Hausa language
|
|
| Hausa (هَوُسَ) | |
|---|---|
| Spoken in: | Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Ghana, Niger, Nigeria, Togo |
| Region: | |
| Total speakers: | 24 million as a first language, 15 million as a second language |
| Ranking: | 41 |
| Genetic classification: | Afro-Asiatic |
| Official status | |
| Official language of: | Northern Nigeria |
| Regulated by: | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | - |
| ISO 639-2 | hau |
| SIL | HUA |
| See also: Language – List of languages | |
Hausa is the Chadic language with the largest number of speakers, spoken as a first language by about 24 million people, and as a second language by about 15 million more.
| Contents |
Classification
Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family.
Geographic distribution
Native speakers of Hausa are mostly to be found in the African country of Niger and in the north of Nigeria, but the language is widely used as a lingua franca(similar to Wolof in Senegal) in a much larger swathe of West Africa, particularly amongst Muslims.
Official status
Hausa is an official language in the north of Nigeria.
Dialects
Eastern Hausa dialects include Kano, Katagum and Hadejiya. Western Hausa dialects include Sokoto, Katsina, Gobirawa, Adarawa, Kebbawa and Zamfarawa. Northern Hausa dialects include Arewa and Arawa.
Derived languages
Barikanchi is a pidgin used in the military.
Sounds
Glottalized Consonants
Hausa has glottalic consonants at four or five places of articulation (depending on the dialect), which are not accommodated by the standard Latin alphabet. They require movement of the throat during pronunciation and have a staccato sound. Each of these is similar to an English consonant and therefore they are written as modified versions of Latin letters. They can also be denoted with an apostrophe, either before or after depending on the letter, as shown below. See the individual articles on pronunciation.
b' / Missing image
Hausa_b.gif
Image:hausa_b.gif
, an implosive consonant, IPA , or sometimes ;
d' / Missing image
Hausa_d.gif
Image:hausa_d.gif
, an implosive , sometimes ;
ts', an ejective consonant, or according to the dialect;
ch', an ejective (does not occur in Kano dialect)
k' / 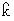 , an ejective ; and are separate consonants;
, an ejective ; and are separate consonants;
'y is not actually a glottalized y, but rather a palatalized glottal stop,
Tones
Hausa is a tone language. Each of its five vowels a,e,i,o and u may have low tone, high tone and falling tone.
For representing tones the French accented vowels may be used:
à è ì ò ù (low tone)
á é í ó ú (high tone)
â ê î ô û (falling tone)
In general writing tone is often not marked. However it is needed for disambiguation in some cases.
Writing system
Hausa has had a written form for more than 200 years, at first with a variant of Arabic script called Ajami, but this has largely been superseded by a Latin alphabet which was introduced at the beginning of the 20th century. There are three additional consonants which are added to the Roman alphabet: ɓ, ɗ and ƙ.
See also
External links
- Ethnologue report on Hausa (http://www.ethnologue.com/show_language.asp?code=HUA)
- Hausa at UCLA (http://www.humnet.ucla.edu/humnet/aflang/Hausa/hausa.html)
- Kofar Hausa dictionary at University of Vienna (http://www.univie.ac.at/afrikanistik/oracle/KofarHausaE.html)
- Hausa phrasebook (http://wikitravel.org/en/Hausa_phrasebook)eo:Hauxsa lingvo de:Hausa fr:Haoussa ha:Hausanl:Hausa (taal) ja:ハウサ語 pl:Język hausa
