arčar): of Lower Moesia; Oescus (colonia Ulpia, Gigen), Novae (near Sistova, the chief seat of Theodoric the Great), Nicopolis ad Istrum (Nikup), really on the Iatrus or Yantra, Odessus (Varna), Tomi (Constanta), to which the poet Ovid was banished. The last two were Greek towns, which, with Istros, Mesambria and Apollonia, formed a pentapolis.
Template:Roman provinces 120 ADbg:Мизия de:Moesia pl:Mezja nl:Moesia